SNVS135E September 1999 – December 2014 LM2660
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (V+ to GND, or GND to OUT) | 6 | V | ||
| LV | (OUT − 0.3 V) to (GND + 3 V) | V | ||
| FC, OSC | The least negative of (OUT − 0.3 V) or (V+ − 6 V) to (V+ + 0.3 V) |
V | ||
| V+ and OUT continuous output current | 120 | mA | ||
| Output short-circuit duration to GND (2) | 1 | second | ||
| Power dissipation SOIC (D)(3) | 735 | mW | ||
| Power dissipation VSSOP (DGK)(3) | 500 | mW | ||
| Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds) | 300 | °C | ||
| Operating junction temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) OUT may be shorted to GND for one second without damage. However, shorting OUT to V+ may damage the device and should be avoided. Also, for temperatures above 85°C, OUT must not be shorted to GND or V+, or device may be damaged.
(3) The maximum allowable power dissipation is calculated by using PDMax = (TJMax − TA)/RθJA, where TJMax is the maximum junction temperature, TA is the ambient temperature, and RθJA is the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance of the specified package.
6.2 Handling Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –65 | 150 | °C | |
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | 2000 | V | |
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V+ (supply voltage) | Inverter, LV = Open | 3.5 | 5.5 | ||
| Inverter, LV = GND | 1.5 | 5.5 | |||
| Doubler, LV = OUT | 2.5 | 5.5 | |||
