ZHCSHC8 December 2017 LM25576-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10器件和文档支持
- 11机械、封装和可订购信息
8.1.15 Bias Power Dissipation Reduction
Buck regulators operating with high input voltage can dissipate an appreciable amount of power for the bias of the IC. The VCC regulator must step-down the input voltage VIN to a nominal VCC level of 7 V. The large voltage drop across the VCC regulator translates into a large power dissipation within the Vcc regulator. There are several techniques that can significantly reduce this bias regulator power dissipation. Figure 18 and Figure 19 depict two methods to bias the IC from the output voltage. In each case the internal VCC regulator is used to initially bias the VCC pin. After the output voltage is established, the VCC pin potential is raised above the nominal 7 V regulation level, which effectively disables the internal VCC regulator. The voltage applied to the VCC pin should never exceed 14 V. The VCC voltage should never be larger than the VIN voltage.
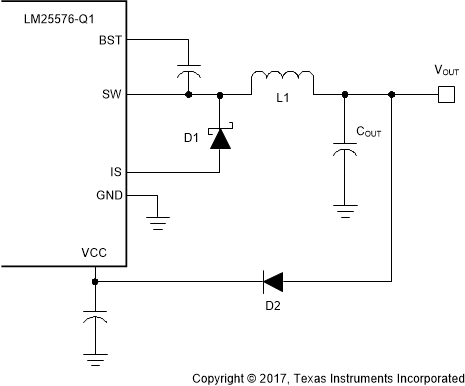 Figure 18. VCC Bias from VOUT for 8 V < VOUT < 14 V
Figure 18. VCC Bias from VOUT for 8 V < VOUT < 14 V
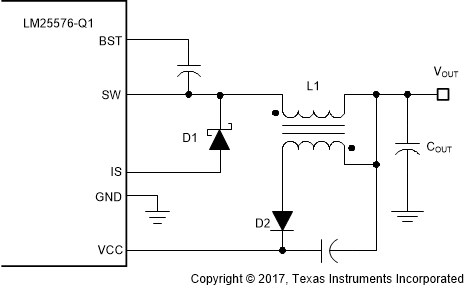 Figure 19. VCC Bias with Additional Winding on the Output Inductor
Figure 19. VCC Bias with Additional Winding on the Output Inductor