SNVS077J May 2004 – June 2016 LM2677
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - 3.3 V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - 5 V
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - 12 V
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics - Adjustable
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics - All Output Voltage Versions
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
8.1.1 Inductor
The inductor is the key component in a switching regulator. For efficiency the inductor stores energy during the switch ON time and then transfers energy to the load while the switch is OFF.
Nomographs are used to select the inductance value required for a given set of operating conditions. The nomographs assume that the circuit is operating in continuous mode (the current flowing through the inductor never falls to zero). The magnitude of inductance is selected to maintain a maximum ripple current of 30% of the maximum load current. If the ripple current exceeds this 30% limit the next larger value is selected.
The inductors offered have been specifically manufactured to provide proper operation under all operating conditions of input and output voltage and load current. Several part types are offered for a given amount of inductance. Both surface mount and through-hole devices are available. The inductors from each of the three manufacturers have unique characteristics.
Renco: ferrite stick core inductors; benefits are typically lowest cost and can withstand ripple and transient peak currents above the rated value. These inductors have an external magnetic field, which may generate EMI.
Pulse Engineering: powdered iron toroid core inductors; these also can withstand higher than rated currents and, being toroid inductors, has low EMI.
Coilcraft: ferrite drum core inductors; these are the smallest physical-size inductors and are available only as surface mount components. These inductors also generate EMI but less than stick inductors.
8.1.2 Output Capacitor
The output capacitor acts to smooth the dc output voltage and also provides energy storage. Selection of an output capacitor, with an associated equivalent series resistance (ESR), impacts both the amount of output ripple voltage and stability of the control loop.
The output ripple voltage of the power supply is the product of the capacitor ESR and the inductor ripple current. The capacitor types recommended in the Input and Output Capacitor Codes were selected for having low ESR ratings.
In addition, both surface mount tantalum capacitors and through-hole aluminum electrolytic capacitors are offered as solutions.
Impacting frequency stability of the overall control loop, the output capacitance, in conjunction with the inductor, creates a double pole inside the feedback loop. In addition the capacitance and the ESR value create a zero. These frequency response effects together with the internal frequency compensation circuitry of the LM2677 modify the gain and phase shift of the closed loop system.
As a general rule for stable switching regulator circuits it is desired to have the unity gain bandwidth of the circuit to be limited to no more than one-sixth of the controller switching frequency. With the fixed 260-kHz switching frequency of the LM2677, the output capacitor is selected to provide a unity gain bandwidth of 40 kHz maximum. Each recommended capacitor value has been chosen to achieve this result.
In some cases multiple capacitors are required either to reduce the ESR of the output capacitor, to minimize output ripple (a ripple voltage of 1% of Vout or less is the assumed performance condition), or to increase the output capacitance to reduce the closed loop unity gain bandwidth (to less than 40 kHz). When parallel combinations of capacitors are required it has been assumed that each capacitor is the exact same part type.
The RMS current and working voltage (WV) ratings of the output capacitor are also important considerations. In a typical step-down switching regulator, the inductor ripple current (set to be no more than 30% of the maximum load current by the inductor selection) is the current that flows through the output capacitor. The capacitor RMS current rating must be greater than this ripple current. The voltage rating of the output capacitor must be greater than 1.3 times the maximum output voltage of the power supply. If operation of the system at elevated temperatures is required, the capacitor voltage rating may be de-rated to less than the nominal room temperature rating. Careful inspection of the manufacturer's specification for de-rating of working voltage with temperature is important.
8.1.3 Input and Output Capacitor Codes
Table 1. Surface-Mount Capacitors(1)
| CAPACITOR REFERENCE CODE | AVX TPS SERIES | SPRAGUE 594D SERIES | KEMET T495 SERIES | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | |
| C1 | 330 | 6.3 | 1.15 | 120 | 6.3 | 1.1 | 100 | 6.3 | 0.82 |
| C2 | 100 | 10 | 1.1 | 220 | 6.3 | 1.4 | 220 | 6.3 | 1.1 |
| C3 | 220 | 10 | 1.15 | 68 | 10 | 1.05 | 330 | 6.3 | 1.1 |
| C4 | 47 | 16 | 0.89 | 150 | 10 | 1.35 | 100 | 10 | 1.1 |
| C5 | 100 | 16 | 1.15 | 47 | 16 | 1 | 150 | 10 | 1.1 |
| C6 | 33 | 20 | 0.77 | 100 | 16 | 1.3 | 220 | 10 | 1.1 |
| C7 | 68 | 20 | 0.94 | 180 | 16 | 1.95 | 33 | 20 | 0.78 |
| C8 | 22 | 25 | 0.77 | 47 | 20 | 1.15 | 47 | 20 | 0.94 |
| C9 | 10 | 35 | 0.63 | 33 | 25 | 1.05 | 68 | 20 | 0.94 |
| C10 | 22 | 35 | 0.66 | 68 | 25 | 1.6 | 10 | 35 | 0.63 |
| C11 | — | — | — | 15 | 35 | 0.75 | 22 | 35 | 0.63 |
| C12 | — | — | — | 33 | 35 | 1 | 4.7 | 50 | 0.66 |
| C13 | — | — | — | 15 | 50 | 0.9 | — | — | — |
Table 2. Through-Hole Capacitors(1)
| CAPACITOR REFERENCE CODE | SANYO OS-CON SA SERIES | SANYO MV-GX SERIES | NICHICON PL SERIES | PANASONIC HFQ SERIES | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | C (µF) | WV (V) | IRMS (A) | |
| C1 | 47 | 6.3 | 1 | 1000 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 680 | 10 | 0.8 | 82 | 35 | 0.4 |
| C2 | 150 | 6.3 | 1.95 | 270 | 16 | 0.6 | 820 | 10 | 0.98 | 120 | 35 | 0.44 |
| C3 | 330 | 6.3 | 2.45 | 470 | 16 | 0.75 | 1000 | 10 | 1.06 | 220 | 35 | 0.76 |
| C4 | 100 | 10 | 1.87 | 560 | 16 | 0.95 | 1200 | 10 | 1.28 | 330 | 35 | 1.01 |
| C5 | 220 | 10 | 2.36 | 820 | 16 | 1.25 | 2200 | 10 | 1.71 | 560 | 35 | 1.4 |
| C6 | 33 | 16 | 0.96 | 1000 | 16 | 1.3 | 3300 | 10 | 2.18 | 820 | 35 | 1.62 |
| C7 | 100 | 16 | 1.92 | 150 | 35 | 0.65 | 3900 | 10 | 2.36 | 1000 | 35 | 1.73 |
| C8 | 150 | 16 | 2.28 | 470 | 35 | 1.3 | 6800 | 10 | 2.68 | 2200 | 35 | 2.8 |
