ZHCSJ59C december 2018 – july 2023 LDC5072-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.2.3 Fixed Gain Mode
Fixed gain mode might be chosen in cases where the variation in INx amplitudes between boards is sufficiently small and the air gap is well controlled. An advantage is that changes in OUTx amplitudes can be measured by the host MCU. This could lead to information about air gap variance. A disadvantage is that the signal path gain will not adjust due to variances, which could lead to saturation if the signal is too large, or increased error due to low SNR if the signal is too small.
To use fixed gain mode, first determine the maximum amplitude of the signal at the INx inputs. This is calculated by knowing the maximum coupling coefficient between the LC exciter coil and the Sin/Cos coils (see Equation 10 and Equation 11).
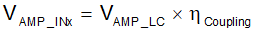
where
- VAMP_INx= differential voltage on the INx pin
- VAMP_LC= differential voltage on LCOUT
- kcoupling= coupling coefficient between exciter and sin/cos coils
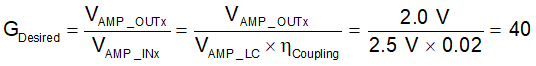
where
- Gdesired= gain setting for the system
- VAMP_OUTx= Differential amplitude between OUTxP and OUTxN
- VAMP_INx= Differential voltage on the INx pin
The single-ended OUTx voltages should stay within 10% to 90% of VREG. For this example, a differential amplitude of 2.0 V was chosen.
When the desired gain is known, the voltage to apply to the AGC_EN pin can be calculated by rearranging Equation 7.
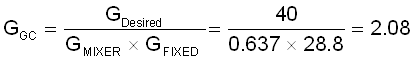
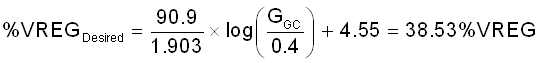
From there, the pullup and pulldown resistors can be calculated to achieve %VREGDesired. These should be 0.1% tolerant resistors and the loading should not violate the ILOAD_REG_EXT specification.
Choose R2 = 10 kΩ
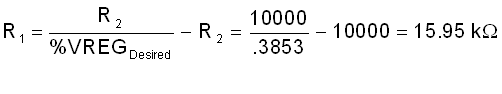
Finally, choose the closest resistor value and double check that the final gain will be within acceptable limits. In this case, choose R1 = 16.0 kΩ.