SNVS082E December 2001 – May 2016 LM2593HV
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - 3.3-V Version
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - 5-V Version
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics - Adjustable Voltage Version
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- KTW|7
订购信息
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum supply voltage, VIN | 63 | V | |||
| SD/SS pin input voltage(2) | 6 | V | |||
| Delay pin voltage(2) | 1.5 | V | |||
| Flag pin voltage | –0.3 | 45 | V | ||
| Feedback pin voltage | –0.3 | 25 | V | ||
| Output voltage to ground, steady-state | –1 | V | |||
| Power dissipation | Internally limited | ||||
| Lead temperature | S package | Vapor phase (60 s) | 215 | °C | |
| Infrared (10 s) | 245 | ||||
| T package, soldering (10 s) | 260 | ||||
| Maximum junction temperature | 150 | °C | |||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | ||
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) Voltage internally clamped. If clamp voltage is exceeded, limit current to a maximum of 1 mA.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1)(2) | ±2000 | V |
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) The human body model is a 100-pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5-k resistor into each pin.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | 4.5 | 60 | V | |
| TJ | Temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM2593HV | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDZ (TO-220) | KTW (TO-263) | |||
| 7 PINS | 7 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 50(2) | 50(3) | °C/W |
| 30(4) | ||||
| 20(5) | ||||
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 2 | 2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | — | — | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | — | — | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | — | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
(2) Junction to ambient thermal resistance (no external heat sink) for the package mounted TO-220 package mounted vertically, with the leads soldered to a printed-circuit board with (1 oz) copper area of approximately 1 in2.
(3) Junction to ambient thermal resistance with the TO-263 package tab soldered to a single-sided printed-circuit board with 0.5 in2 of (1 oz) copper area.
(4) Junction to ambient thermal resistance with the TO-263 package tab soldered to a single-sided printed-circuit board with 2.5 in2 of (1 oz) copper area.