| Junction temperature (TJ) | –40 | 85 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM2660 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOIC (D) | VSSOP (DGK) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 170 | 250 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Limits in for typical (TYP) values are for TJ = 25°C, and limits in for minimum (MIN) and maximum (MAX) values apply over the full operating temperature range; V+ = 5V, FC = Open, C1 = C2 = 150 μF, unless otherwise specified in the Test Conditions.(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V+ | Supply voltage | RL = 1k | Inverter, LV = Open | 3.5 | 5.5 | ||
| Inverter, LV = GND | 1.5 | 5.5 | V | ||||
| Doubler, LV = OUT | 2.5 | 5.5 | |||||
| IQ | Supply current | No Load | FC = Open | 0.12 | 0.5 | mA | |
| LV = Open | FC = V+ | 1 | 3 | ||||
| IL | Output current | TA ≤ 85°C, OUT ≤ −4 V | 100 | mA | |||
| TA > 85°C, OUT ≤ −3.8 V | 100 | ||||||
| ROUT | Output resistance(2) | IL = 100 mA | TA ≤ 85°C | 6.5 | 10 | Ω | |
| TA > 85°C | 12 | ||||||
| fOSC | Oscillator frequency | OSC = Open | FC = Open | 5 | 10 | kHz | |
| FC = V+ | 40 | 80 | |||||
| fSW | Switching frequency(3) | OSC = Open | FC = Open | 2.5 | 5 | kHz | |
| FC = V+ | 20 | 40 | |||||
| IOSC | OSC input current | FC = Open | ±2 | µA | |||
| FC = V+ | ±16 | ||||||
| PEFF | Power efficiency | RL (1k) between V+ and OUT | 96% | 98% | |||
| RL (500) between GND and OUT | 92% | 96% | |||||
