ZHCS538M September 2008 – October 2020 LM22678 , LM22678-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
8.2.1.2.2 Input Capacitor
The input capacitor selection is based on both input voltage ripple and RMS current. Good quality input capacitors are necessary to limit the ripple voltage at the VIN pin while supplying most of the regulator current during switch on-time. Low-ESR ceramic capacitors are preferred. Larger values of input capacitance are desirable to reduce voltage ripple and noise on the input supply. This noise can find its way into other circuitry, sharing the same input supply, unless adequate bypassing is provided. A very approximate formula for determining the input voltage ripple is shown in Equation 14.
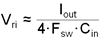
where
- Vri is the peak-to-peak ripple voltage at the switching frequency.
Another concern is the RMS current passing through this capacitor. Equation 15 determines an approximation to this current.
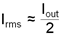
The capacitor must be rated for at least this level of RMS current at the switching frequency.
All ceramic capacitors have large voltage coefficients, in addition to normal tolerances and temperature coefficients. To help mitigate these effects, multiple capacitors can be used in parallel to bring the minimum capacitance up to the desired value. This can also help with RMS current constraints by sharing the current among several capacitors. Many times it is desirable to use an electrolytic capacitor on the input, in parallel with the ceramics. The moderate ESR of this capacitor can help to damp any ringing on the input supply caused by long power leads. This method can also help to reduce voltage spikes that may exceed the maximum input voltage rating of the LM22678 device.
It is good practice to include a high frequency bypass capacitor as close as possible to the LM22678 device. This small case size, low ESR ceramic capacitor should be connected directly to the VIN and GND pins with the shortest possible PCB traces. Values in the range of 0.47 µF to 1 µF are appropriate. This capacitor helps to provide a low impedance supply to sensitive internal circuitry. It also helps to suppress any fast noise spikes on the input supply that may lead to increased EMI.