(5) Junction to ambient thermal resistance with the TO-263 package tab soldered to a double-sided printed-circuit board with 3 in2 of (1 oz) copper area on the LM2593HVS side of the board, and approximately 16 in2 of copper on the other side of the printed-circuit board.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = 25°C, VIN = 12 V for the 3.3-V, 5-V, and adjustable versions, and ILOAD = 500 mA (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(1) | TYP(2) | MAX(1) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
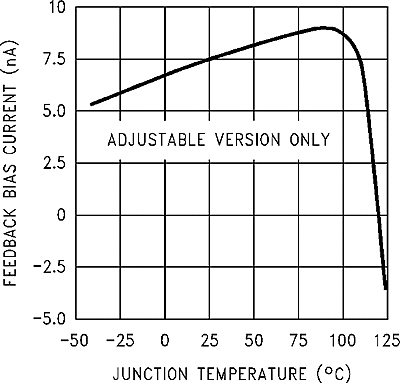
| Ib | Feedback bias current | Adjustable version only, VFB = 1.3 V | 50 | 10 | 100 | nA | |
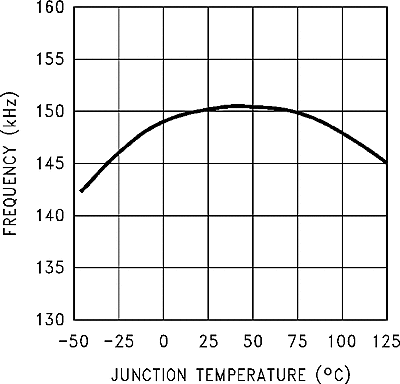
| fO | Oscillator frequency(3) | TJ = 25°C | 127 | 150 | 173 | kHz | |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 110 | 173 | |||||
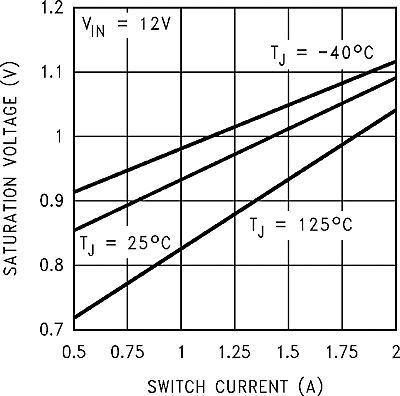
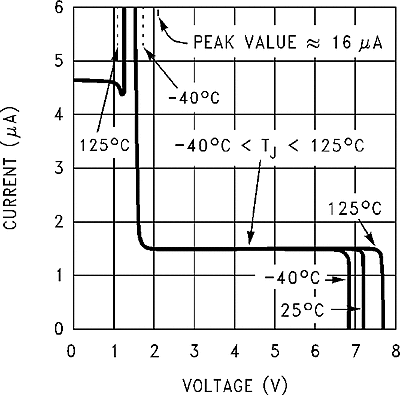
| VSAT | Saturation voltage | IOUT = 2 A; no diode, inductor or capacitor connected to output pin(4); Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 0 V to force the output transistor switch ON(5) | TJ = 25°C | 1.1 | 1.3 | V | |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 1.4 | ||||||
| DC | Max duty cycle (ON) | Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 0 V to force the output transistor switch ON | 100% | ||||
| Min duty cycle (OFF) | Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 12 V for the 3.3-V, 5-V, and the adjustable versions to force the output transistor switch OFF | 0% | |||||
| ICLIM | Switch current limit | Peak current; no diode, inductor or capacitor connected to output pin; Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 0 V to force the output transistor switch ON | TJ = 25°C | 2.4 | 3 | 3.7 | A |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 2.3 | 4 | |||||
| IL | Output leakage current | Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 12 V for the 3.3-V, 5-V, and the adjustable version to force the output transistor switch OFF; VIN = 60 V, output = 0 V, output = −1 V |
50 | 5 | 30 | mA | |
| IQ | Operating quiescent current | SD and SS pin open, Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 12 V for the 3.3-V, 5-V, and the adjustable version to force the output transistor switch OFF | 5 | 10 | mA | ||
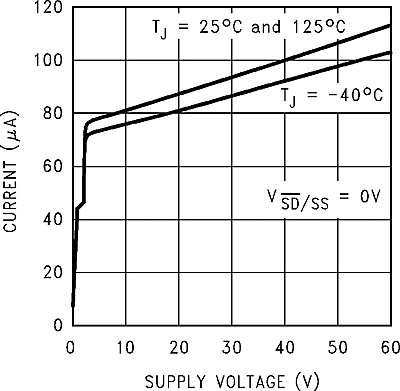
| ISTBY | Standby quiescent current | SD and SS pin = 0 V, VIN = 60 V |
TJ = 25°C | 90 | 200 | µA | |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 250 | ||||||
| SHUTDOWN AND SOFT-START CONTROL | |||||||
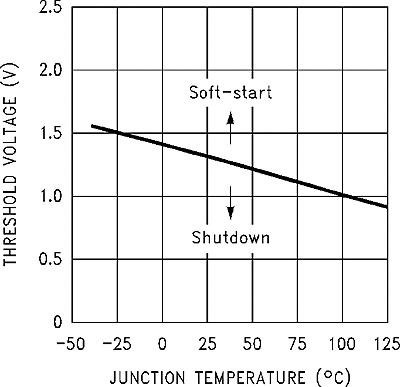
| VSD | Shutdown threshold voltage | Low (shutdown mode) | 1.3 | 0.6 | V | ||
| High (soft-start mode) | 2 | ||||||