| C9 | 100 | 20 | 2.25 | 680 | 35 | 1.4 | 180 | 16 | 0.41 | 56 | 50 | 0.36 |
| C10 | 47 | 25 | 2.09 | 1000 | 35 | 1.7 | 270 | 16 | 0.55 | 100 | 50 | 0.5 |
| C11 | — | — | — | 220 | 63 | 0.76 | 470 | 16 | 0.77 | 220 | 50 | 0.92 |
| C12 | — | — | — | 470 | 63 | 1.2 | 680 | 16 | 1.02 | 470 | 50 | 1.44 |
| C13 | — | — | — | 680 | 63 | 1.5 | 820 | 16 | 1.22 | 560 | 50 | 1.68 |
| C14 | — | — | — | 1000 | 63 | 1.75 | 1800 | 16 | 1.88 | 1200 | 50 | 2.22 |
| C15 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 220 | 25 | 0.63 | 330 | 63 | 1.42 |
| C16 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 220 | 35 | 0.79 | 1500 | 63 | 2.51 |
| C17 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 560 | 35 | 1.43 | — | — | — |
| C18 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2200 | 35 | 2.68 | — | — | — |
| C19 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 150 | 50 | 0.82 | — | — | — |
| C20 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 220 | 50 | 1.04 | — | — | — |
| C21 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 330 | 50 | 1.3 | — | — | — |
| C22 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 100 | 63 | 0.75 | — | — | — |
| C23 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 390 | 63 | 1.62 | — | — | — |
| C24 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 820 | 63 | 2.22 | — | — | — |
| C25 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1200 | 63 | 2.51 | — | — | — |
8.1.4 Input Capacitor
Fast changing currents in high-current switching regulators place a significant dynamic load on the unregulated power source. An input capacitor helps to provide additional current to the power supply as well as smooth out input voltage variations.
Like the output capacitor, the key specifications for the input capacitor are RMS current rating and working voltage. The RMS current flowing through the input capacitor is equal to one-half of the maximum dc load current so the capacitor must be rated to handle this. Paralleling multiple capacitors proportionally increases the current rating of the total capacitance. The voltage rating must also be selected to be 1.3 times the maximum input voltage. Depending on the unregulated input power source, under light load conditions the maximum input voltage could be significantly higher than normal operation and must be considered when selecting an input capacitor.
The input capacitor must be placed very close to the input pin of the LM2677. Due to relative high-current operation with fast transient changes, the series inductance of input connecting wires or PCB traces can create ringing signals at the input terminal which could possibly propagate to the output or other parts of the circuitry. It may be necessary in some designs to add a small valued (0.1 μF to 0.47 μF) ceramic type capacitor in parallel with the input capacitor to prevent or minimize any ringing.
8.1.5 Catch Diode
When the power switch in the LM2677 turns OFF, the current through the inductor continues to flow. The path for this current is through the diode connected between the switch output and ground. This forward biased diode clamps the switch output to a voltage less than ground. This negative voltage must be greater than −1 V, so TI recommends a low voltage drop (particularly at high current levels) Schottky diode. Total efficiency of the entire power supply is significantly impacted by the power lost in the output catch diode. The average current through the catch diode is dependent on the switch duty cycle (D) and is equal to the load current times (1-D). Use of a diode rated for much higher current than is required by the actual application helps to minimize the voltage drop and power loss in the diode.
During the switch ON-time the diode is reversed biased by the input voltage. The reverse voltage rating of the diode must be at least 1.3 times greater than the maximum input voltage.
8.1.6 Boost Capacitor
The boost capacitor creates a voltage used to overdrive the gate of the internal power MOSFET. This improves efficiency by minimizing the on-resistance of the switch and associated power loss. For all applications, TI recommends using a 0.01-μF, 50-V ceramic capacitor.
8.1.7 SYNC Components
When synchronizing the LM2677 with an external clock TI recommends connecting the clock to pin 5 through a series 100-pF capacitor, and connecting a 1-kΩ resistor to ground from pin 5. This RC network creates a short
100-nS pulse on each positive edge of the clock to reset the internal ramp oscillator. The reset time of the oscillator is approximately 300 nS.
8.1.8 Additional Application Information
When the output voltage is greater than approximately 6 V, and the duty cycle at minimum input voltage is greater than approximately 50%, the designer must exercise caution in selection of the output filter components. When an application designed to these specific operating conditions is subjected to a current limit fault condition, it may be possible to observe a large hysteresis in the current limit. This can affect the output voltage of the device until the load current is reduced sufficiently to allow the current limit protection circuit to reset itself.
Under current limiting conditions, the LM267x is designed to respond in the following manner:
- At the moment when the inductor current reaches the current limit threshold, the ON-pulse is immediately terminated. This happens for any application condition.
- However, the current limit block is also designed to momentarily reduce the duty cycle to below 50% to avoid subharmonic oscillations, which could cause the inductor to saturate.
- Thereafter, once the inductor current falls below the current limit threshold, there is a small relaxation time during which the duty cycle progressively rises back above 50% to the value required to achieve regulation.
If the output capacitance is sufficiently large, it may be possible that as the output tries to recover, the output capacitor charging current is large enough to repeatedly re-trigger the current limit circuit before the output has fully settled. This condition is exacerbated with higher output voltage settings because the energy requirement of the output capacitor varies as the square of the output voltage (½ CV2), thus requiring an increased charging current.
A simple test to determine if this condition might exist for a suspect application is to apply a short circuit across the output of the converter, and then remove the shorted output condition. In an application with properly selected external components, the output recovers smoothly.
