ZHCS547K January 2010 – February 2018 LM27402
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Wide Input Voltage Range
- 7.3.2 UVLO
- 7.3.3 Precision Enable
- 7.3.4 Soft-Start and Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.5 Output Voltage Setpoint and Accuracy
- 7.3.6 Voltage-Mode Control
- 7.3.7 Power Good
- 7.3.8 Inductor-DCR-Based Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.9 Current Sensing
- 7.3.10 Power MOSFET Gate Drivers
- 7.3.11 Pre-Bias Start-up
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Converter Design
- 8.1.2 Inductor Selection (L)
- 8.1.3 Output Capacitor Selection (COUT)
- 8.1.4 Input Capacitor Selection (CIN)
- 8.1.5 Using Precision Enable
- 8.1.6 Setting the Soft-Start Time
- 8.1.7 Tracking
- 8.1.8 Setting the Switching Frequency
- 8.1.9 Setting the Current Limit Threshold
- 8.1.10 Control Loop Compensation
- 8.1.11 MOSFET Gate Drivers
- 8.1.12 Power Loss and Efficiency Calculations
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
8.1.12.2 High-Side Power MOSFET
The next set of equations are used to calculate the losses associated with the high-side MOSFET.
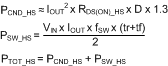
PCND_HS is the conduction loss of the high-side MOSFET during the D interval. this equation includes a self heating coefficient of 1.3 to approximate the effects of the RDS(on) temperature coefficient. RDS(ON)_HS is the drain to source resistance, IOUT is the output current and D is the duty ratio. PSW_HS is the switching power loss during the high-side MOSFET transition time. VIN is the input voltage, fSW is the switching frequency, and tr and tf are the rise and fall times of the switch-node voltage, respectively. PTOT_HS is the total power dissipation of the high-side MOSFET.
The gate charge of the high-side MOSFET greatly affects the turn-on transition time, and therefore efficiency. Furthermore, consider the ratio of switching loss to conduction loss associated with the high-side MOSFET. If the duty ratio is small and the input voltage is high, it is beneficial to tradeoff QG for higher RDS(on) to avoid high switching losses relative to conduction losses. If the duty ratio is large and the input voltage is low, then a lower RDS(on) MOSFET in tandem with a higher QG may result in less power dissipation.