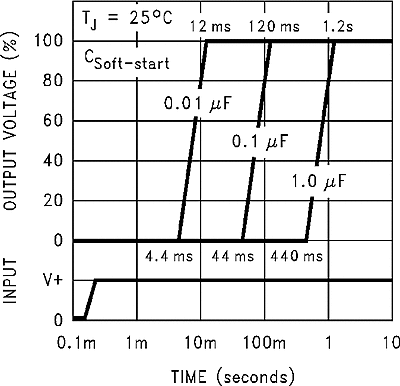
| VSS | Soft-start voltage | VOUT = 20% of nominal output voltage | 2 | V | |||
| VOUT = 100% of nominal output voltage | 3 | ||||||
| ISD | Shutdown current | VSHUTDOWN = 0.5 V | 5 | 10 | µA | ||
| ISS | Soft-start current | VSoft-start = 2.5 V | 1.5 | 5 | µA | ||
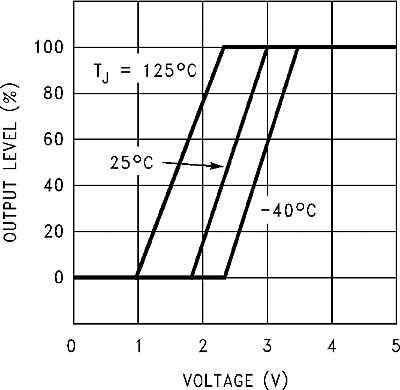
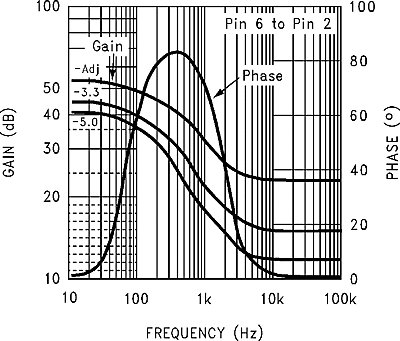
| Regulator dropout detector | Low (flag ON) | 96% | |||||
| Threshold voltage | Low (flag ON) | 92% | 98% | ||||
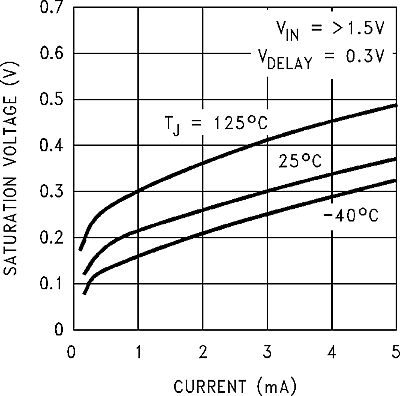
| VFSAT | Flag output saturation voltage | ISINK = 3 mA, VDELAY = 0.5 V | 0.3 | µA | |||
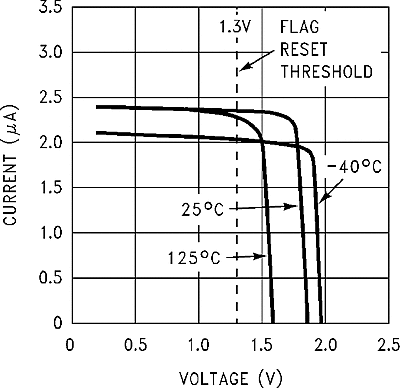
| IFL | Flag output leakage current | VFLAG = 60 V | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1 | V | |
| Delay pin threshold voltage | Low (flag ON), high (flag OFF) and VOUT regulated | 1.21 | 1.25 | 1.29 | V | ||
| Delay pin source current | VDELAY = 0.5 V | 3 | 6 | µA | |||
| Delay pin saturation | Low (flag ON) | 350 | 70 | 400 | mV | ||
(1) All limits specified at room temperature unless otherwise noted. All room temperature limits are 100% production tested. All limits at temperature extremes are ensured via correlation using standard Statistical Quality Control (SQC) methods. All limits are used to calculate Average Outgoing Quality Level (AOQL).
(2) Typical numbers are at 25°C and represent the most likely norm.
(3) The switching frequency is reduced when the second stage current limit is activated. The amount of reduction is determined by the severity of current overload.
(4) No diode, inductor or capacitor connected to output pin.
(5) Feedback pin removed from output and connected to 0 V to force the output transistor switch ON.
6.6 Electrical Characteristics – 3.3-V Version
TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYSTEM PARAMETERS | |||||||
| VOUT | Output voltage | 4.75 V ≤ VIN ≤ 60 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILOAD ≤ 2 A |
TJ = 25°C | 3.168 | 3.3 | 3.432 | V |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 3.135 | 3.465 | |||||
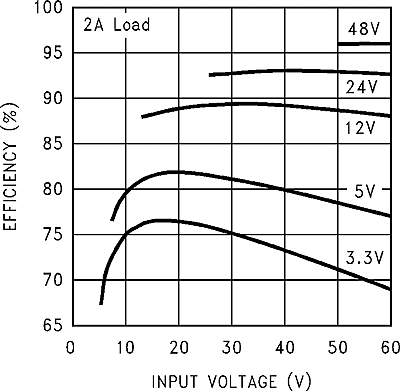
| η | Efficiency | VIN = 12 V, ILOAD = 2 A | 76% | ||||
6.7 Electrical Characteristics – 5-V Version
TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | Output voltage | 7 V ≤ VIN ≤ 60 V, 0.2 A ≤ILOAD ≤ 2 A |
TJ = 25°C | 4.8 | 5 | 5.2 | V |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 4.75 | 5.25 | |||||
| η | Efficiency | VIN = 12 V, ILOAD = 2 A | 81% | ||||
6.8 Electrical Characteristics – Adjustable Voltage Version
TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VFB | Feedback voltage | 4.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 60 V, 0.2 A ≤ ILOAD ≤ 2 A, VOUT programmed for 3 V (see Test Circuits) |
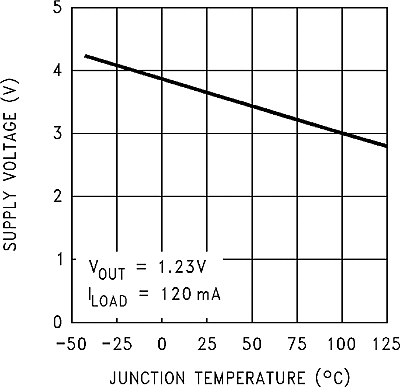
TJ = 25°C | 1.193 | 1.23 | 1.267 | V |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 1.18 | 1.28 | |||||
| η | Efficiency | VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3 V, ILOAD = 2 A | 75% | ||||
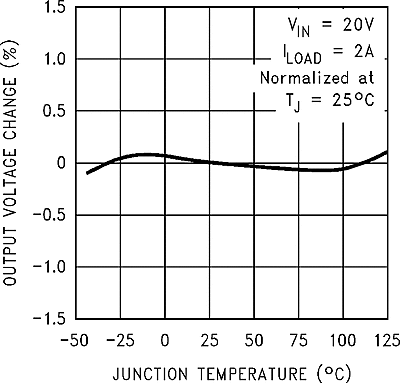
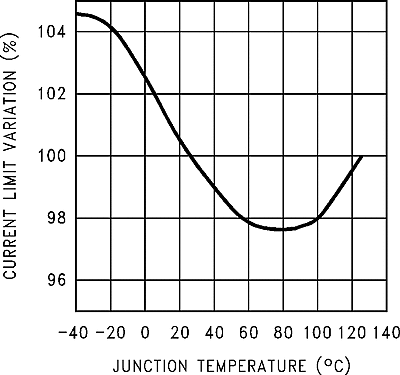
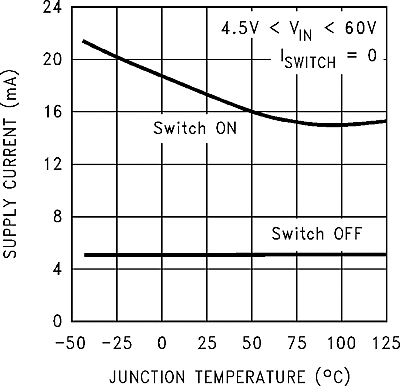
6.9 Typical Characteristics
Horizontal Time Base: 2 µs/div.
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 2 A,
L = 32 µH, COUT = 220 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Pin Voltage, 10 V/div.
Inductor Current, 1 A/div.
Output Ripple Voltage, 50 mV/div.
Figure 19. Continuous Mode Switching Waveforms
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 2 A,
L = 32 µH, COUT = 220 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Pin Voltage, 10 V/div.
Inductor Current, 1 A/div.
Output Ripple Voltage, 50 mV/div.
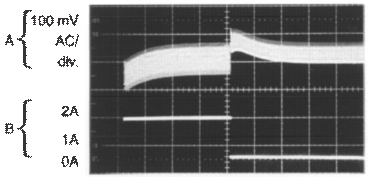
Horizontal Time Base: 50 µs/div.
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA to 2 A,
L = 32 µH, COUT = 220 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Voltage, 100 mV/div. (AC)
500-mA to 2-A Load Pulse
Figure 21. Load Transient ResponseVIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA to 2 A,
L = 32 µH, COUT = 220 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Voltage, 100 mV/div. (AC)
500-mA to 2-A Load Pulse
for Continuous Mode
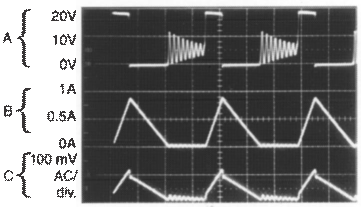
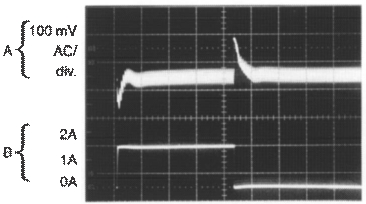
Horizontal Time Base: 2 µs/div.
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA,
L = 10 µH, COUT = 330 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Pin Voltage, 10 V/div.
Inductor Current, 0.5 A/div.
Output Ripple Voltage, 100 mV/div.
Figure 20. Discontinuous Mode Switching Waveforms
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA,
L = 10 µH, COUT = 330 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Pin Voltage, 10 V/div.
Inductor Current, 0.5 A/div.
Output Ripple Voltage, 100 mV/div.
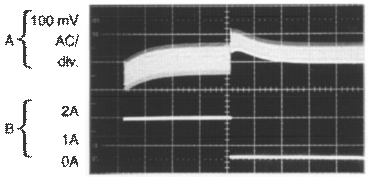
Horizontal Time Base: 200 µs/div.
VIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA to 2 A,
L = 10 µH, COUT = 330 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Voltage, 100 mV/div. (AC)
500-mA to 2-A Load Pulse
Figure 22. Load Transient ResponseVIN = 20 V, VOUT = 5 V, ILOAD = 500 mA to 2 A,
L = 10 µH, COUT = 330 µF, COUT ESR = 50 mΩ
Output Voltage, 100 mV/div. (AC)
500-mA to 2-A Load Pulse
for Discontinuous Mode