Practical values of external components that have been experimentally found to work well under these specific operating conditions are COUT = 47 µF, L = 22 µH. It must be noted that even with these components, for a device’s current limit of ICLIM, the maximum load current under which the possibility of the large current limit hysteresis can be minimized is ICLIM/ 2. For example, if the input is 24 V and the set output voltage is 18 V, then for a desired maximum current of 1.5 A, the current limit of the chosen switcher must be confirmed to be at least 3 A.
Under extreme over-current or short circuit conditions, the LM267X employs frequency foldback in addition to the current limit. If the cycle-by-cycle inductor current increases above the current limit threshold (due to short circuit or inductor saturation for example) the switching frequency is automatically reduced to protect the IC. Frequency below 100 kHz is typical for an extreme short circuit condition.
8.2 Typical Application
8.2.1 Fixed Output Voltage Applications
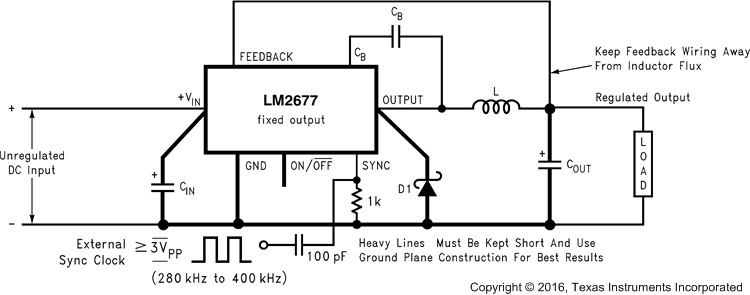 Figure 16. Basic Circuit For Fixed Output Voltage Applications
Figure 16. Basic Circuit For Fixed Output Voltage Applications
8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
Table 3 lists the design requirements for the adjustable output voltage application.
Table 3. Design Parameters
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Required output voltage, VOUT | 3.3 V |
| Maximum DC input voltage, VIN_MAX | 16 V |
| Maximum output load current, ILOAD_MAX | 2.5 A |
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
A system logic power supply bus of 3.3 V is to be generated from a wall adapter which provides an unregulated DC voltage of 13 V to 16 V. The maximum load current is 2.5 A. Through-hole components are preferred.
Step 1: Select an LM2677T, 3.3 V. The output voltage has a tolerance of ±2% at room temperature and ±3% over the full operating temperature range.
Step 2: Use the nomograph for the 3.3 V device, Figure 17. The intersection of the 16-V horizontal line (Vin max) and the 2.5-A vertical line (Iload max) indicates that L33, a 22-μH inductor, is required. From Table 4, L33 in a through-hole component is available from Renco with part number RL-1283-22-43 or part number PE-53933 from Pulse Engineering.
Table 4. Inductor Manufacturer Part Numbers(1)
| INDUCTOR REF. # |
INDUCTANCE (µH) |
CURRENT (A) |
RENCO | PULSE ENGINEERING | COILCRAFT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THROUGH HOLE | SURFACE MOUNT | THROUGH HOLE | SURFACE MOUNT | SURFACE MOUNT | |||
| L23 | 33 | 1.35 | RL-5471-7 | RL1500-33 | PE-53823 | PE-53823S | DO3316-333 |
| L24 | 22 | 1.65 | RL-1283-22-43 | RL1500-22 | PE-53824 | PE-53824S | DO3316-223 |
| L25 | 15 | 2.00 | RL-1283-15-43 | RL1500-15 | PE-53825 | PE-53825S | DO3316-153 |
| L29 | 100 | 1.41 | RL-5471-4 | RL-6050-100 | PE-53829 | PE-53829S | DO5022P-104 |
| L30 | 68 | 1.71 | RL-5471-5 | RL6050-68 | PE-53830 | PE-53830S | DO5022P-683 |
| L31 | 47 | 2.06 | RL-5471-6 | RL6050-47 | PE-53831 | PE-53831S | DO5022P-473 |
| L32 | 33 | 2.46 | RL-5471-7 | RL6050-33 | PE-53932 | PE-53932S | DO5022P-333 |
| L33 | 22 | 3.02 | RL-1283-22-43 | RL6050-22 | PE-53933 | PE-53933S | DO5022P-223 |
| L34 | 15 | 3.65 | RL-1283-15-43 | — | PE-53934 | PE-53934S | DO5022P-153 |
| L38 | 68 | 2.97 | RL-5472-2 | — | PE-54038 | PE-54038S | — |
| L39 | 47 | 3.57 | RL-5472-3 | — | PE-54039 | PE-54039S | — |
| L40 | 33 | 4.26 | RL-1283-33-43 | — | PE-54040 | PE-54040S | — |
| L41 | 22 | 5.22 | RL-1283-22-43 | — | PE-54041 | P0841 | — |
| L44 | 68 | 3.45 | RL-5473-3 | — | PE-54044 | — | — |
| L45 | 10 | 4.47 | RL-1283-10-43 | — | — | P0845 | DO5022P-103HC |
| L46 | 15 | 5.60 | RL-1283-15-43 | — | — | P0846 | DO5022P-153HC |
| L47 | 10 | 5.66 | RL-1283-10-43 | — | — | P0847 | DO5022P-103HC |
