ZHCSDV2 July 2015 ISO7820
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Rating
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics, 5 V
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics, 3.3 V
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics, 2.5 V
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics, 5 V
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics, 3.3 V
- 6.11 Switching Characteristics, 2.5 V
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
ISO7820 employs an ON-OFF Keying (OOK) modulation scheme to transmit the digital data across a silicon dioxide based isolation barrier. The transmitter sends a high frequency carrier across the barrier to represent one digital state and sends no signal to represent the other digital state. The receiver demodulates the signal after advanced signal conditioning and produces the output through a buffer stage. These devices also incorporates advanced circuit techniques to maximize the CMTI performance and minimize the radiated emissions due the high frequency carrier and IO buffer switching. The conceptual block diagram of a digital capacitive isolator, Figure 10, shows a functional block diagram of a typical channel.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
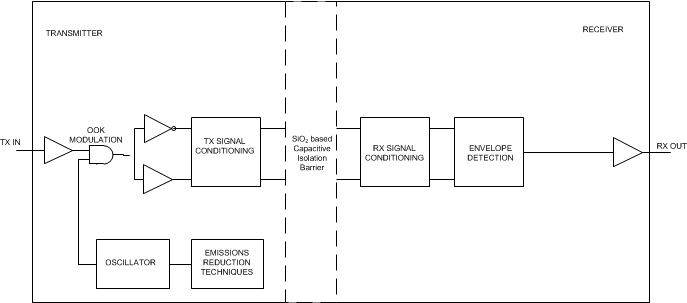 Figure 10. Conceptual Block Diagram of a Digital Capacitive Isolator
Figure 10. Conceptual Block Diagram of a Digital Capacitive Isolator
Also a conceptual detail of how the ON/OFF Keying scheme works is shown in Figure 11.
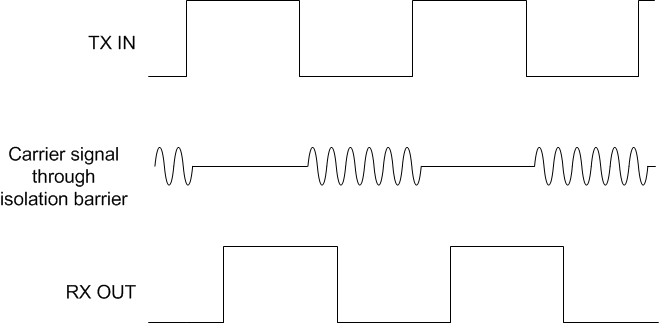 Figure 11. On-Off Keying (OOK) Based Modulation Scheme
Figure 11. On-Off Keying (OOK) Based Modulation Scheme
8.3 Feature Description
ISO7820 is available in two channel configurations and default output state options to enable a variety of application uses.
| PRODUCT | CHANNEL DIRECTION | RATED ISOLATION | MAX DATA RATE | DEFAULT OUTPUT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO7820 | 2 Forward, 0 Reverse
|
5700 VRMS / 8000 VPK(1) | 100 Mbps | High |
| ISO7820F | 2 Forward, 0 Reverse
|
5700 VRMS / 8000 VPK(1) | 100 Mbps | Low |
8.3.1 High Voltage Feature Description
8.3.1.1 Package Insulation and Safety-Related Specifications
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L(I01) | Minimum air gap (clearance) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance through air | DW-16 | 8 | mm | ||
| L(I02)(1) | Minimum external tracking (creepage) | Shortest terminal-to-terminal distance across the package surface | DW-16 | 8 | mm | ||
| CTI | Tracking resistance (comparative tracking index) | DIN EN 60112 (VDE 0303-11); IEC 60112; UL 746A | 600 | V | |||
| RIO | Isolation resistance, input to output(2) | VIO = 500 V, TA = 25°C | 1012 | Ω | |||
| VIO = 500 V, 100°C ≤ TA ≤ max | 1011 | Ω | |||||
| CIO | Barrier capacitance, input to output(2) | VIO = 0.4 x sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz | 2 | pF | |||
| CI | Input capacitance(3) | VI = VCC/2 + 0.4 x sin (2πft), f = 1 MHz, VCC = 5 V | 2 | pF | |||
NOTE
Creepage and clearance requirements should be applied according to the specific equipment isolation standards of an application. Care should be taken to maintain the creepage and clearance distance of a board design to ensure that the mounting pads of the isolator on the printed-circuit board do not reduce this distance.
