ZHCSOW3 September 2020 INA848
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
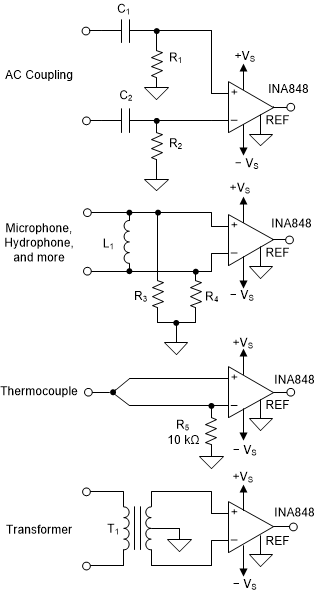
9.1.2 Input Bias Current Return Path
The input impedance of the INA848 is extremely high (approximately 100 GΩ). However, a path must be provided for the input bias current of both inputs. This input bias current is typically 25 nA. High input impedance means that this input bias current changes little with varying input voltage.
Input circuitry must provide a path for this input bias current for proper operation. Figure 9-3 shows various provisions for an input bias current path. Without a bias current path, the inputs float to a potential that exceeds the common-mode range of the INA848, and the input amplifiers saturate. If the differential source resistance is low, the bias current return path connects to one input (as shown in the thermocouple example in Figure 9-3). With a higher source impedance, using two equal resistors provides a balanced input with possible advantages of a lower input offset voltage as a result of bias current, and better high-frequency common-mode rejection.