| L48 | 47 | 5.61 | RL-1282-47-43 | — | — | P0848 | — |
| L49 | 33 | 5.61 | RL-1282-33-43 | — | — | P0849 | — |
Step 3: Use Table 5 to determine an output capacitor. With a 3.3-V output and a 22-μH inductor there are four through-hole output capacitor solutions with the number of same type capacitors to be paralleled and an identifying capacitor code given. Table 1 provides the actual capacitor characteristics. Any of the following choices works in the circuit:
- 1 × 220-μF, 10-V Sanyo OS-CON (code C5)
- 1 × 1000-μF, 35-V Sanyo MV-GX (code C10)
- 1 × 2200-μF, 10-V Nichicon PL (code C5)
- 1 × 1000-μF, 35-V Panasonic HFQ (code C7)
Table 5. Output Capacitors for Fixed Output Voltage Application(1)
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V) | INDUCTANCE (µH) | SURFACE MOUNT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVX TPS SERIES | SPRAGUE 594D SERIES | KEMET T495 SERIES | |||||
| NO.(2) | C CODE(3) | NO.(2) | C Code(3) | NO.(2) | C CODE(3) | ||
| 3.3 | 10 | 5 | C1 | 5 | C1 | 5 | C2 |
| 15 | 4 | C1 | 4 | C1 | 4 | C3 | |
| 22 | 3 | C2 | 2 | C7 | 3 | C4 | |
| 33 | 1 | C1 | 2 | C7 | 3 | C4 | |
| 5 | 10 | 4 | C2 | 4 | C6 | 4 | C4 |
| 15 | 3 | C3 | 2 | C7 | 3 | C5 | |
| 22 | 3 | C2 | 2 | C7 | 3 | C4 | |
| 33 | 2 | C2 | 2 | C3 | 2 | C4 | |
| 47 | 2 | C2 | 1 | C7 | 2 | C4 | |
| 12 | 10 | 4 | C5 | 3 | C6 | 5 | C9 |
| 15 | 3 | C5 | 2 | C7 | 4 | C9 | |
| 22 | 2 | C5 | 2 | C6 | 3 | C8 | |
| 33 | 2 | C5 | 1 | C7 | 3 | C8 | |
| 47 | 2 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C8 | |
| 68 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C5 | 2 | C7 | |
| 100 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C8 | |
Step 4: Use Table 6 to select an input capacitor. With 3.3-V output and 22-μH there are three through-hole solutions. These capacitors provide a sufficient voltage rating and an rms current rating greater than 1.25 A (1/2 Iload max). Again using Table 1 for specific component characteristics the following choices are suitable:
- 1 × 1000-μF, 63-V Sanyo MV-GX (code C14)
- 1 × 820-μF, 63-V Nichicon PL (code C24)
- 1 × 560-μF, 50-V Panasonic HFQ (code C13)
Table 6. Input Capacitors for Fixed Output Voltage Application(1)
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V) | INDUCTANCE (µH) | SURFACE MOUNT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVX TPS SERIES(2) | SPRAGUE 594D SERIES | KEMET T495 SERIES | |||||
| NO.(3) | C CODE(4) | NO.(3) | C CODE(4) | NO.(3) | C CODE(4) | ||
| 3.3 | 10 | 3 | C7 | 2 | C10 | 3 | C9 |
| 15 | * | * | 3 | C13 | 4 | C12 | |
| 22 | * | * | 2 | C13 | 3 | C12 | |
| 33 | * | * | 2 | C13 | 3 | C12 | |
| 5 | 10 | 3 | C4 | 2 | C6 | 3 | C9 |
| 15 | 4 | C9 | 3 | C12 | 4 | C10 | |
| 22 | * | * | 3 | C13 | 4 | C12 | |
| 33 | * | * | 2 | C13 | 3 | C12 | |
| 47 | * | * | 1 | C13 | 2 | C12 | |
| 12 | 10 | 4 | C9 | 2 | C10 | 4 | C10 |
| 15 | 4 | C8 | 2 | C10 | 4 | C10 | |
| 22 | 4 | C9 | 3 | C12 | 4 | C10 | |
| 33 | * | * | 3 | C13 | 4 | C12 | |
| 47 | * | * | 2 | C13 | 3 | C12 | |
| 68 | * | * | 2 | C13 | 2 | C12 | |
| 100 | * | * | 1 | C13 | 2 | C12 | |
Step 5: From Table 7 a 3-A Schottky diode must be selected. For through-hole components, 20-V rated diodes are sufficient and 2 part types are suitable, 1N5820 and SR302.
Table 7. Schottky Diode Selection Table
| REVERSE VOLTAGE (V) | SURFACE MOUNT | THROUGH HOLE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 A | 5 A OR MORE | 3 A | 5 A OR MORE | |
| 20 | SK32 | — | 1N5820 | — |
| — | SR302 | — | ||
| 30 | SK33 | MBRD835L | 1N5821 | — |
| 30WQ03F | 31DQ03 | — | ||
| 40 | SK34 | MBRB1545CT | 1N5822 | — |
| 30BQ040 | 6TQ045S | MBR340 | MBR745 | |
| 30WQ04F | — | 31DQ04 | 80SQ045 | |
| MBRS340 | — | SR403 | 6TQ045 | |
| MBRD340 | — | — | — | |
| 50 or more | SK35 | — | MBR350 | — |
| 30WQ05F | — | 31DQ05 | — | |
| — | — | SR305 | — | |
Step 6: A 0.01-μF capacitor is used for CBoost.