| IL = 100 mA to GND | 88% | ||||||
| VOEFF | Voltage conversion efficiency | No Load | 99% | 99.96% | |||
(1) In the test circuit, capacitors C1 and C2 are 0.2-Ω maximum ESR capacitors. Capacitors with higher ESR will increase output resistance, reduce output voltage and efficiency.
(2) Specified output resistance includes internal switch resistance and capacitor ESR.
(3) The output switches operate at one half of the oscillator frequency, fOSC = 2fSW.
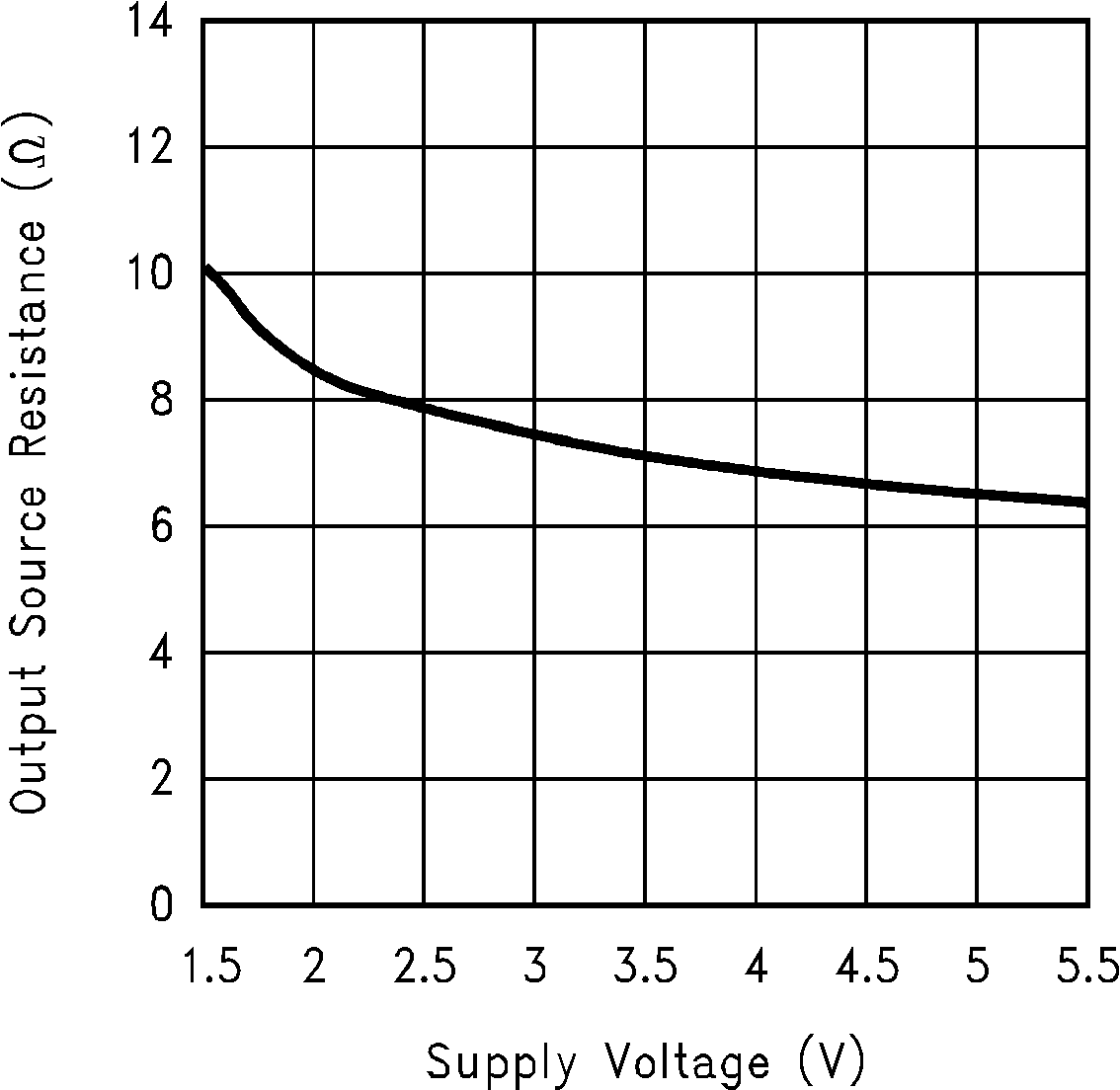