Creepage and clearance on a printed-circuit board become equal in certain cases. Techniques such as inserting grooves and/or ribs on a printed circuit board are used to help increase these specifications.
8.3.1.2 Insulation Characteristics
| PARAMETER(1) | TEST CONDITIONS | SPECIFICATION | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTI | Distance through the insulation | Minimum internal gap (internal clearance) | 21 | μm |
| VIOWM | Maximum isolation working voltage | Time dependent dielectric breakdown (TDDB) test | 1500 | VRMS |
| 2121 | VDC | |||
| DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12 | ||||
| VIOTM | Maximum transient isolation voltage | VTEST = VIOTM
t = 60 sec (qualification) t= 1 sec (100% production) |
8000 | VPK |
| VIOSM | Maximum surge isolation voltage | Test method per IEC 60065, 1.2/50 µs waveform, VTEST = 1.6 x VIOSM = 12800 VPK (qualification) |
8000 | VPK |
| VIORM | Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage | 2121 | VPK | |
| VPR | Input-to-output test voltage | Method a, After Input/Output safety test subgroup 2/3, VPR = VIORM x 1.2, t = 10 s, Partial discharge < 5 pC |
2545 | VPK |
| Method a, After environmental tests subgroup 1, VPR = VIORM x 1.6, t = 10 s, Partial Discharge < 5 pC |
3394 | |||
| Method b1,After environmental tests subgroup 1, VPR = VIORM x 1.875, t = 1 s (100% Production test) Partial discharge < 5 pC |
3977 | |||
| RS | Isolation resistance | VIO = 500 V at TS | >109 | Ω |
| Pollution degree | 2 | |||
| UL 1577 | ||||
| VISO | Withstanding isolation voltage | VTEST = VISO = 5700 VRMS, t = 60 sec (qualification); VTEST = 1.2 x VISO = 6840 VRMS , t = 1 sec (100% production) |
5700 | VRMS |
8.3.1.3 IEC 60664-1 Ratings Table
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | SPECIFICATION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic isolation group | Material group | I | |
| Installation classification | DW package | Rated mains voltage ≤ 600 VRMS | I–IV |
| Rated mains voltage ≤ 1000 VRMS | I–III | ||
8.3.1.4 Regulatory Information
DW package certifications are complete.
| VDE | CSA | UL | CQC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certified according to DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12 and DIN EN 60950-1 (VDE 0805 Teil 1):2011-01 | Approved under CSA Component Acceptance Notice 5A, IEC 60950-1, IEC 61010-1, and IEC 60601-1 | Recognized under UL 1577 Component Recognition Program | Certified according to GB 4943.1-2011 |
| Reinforced insulation Maximum transient isolation voltage, 8000 VPK; Maximum repetitive peak isolation voltage, 2121 VPK; Maximum surge isolation voltage, 8000 VPK |
Reinforced insulation per CSA 61010-1-12 and IEC 61010-1 3rd Ed., 300 VRMS max working voltage; |
Single protection, 5700 VRMS(1) | Reinforced Insulation, Altitude ≤ 5000 m, Tropical Climate, 250 VRMS maximum working voltage |
| Reinforced insulation per CSA 60950-1-07+A1+A2 and IEC 60950-1 2nd Ed., 800 VRMS max working voltage (pollution degree 2, material group I); |
|||
| 2 MOPP (Means of Patient Protection) per CSA 60601-1:14 and IEC 60601-1 Ed. 3.1, 250 VRMS (354 VPK) max working voltage |
|||
| Certificate number: 40040142 | Master contract number: 220991 | File number: E181974 | Certificate number: CQC15001121716 |
8.3.1.5 Safety Limiting Values
Safety limiting intends to prevent potential damage to the isolation barrier upon failure of input or output circuitry. A failure of the I/O can allow low resistance to ground or the supply and, without current limiting, dissipate sufficient power to overheat the die and damage the isolation barrier potentially leading to secondary system failures.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS (DW-16) | Safety input, output, or supply current for DW-16 package | RθJA = 84.7°C/W, VI = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 268 | mA | ||
| RθJA = 84.7°C/W, VI = 3.6 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 410 | |||||
| RθJA = 84.7°C/W, VI = 2.75 V, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 537 | |||||
| PS | Safety input, output, or total power | RθJA = 84.7°C/W, TJ = 150°C, TA = 25°C | 1476 | mW | ||
| TS | Maximum case temperature | 150 | °C | |||
The maximum safety temperature is the maximum junction temperature specified for the device. The power dissipation and junction-to-air thermal impedance of the device installed in the application hardware determines the junction temperature. The assumed junction-to-air thermal resistance in the Thermal Informationis that of a device installed on a High-K test board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages. The power is the recommended maximum input voltage times the current. The junction temperature is then the ambient temperature plus the power times the junction-to-air thermal resistance.