8.2.1.3 Application Curves
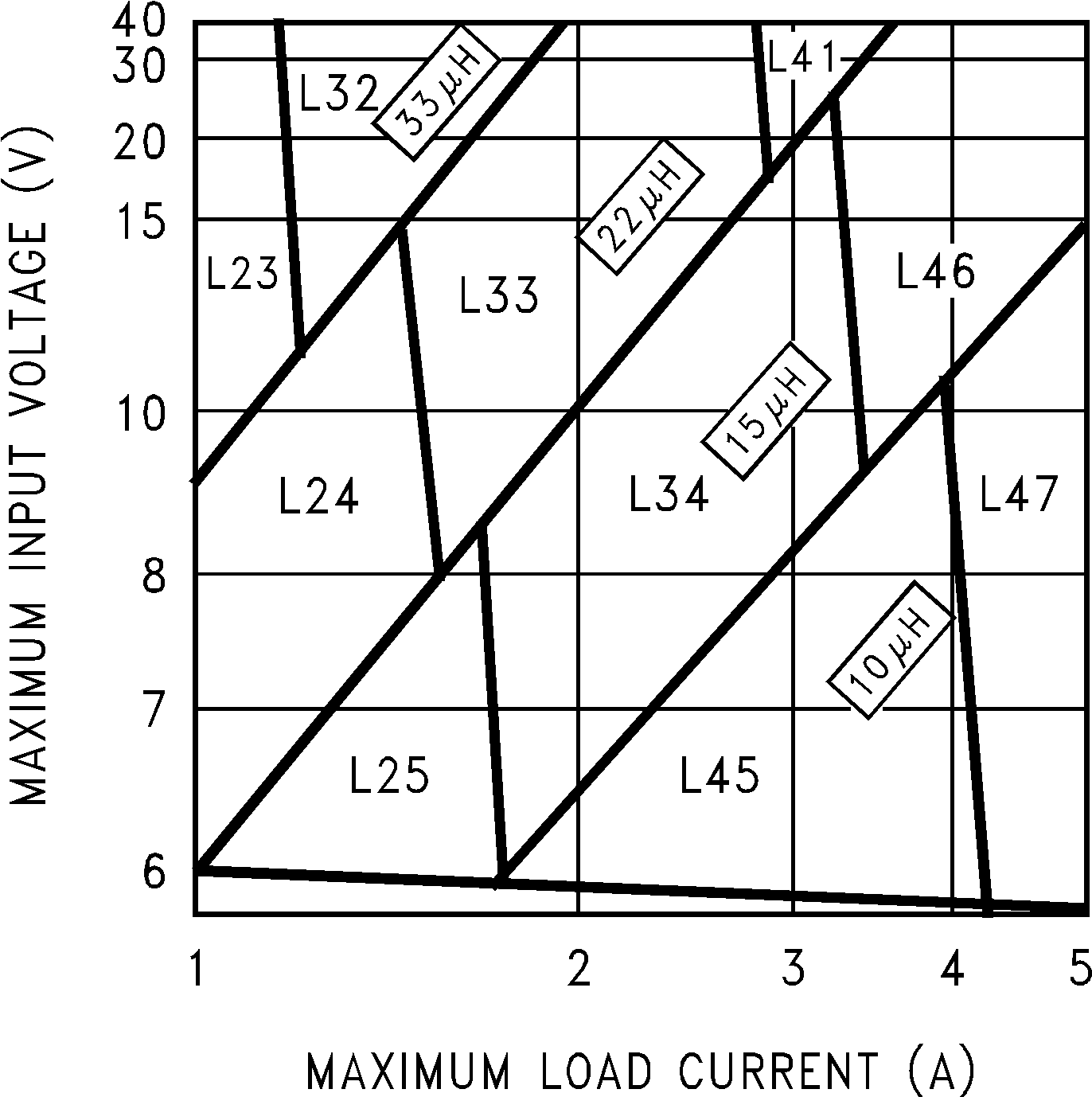 Figure 17. LM2677, 3.3 V
Figure 17. LM2677, 3.3 V
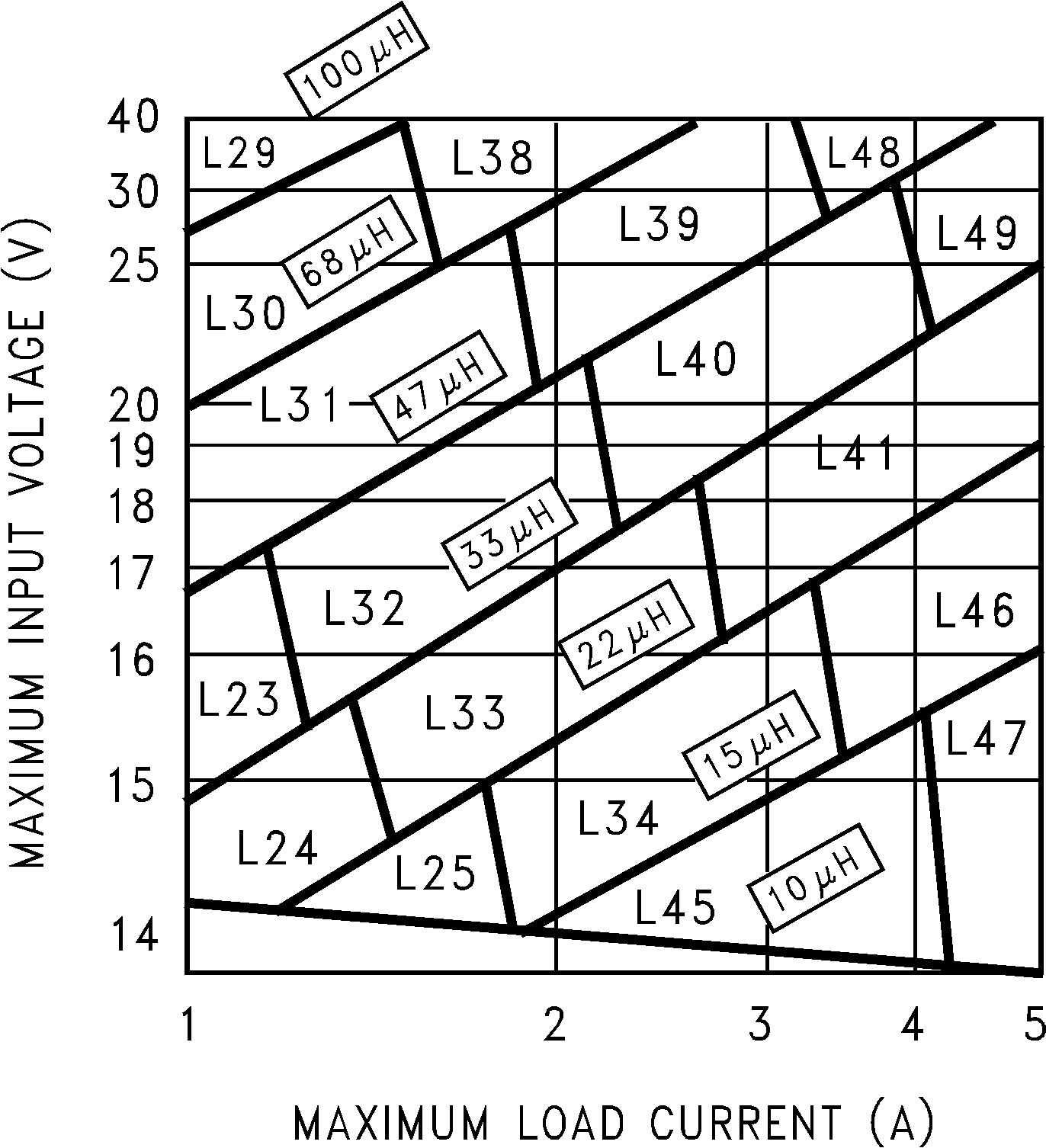 Figure 19. LM2677, 12 V
Figure 19. LM2677, 12 V
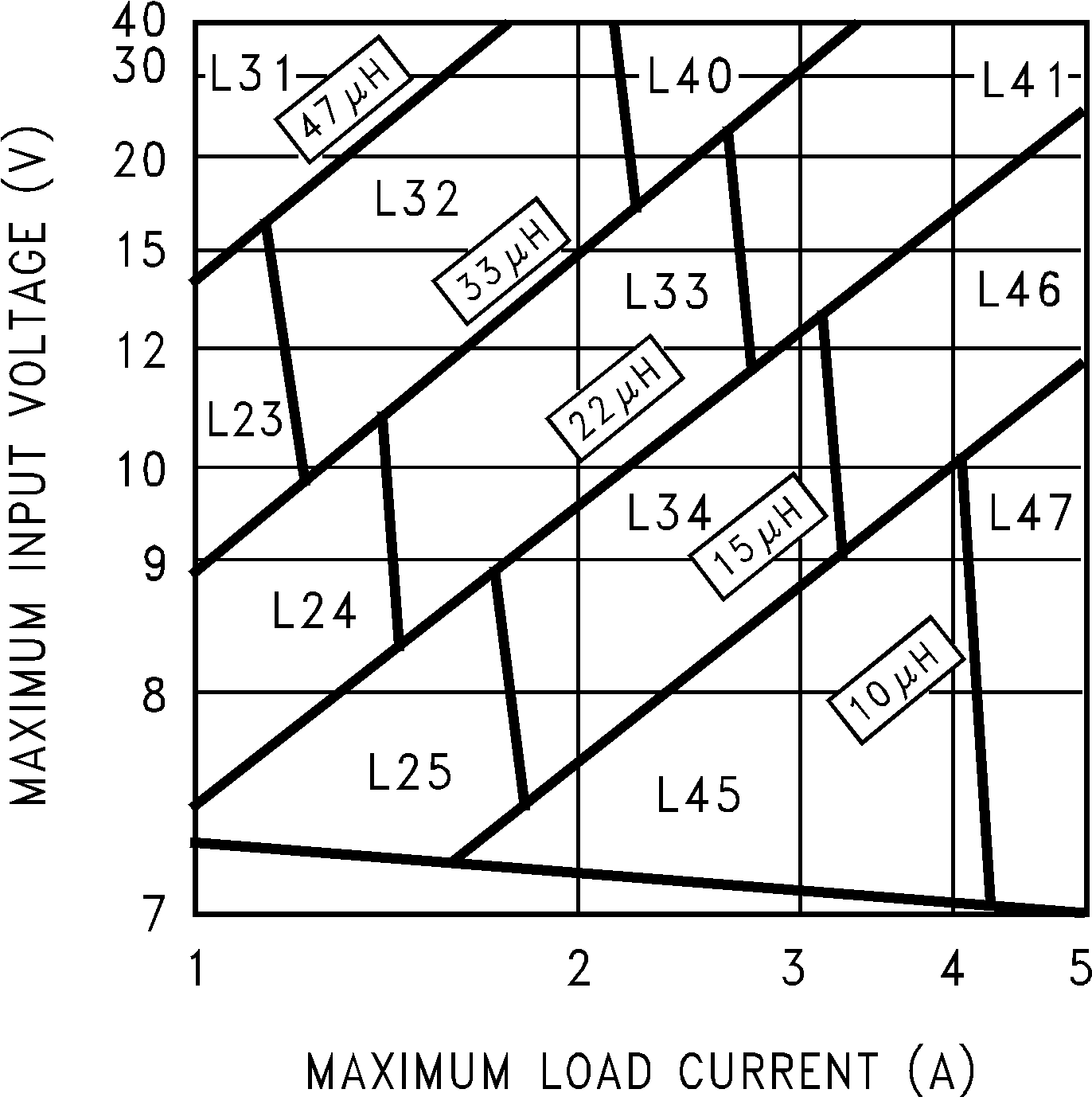 Figure 18. LM2677, 5 V
Figure 18. LM2677, 5 V
8.2.2 Adjustable Output Voltage Applications
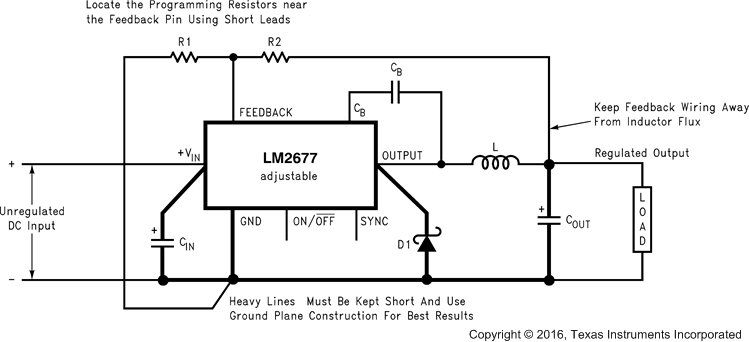 Figure 20. Basic Circuit For Adjustable Output Voltage Applications
Figure 20. Basic Circuit For Adjustable Output Voltage Applications
8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
Table 8 lists the design requirements for the adjustable output voltage application.
Table 8. Design Parameters
| PARAMETER | VALUE |
|---|---|
| Required output voltage, VOUT | 14.8 V |
| Maximum DC input voltage, VIN_MAX | 28 V |
| Maximum output load current, ILOAD_MAX | 2 A |
8.2.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
In this example it is desired to convert the voltage from a two-battery automotive power supply (voltage range of 20 V to 28 V, typical in large truck applications) to the 14.8 VDC alternator supply typically used to power electronic equipment from single battery 12-V vehicle systems. The load current required is 2 A maximum. It is also desired to implement the power supply with all surface mount components.
Step 1: Select an LM2677S-ADJ to set the output voltage to 14.9 V that chooses between two required resistors (R1 and R2 in Figure 20). For the adjustable device, the output voltage is set by Equation 1.
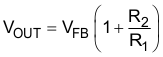
where
- VFB is the feedback voltage of typically 1.21 V
A recommended value to use for R1 is 1K. In this example then R2 is determined with Equation 2.
