ZHCSNB5A June 2021 – February 2023 LM25148-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 8.3.2 High-Voltage Bias Supply Regulator (VCC, VCCX, VDDA)
- 8.3.3 Precision Enable (EN)
- 8.3.4 Power-Good Monitor (PG)
- 8.3.5 Switching Frequency (RT)
- 8.3.6 Dual Random Spread Spectrum (DRSS)
- 8.3.7 Soft Start
- 8.3.8 Output Voltage Setpoint (FB)
- 8.3.9 Minimum Controllable On Time
- 8.3.10 Error Amplifier and PWM Comparator (FB, EXTCOMP)
- 8.3.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.12 Inductor Current Sense (ISNS+, VOUT)
- 8.3.13 Hiccup Mode Current Limiting
- 8.3.14 High-Side and Low-Side Gate Drivers (HO, LO)
- 8.3.15 Output Configurations (CNFG)
- 8.3.16 Single-Output Dual-Phase Operation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.11 Slope Compensation
The LM25148-Q1 provides internal slope compensation for stable operation with peak current-mode control and a duty cycle greater than 50%. Calculate the buck inductance to provide a slope compensation contribution equal to one times the inductor downslope using Equation 9.
Equation 9. 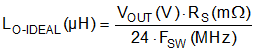
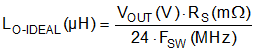
- A lower inductance value generally increases the peak-to-peak inductor current, which minimizes size and cost, and improves transient response at the cost of reduced light-load efficiency due to higher cores losses and peak currents.
- A higher inductance value generally decreases the peak-to-peak inductor current, reducing switch peak and RMS currents at the cost of requiring larger output capacitors to meet load-transient specifications.