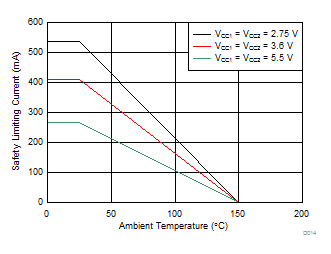 Figure 12. θJC Thermal Derating Curve per VDE for
Figure 12. θJC Thermal Derating Curve per VDE for DW-16 Package
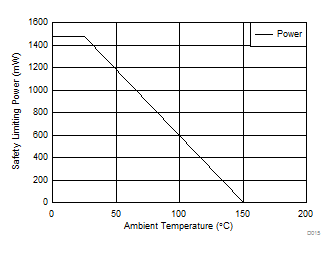 Figure 13. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power per VDE
Figure 13. Thermal Derating Curve for Safety Limiting Power per VDE
8.4 Device Functional Modes
ISO7820DW functional modes are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. ISO7820DW Function Table(1)
| VCCI | VCCO | INPUT (INx)(3) |
OUTPUT (OUTx) |
COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU | PU | H | H | Normal Operation: A channel output assumes the logic state of its input. |
| L | L | |||
| Open | Default | Default mode: When INx is open, the corresponding channel output goes to its default high logic state. Default= High for ISO7820 and Low for ISO7820F. | ||
| PD | PU | X | Default | Default mode: When VCCI is unpowered, a channel output assumes the logic state based on the selected default option.Default= High for ISO7820 and Low for ISO7820F. When VCCI transitions from unpowered to powered-up, a channel output assumes the logic state of its input. When VCCI transitions from powered-up to unpowered, channel output assumes the selected default state. |
| X | PD | X | Undetermined | When VCCO is unpowered, a channel output is undetermined (2). When VCCO transitions from unpowered to powered-up, a channel output assumes the logic state of its input |
8.4.1 Device I/O Schematics
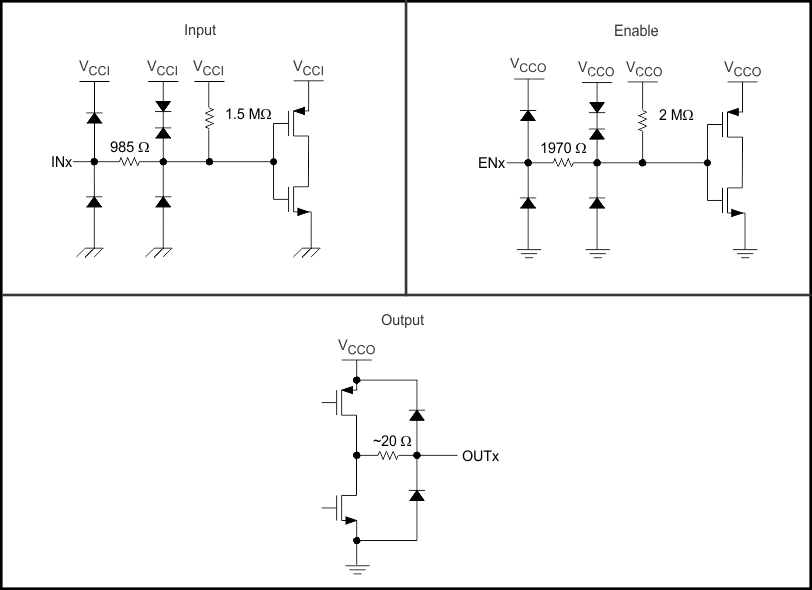 Figure 14. Device I/O Schematics
Figure 14. Device I/O Schematics