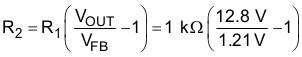
R2 = 11.2 kΩ
The closest standard 1% tolerance value to use is 11.3 kΩ. This sets the nominal output voltage to 14.88 V which is within 0.5% of the target value.
Step 2: To use the nomograph for the adjustable device, Figure 21, requires a calculation of the inductor Volt•microsecond constant (E × T expressed in V × μS) from Equation 3.
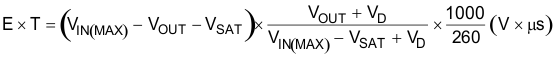
where
- VSAT is the voltage drop across the internal power switch which is Rds(ON) times Iload
In this example, this would be typically 0.15 Ω × 2 A or 0.3 V and VD is the voltage drop across the forward bisased Schottky diode, typically 0.5 V. The switching frequency of 260 kHz is the nominal value to use to estimate the ON-time of the switch during which energy is stored in the inductor. For this example E × T is found with Equation 4 and Equation 5.
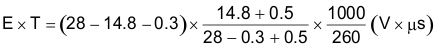
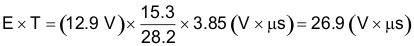
Using Figure 21, the intersection of 27 V × μS horizontally and the 2-A vertical line (Iload max) indicates that L38 , a 68-μH inductor, must be used. L38 in a surface mount component is available from Pulse Engineering with part number PE-54038S.
Step 3: Use Table 9 and Table 10 to determine an output capacitor. With a 14.8-V output the 12.5-V to 15-V row is used and with a 68-μH inductor there are three surface mount output capacitor solutions. Table 1 provides the actual capacitor characteristics based on the C Code number. Any of the following choices can be used:
- 1 × 33-μF, 20-V AVX TPS (code C6)
- 1 × 47-μF, 20-V Sprague 594 (code C8)
- 1 × 47-μF, 20-V Kemet T495 (code C8)
Table 9. Surface-Mount Output Capacitors
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V) | INDUCTANCE (µH) | AVX TPS SERIES | SPRAGUE 594D SERIES | KEMET T495 SERIES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | ||
| 1.21 to 2.50 | 33(3) | 7 | C1 | 6 | C2 | 7 | C3 |
| 47(3) | 5 | C1 | 4 | C2 | 5 | C3 | |
| 2.5 to 3.75 | 33(3) | 4 | C1 | 3 | C2 | 4 | C3 |
| 47(3) | 3 | C1 | 2 | C2 | 3 | C3 | |
| 3.75 to 5 | 22 | 4 | C1 | 3 | C2 | 4 | C3 |
| 33 | 3 | C1 | 2 | C2 | 3 | C3 | |
| 47 | 2 | C1 | 2 | C2 | 2 | C3 | |
| 5 to 6.25 | 22 | 3 | C2 | 1 | C3 | 3 | C4 |
| 33 | 2 | C2 | 2 | C3 | 2 | C4 | |
| 47 | 2 | C2 | 2 | C3 | 2 | C4 | |
| 68 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C4 | |
| 6.25 to 7.5 | 22 | 3 | C2 | 1 | C4 | 3 | C4 |
| 33 | 2 | C2 | 1 | C3 | 2 | C4 | |
| 47 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | |
| 68 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C4 | |
| 7.5 to 10 | 33 | 2 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C8 |
| 47 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C8 | |
| 68 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | |
| 100 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C8 | |
| 10 to 12.5 | 33 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C8 |
| 47 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C8 | |
| 68 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | |
| 100 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | |
| 12.5 to 15 | 33 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C8 |
| 47 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C8 | |
| 68 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C8 | |
| 100 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C8 | |
| 15 to 20 | 33 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C10 | 2 | C10 |
| 47 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C9 | 2 | C10 | |
| 68 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C9 | 2 | C10 | |
| 100 | 1 | C8 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C10 | |
| 20 to 30 | 33 | 2 | C9 | 2 | C11 | 2 | C11 |
| 47 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C12 | 1 | C11 | |
| 68 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C12 | 1 | C11 | |
| 100 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C12 | 1 | C11 | |
| 30 to 37 | 10 | — | — | 4 | C13 | 8 | C12 |
| 15 | — | — | 3 | C13 | 5 | C12 | |
| 22 | No values available |
2 | C13 | 4 | C12 | ||
| 33 | 1 | C13 | 3 | C12 | |||
| 47 | — | — | 1 | C13 | 2 | C12 | |
| 68 | — | — | 1 | C13 | 2 | C12 | |
Table 10. Through-Hole Output Capacitors
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V) | INDUCTANCE (µH) | SANYO OS-CON SA SERIES | SANYO MV-GX SERIES | NICHICON PL SERIES | PANASONIC HFQ SERIES | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | NO.(1) | C CODE(2) | ||
| 1.21 to 2.50 | 33(3) | 2 | C3 | 5 | C1 | 5 | C3 | 3 | C |
| 47(3) | 2 | C2 | 4 | C1 | 3 | C3 | 2 | C5 | |
| 2.5 to 3.75 | 33(3) | 1 | C3 | 3 | C1 | 3 | C1 | 2 | C5 |
| 47(3) | 1 | C2 | 2 | C1 | 2 | C3 | 1 | C5 | |
| 3.75 to 5 | 22 | 1 | C3 | 3 | C1 | 3 | C1 | 2 | C5 |
| 33 | 1 | C2 | 2 | C1 | 2 | C1 | 1 | C5 | |
| 47 | 1 | C2 | 2 | C1 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C5 | |
| 5 to 6.25 | 22 | 1 | C5 | 2 | C6 | 2 | C3 | 2 | C5 |
| 33 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C1 | 1 | C5 | |
| 47 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C5 | |
| 68 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C1 | 1 | C5 | |
| 6.25 to 7.5 | 22 | 1 | C5 | 1 | C6 | 2 | C1 | 1 | C5 |
| 33 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C3 | 1 | C5 | |
| 47 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C1 | 1 | C5 | |
| 68 | 1 | C4 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C1 | 1 | C5 | |
| 7.5 to 10 | 33 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C5 |
| 47 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C5 | |
| 68 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C2 | |
| 100 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C2 | |
| 10 to 12.5 | 33 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C6 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C5 |
| 47 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C14 | 1 | C5 | |
| 68 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C2 | |
| 100 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C2 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C2 | |
| 12.5 to 15 | 33 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 |
| 47 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 68 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 100 | 1 | C9 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 15 to 20 | 33 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 |
| 47 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 68 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 100 | 1 | C10 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C15 | 1 | C2 | |
| 20 to 30 | 33 | — | — | 1 | C7 | 1 | C16 | 1 | C2 |
| 47 | No values available |
1 | C7 | 1 | C16 | 1 | C2 | ||
| 68 | 1 | C7 | 1 | C16 | 1 | C2 | |||
| 100 | — | — | 1 | C7 | 1 | C16 | 1 | C2 | |
| 30 to 37 | 10 | — | — | 1 | C12 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C10 |
| 15 | — | — | 1 | C11 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C11 | |
| 22 | No values available |
1 | C11 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C10 | ||
| 33 | 1 | C11 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C10 | |||
| 47 | — | — | 1 | C11 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C10 | |
| 68 | — | — | 1 | C11 | 1 | C20 | 1 | C10 | |
NOTE
When using the adjustable device in low voltage applications (less than 3-V output), if the nomograph, Figure 21, selects an inductance of 22 μH or less, Table 9 does not provide an output capacitor solution. With these conditions the number of output capacitors required for stable operation becomes impractical. TI recommends using either a 33-μH or 47-μH inductor and the output capacitors from Table 9.