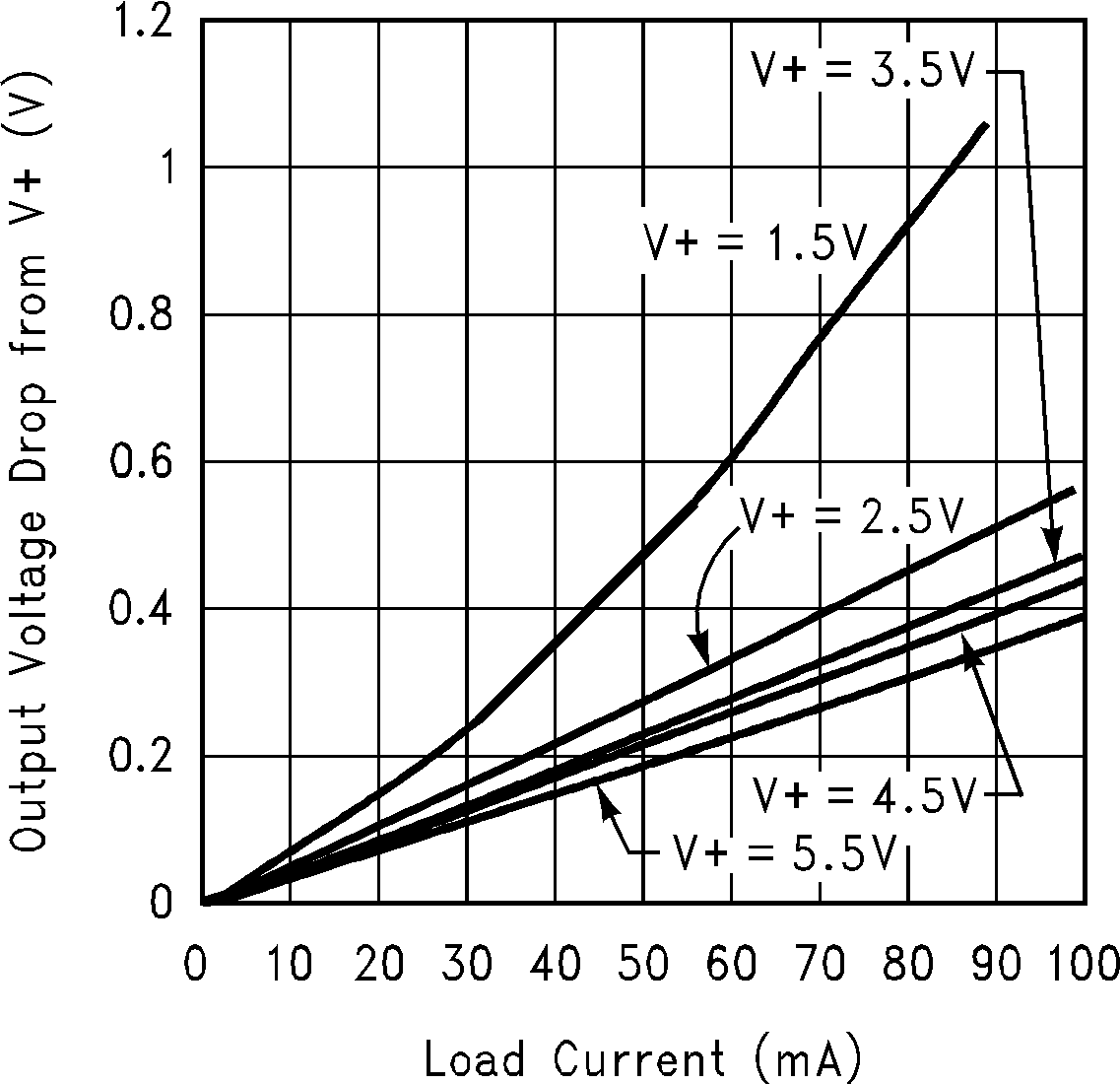
6.6 Typical Characteristics
(Circuit of Figure 12)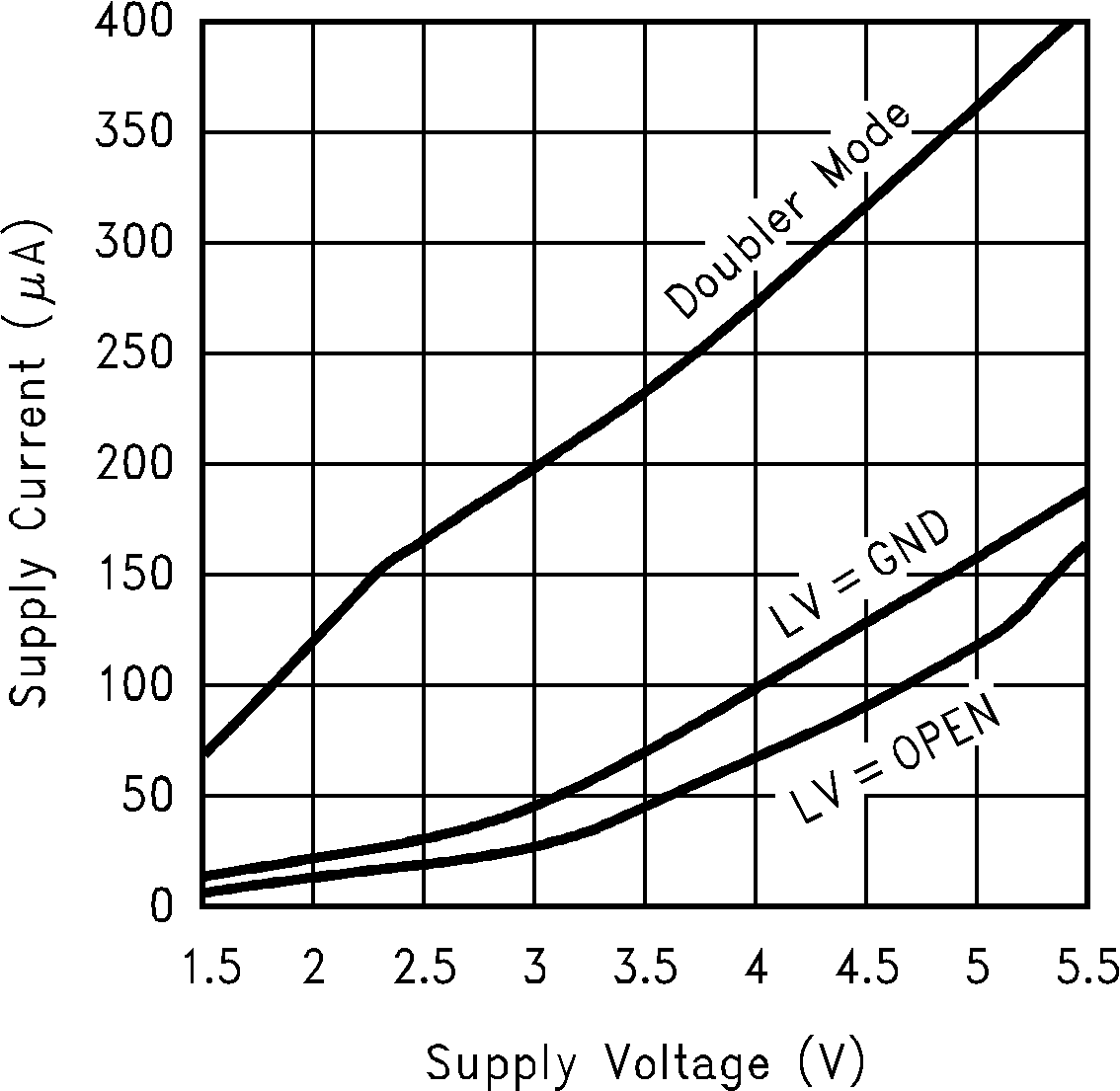
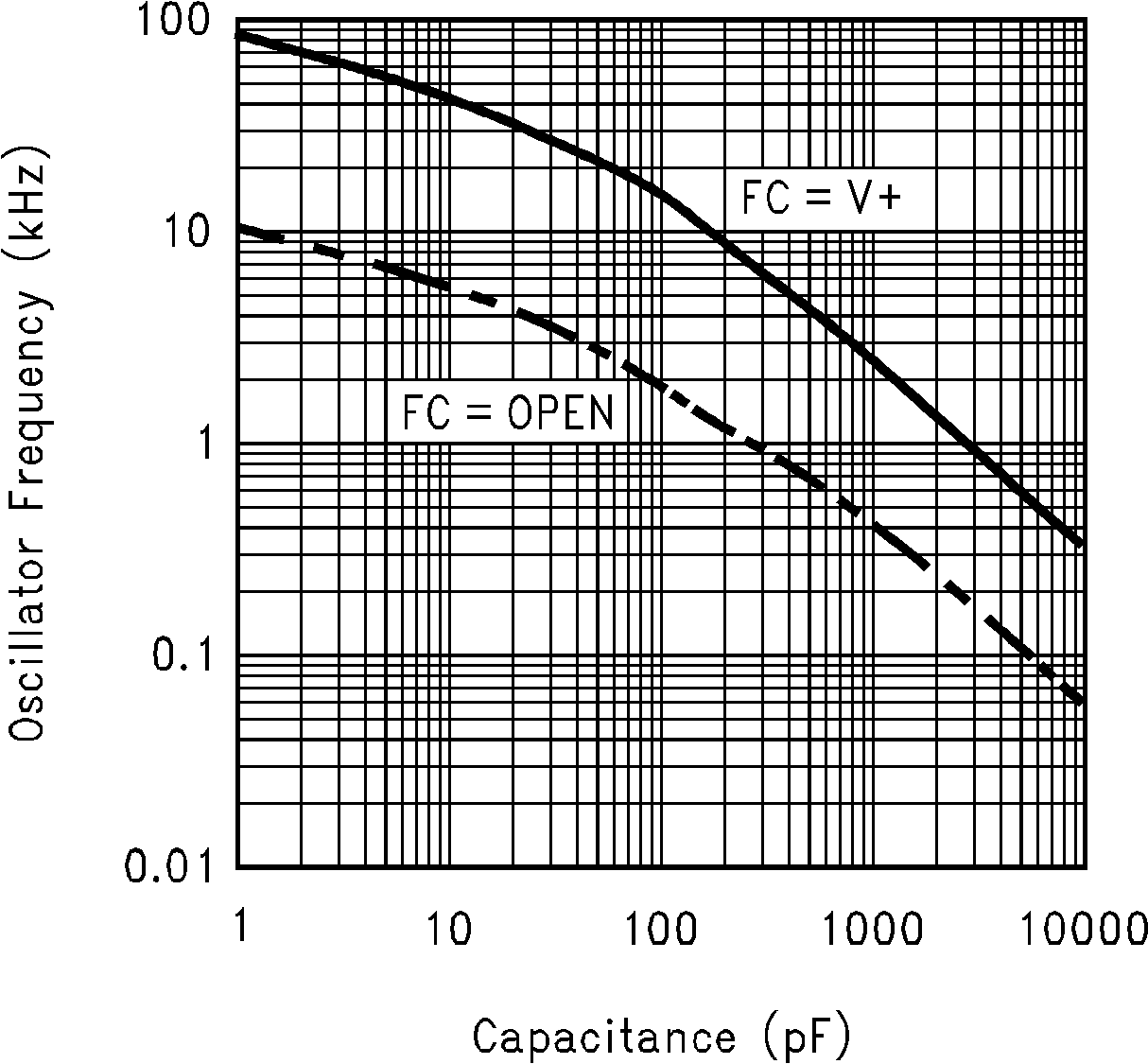
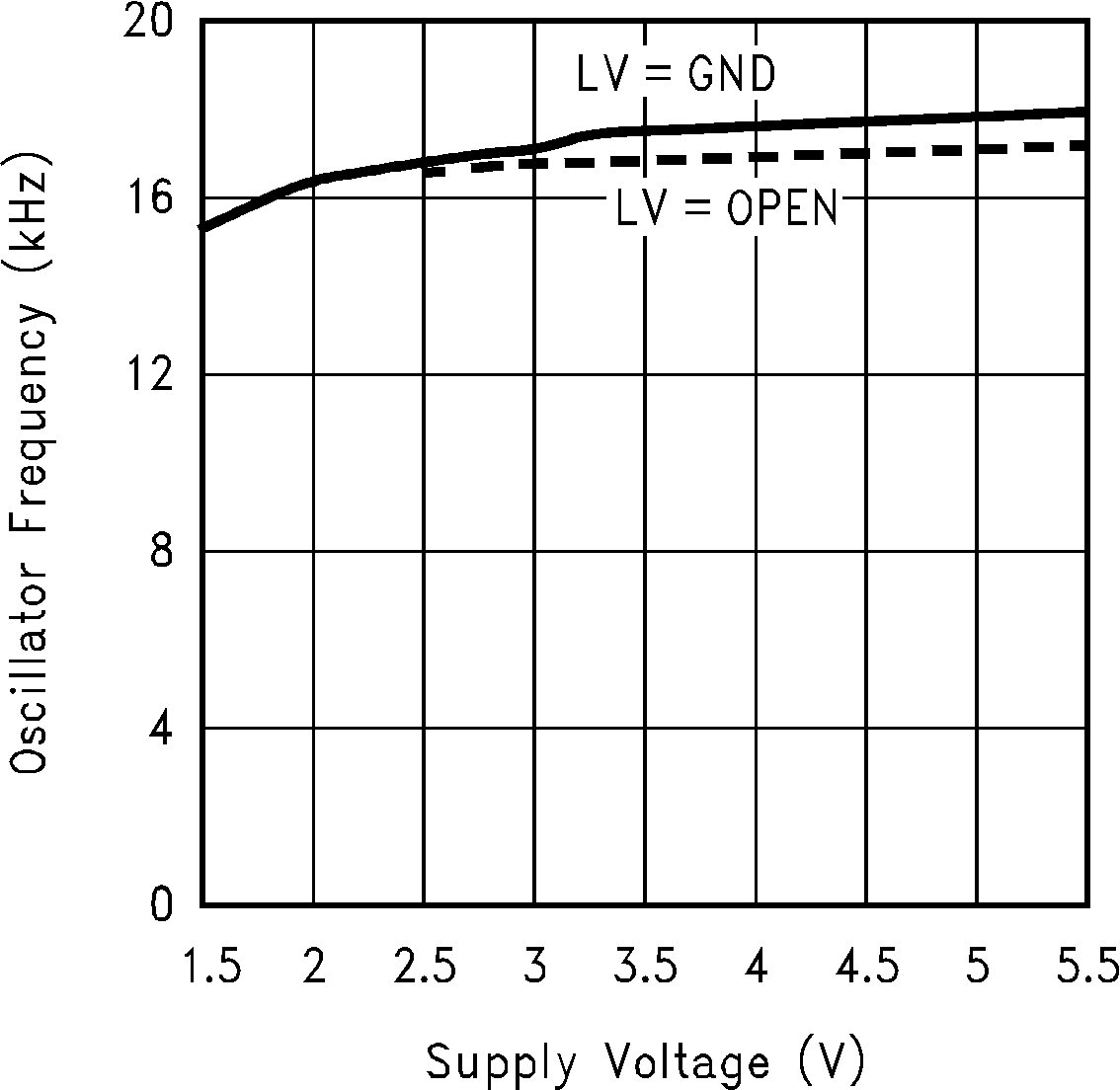
(Fc = Open)
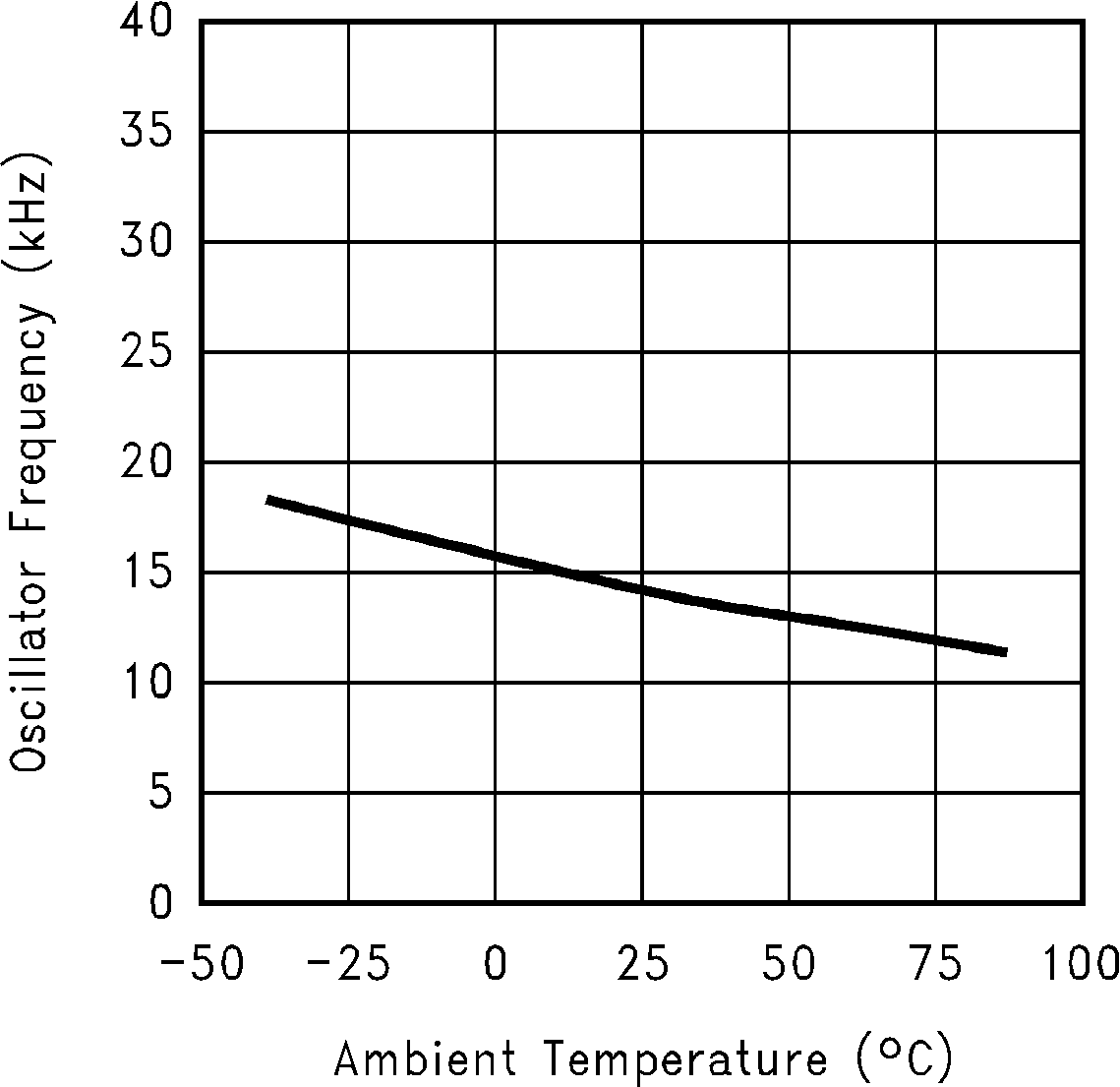
(Fc = Open)
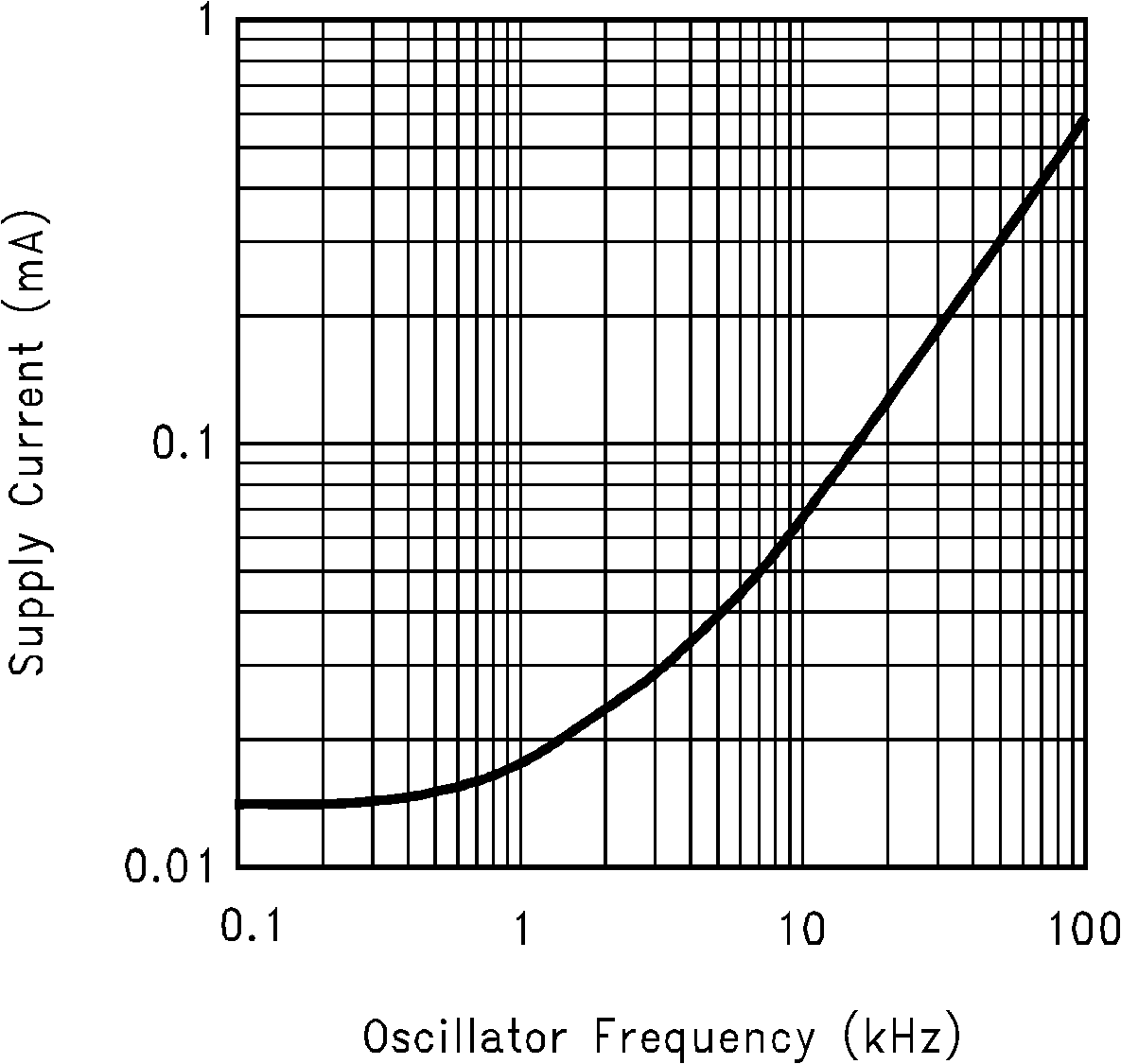
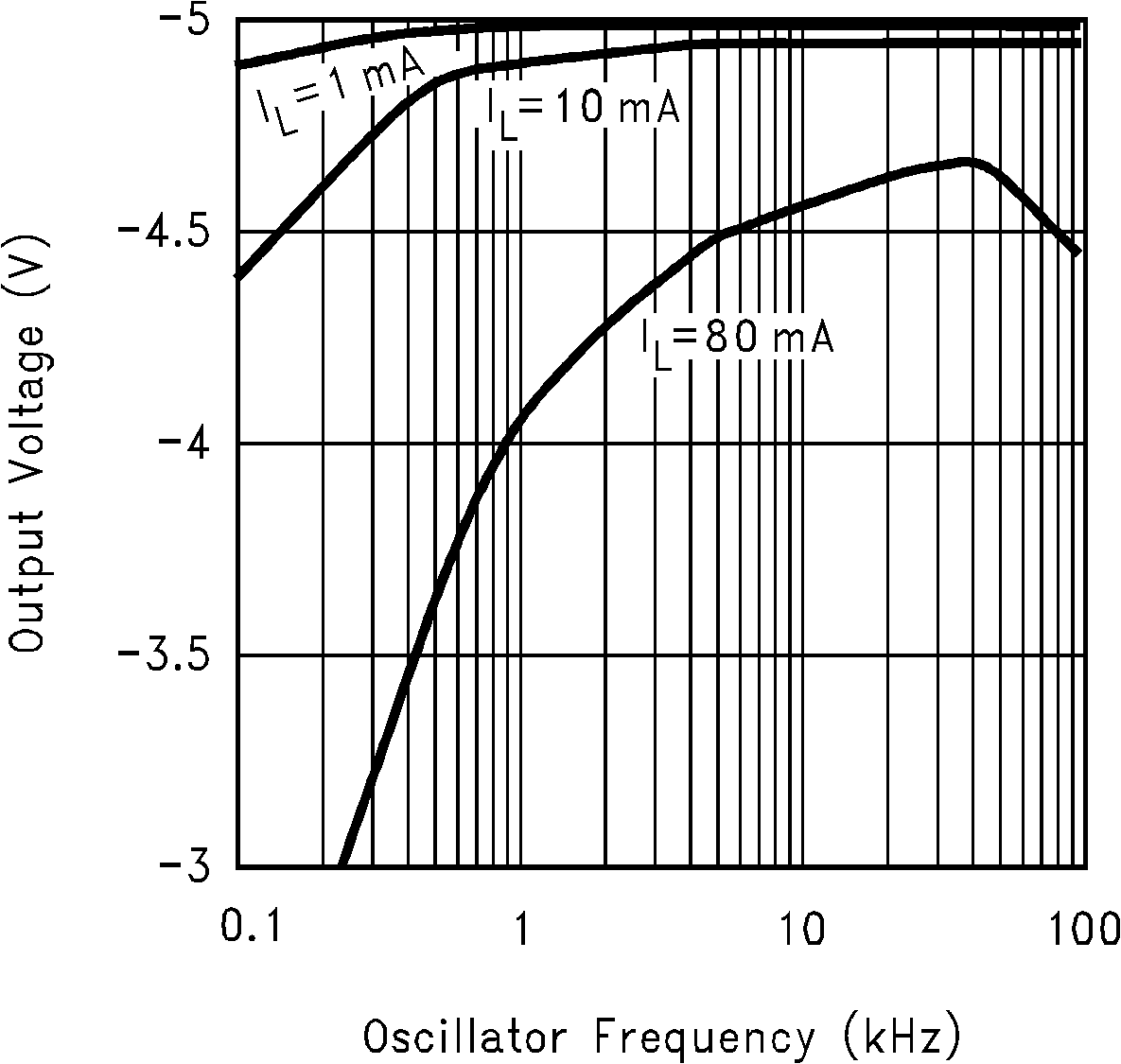
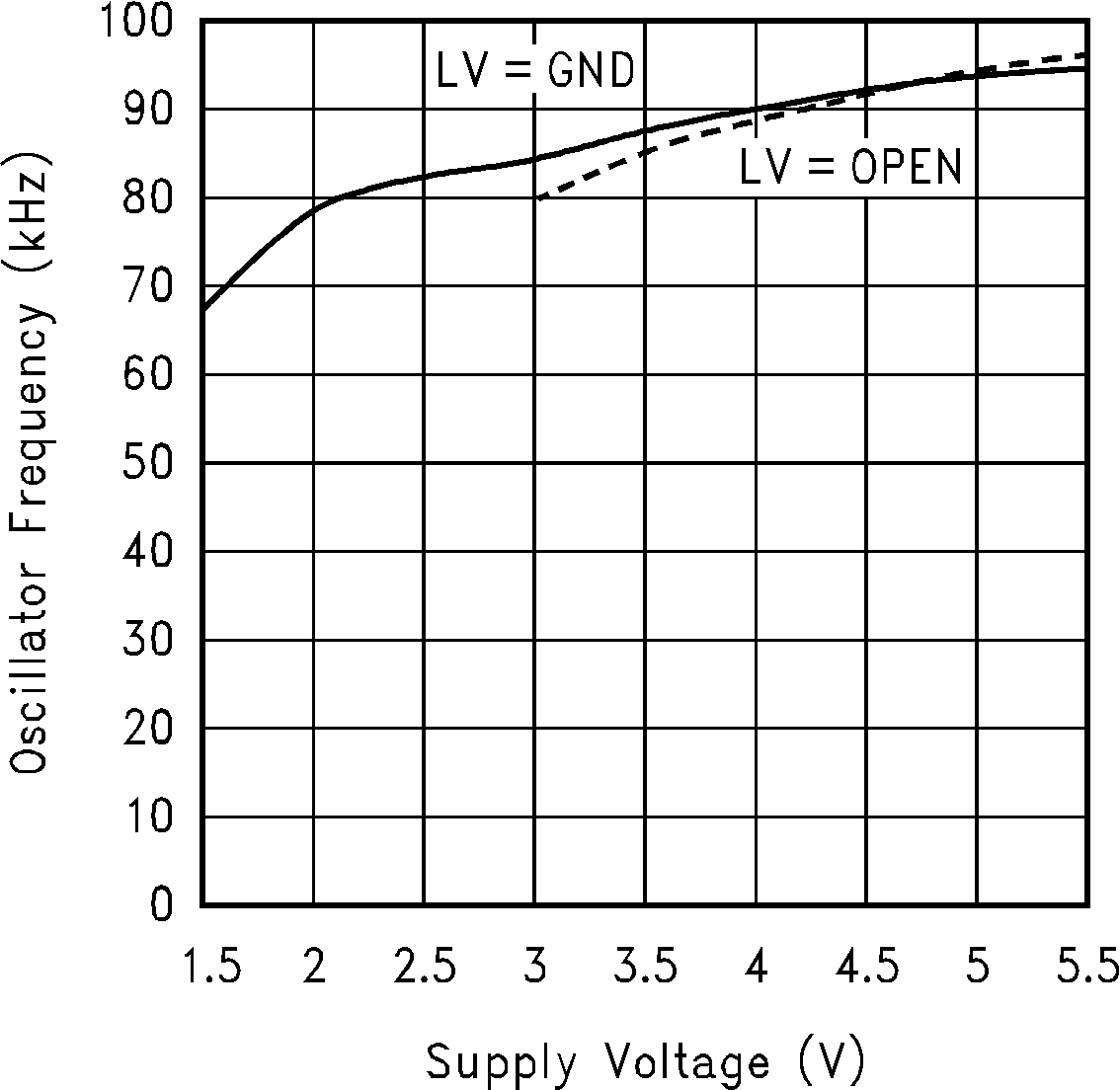
(Fc = V+)
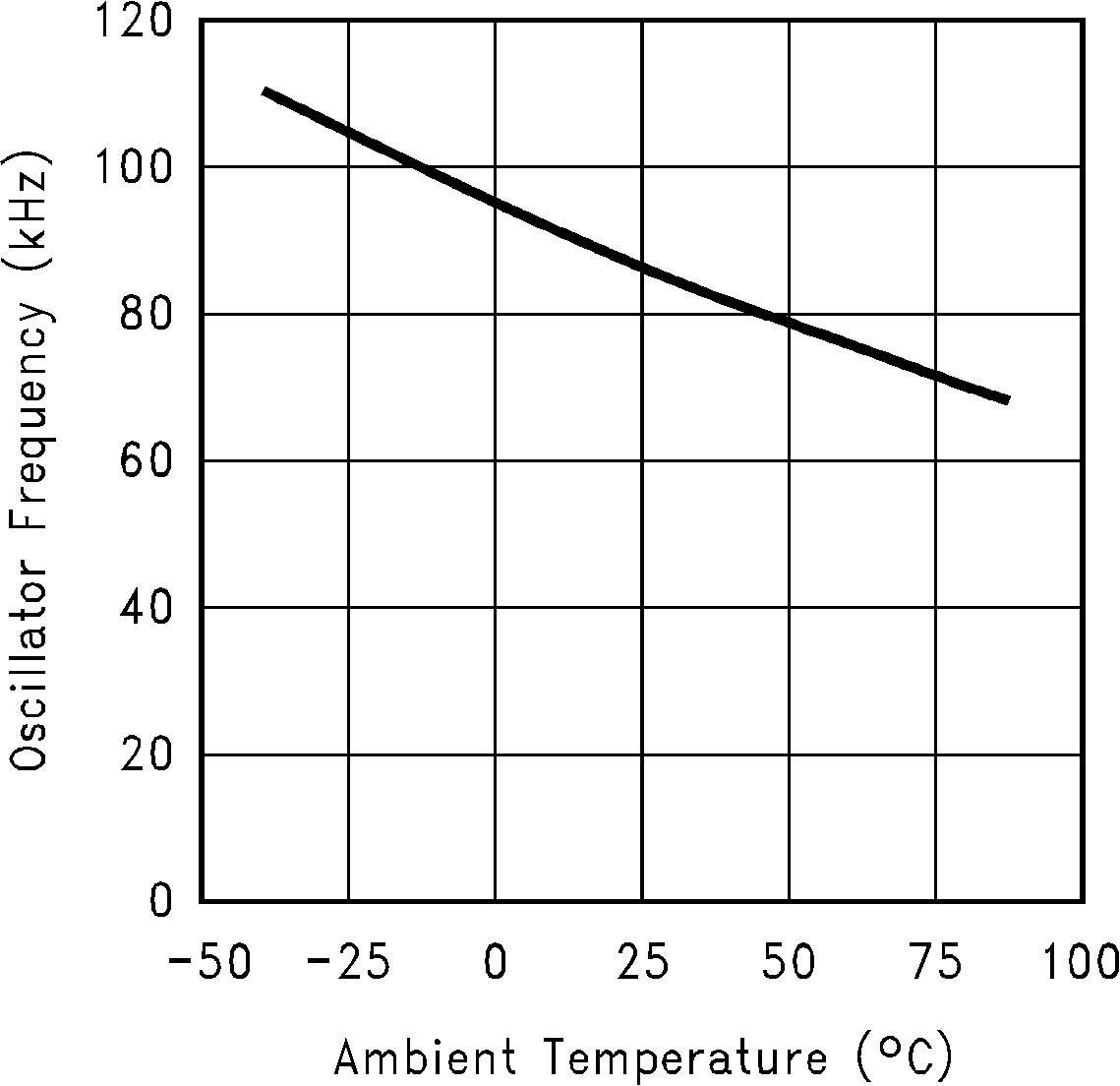
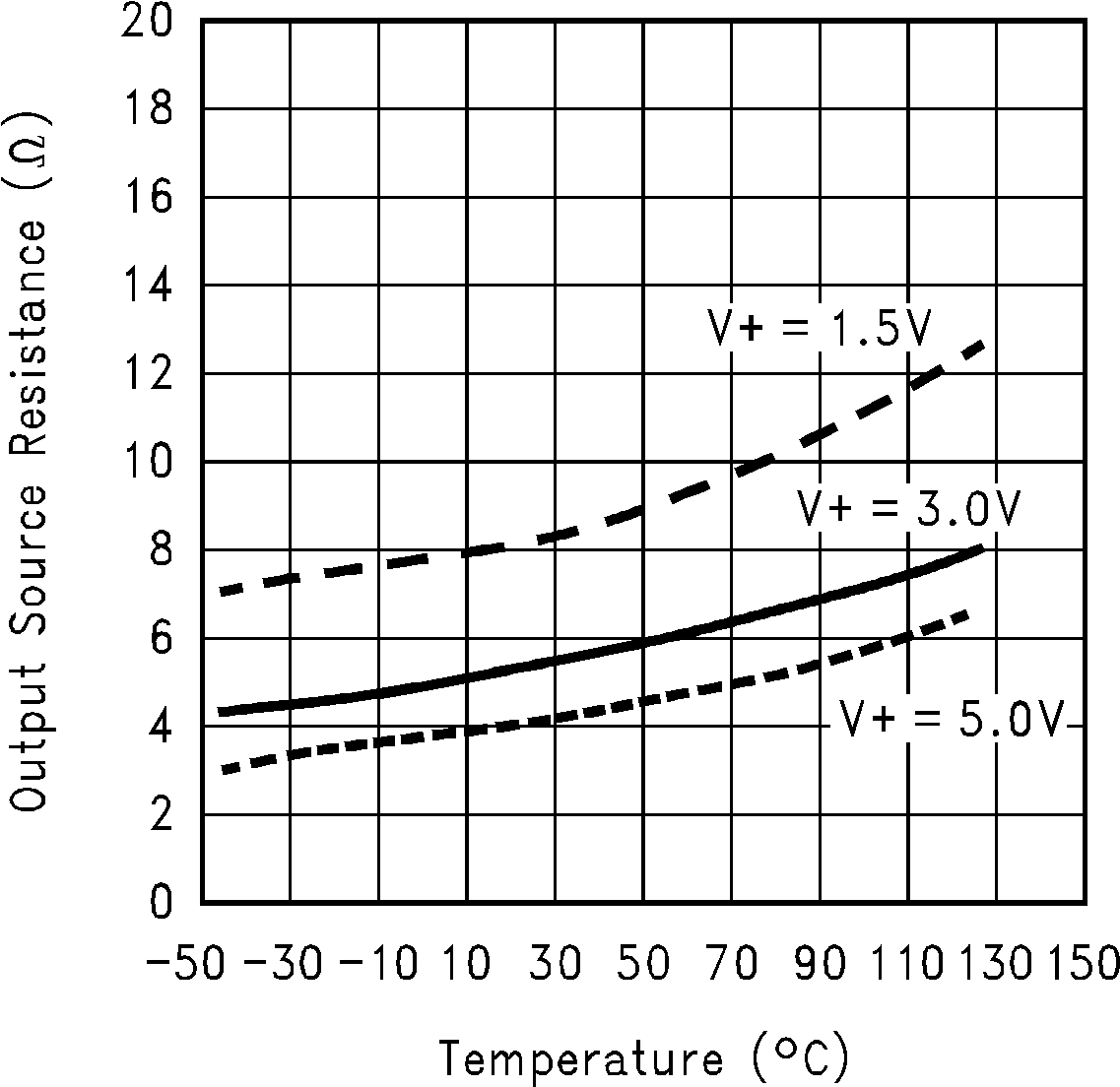
(Fc = V+)