Step 4: An input capacitor for this example requires at least a 35-V WV rating with an rms current rating of 1 A (1/2 Iout max). From Table 1 it can be seen that C12, a 33-μF, 35-V capacitor from Sprague, has the required voltage/current rating of the surface mount components.
Step 5: From Table 7 a 3-A Schottky diode must be selected. For surface mount diodes with a margin of safety on the voltage rating one of five diodes can be used:
- SK34
- 30BQ040
- 30WQ04F
- MBRS340
- MBRD340
Step 6: A 0.01-μF capacitor is used for Cboost.
8.2.2.3 Application Curve
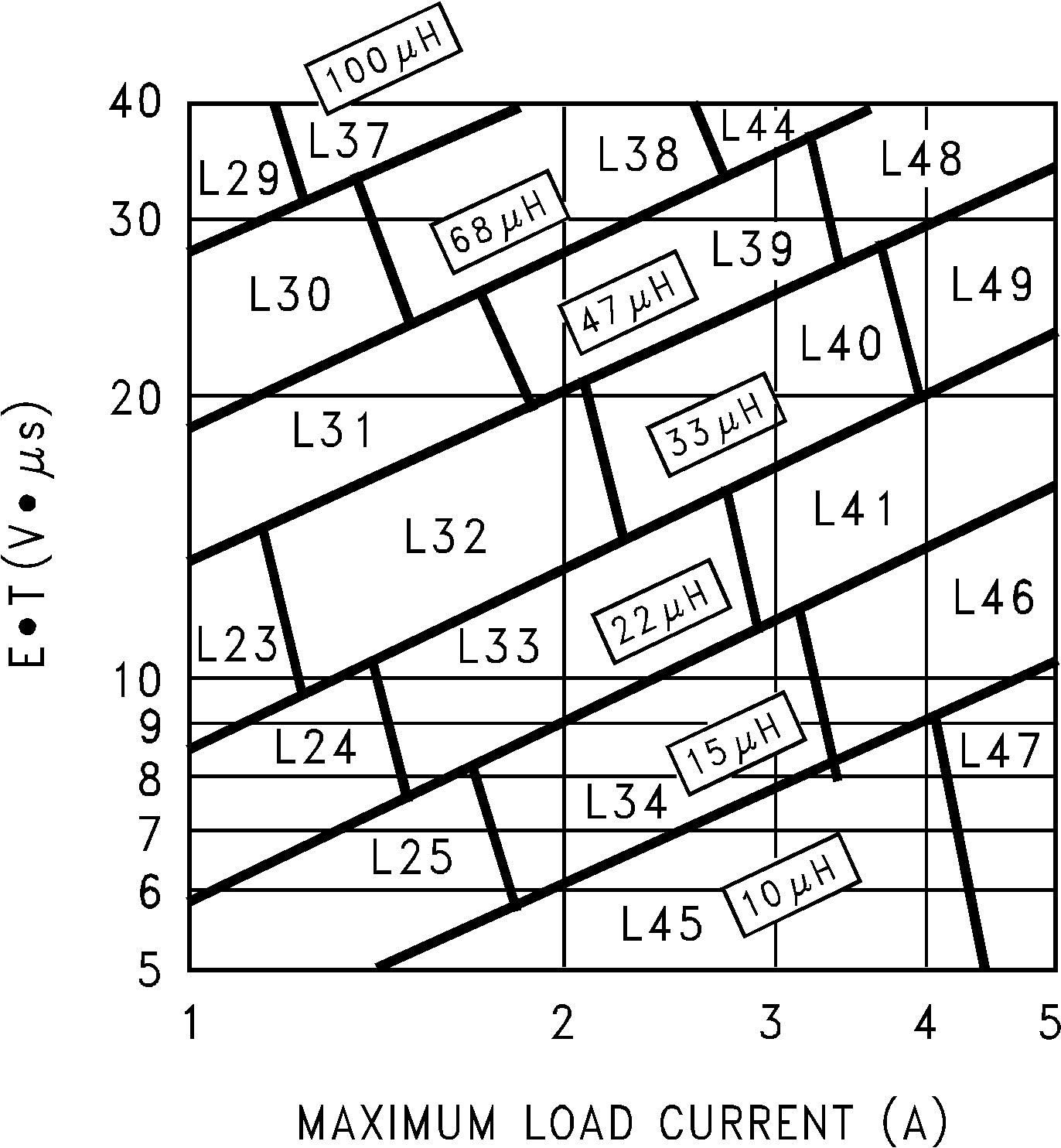 Figure 21. LM2677, Adjustable
Figure 21. LM2677, Adjustable