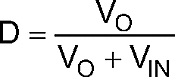SNVSB96 July 2019 LM3424-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Current Regulators
- 7.3.2 Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.3 Average LED Current
- 7.3.4 Thermal Foldback and Analog Dimming
- 7.3.5 Current Sense and Current Limit
- 7.3.6 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.7 Control Loop Compensation
- 7.3.8 Start-Up Regulator and Soft-Start
- 7.3.9 Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 7.3.10 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.11 PWM Dimming
- 7.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Basic Topology Schematics
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Operating Point
- 8.2.1.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Average LED Current
- 8.2.1.2.4 Thermal Foldback
- 8.2.1.2.5 Inductor Ripple Current
- 8.2.1.2.6 LED Ripple Current
- 8.2.1.2.7 Peak Current Limit
- 8.2.1.2.8 Slope Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.9 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.10 Input Capacitance
- 8.2.1.2.11 NFET
- 8.2.1.2.12 Diode
- 8.2.1.2.13 Output OVLO
- 8.2.1.2.14 Input UVLO
- 8.2.1.2.15 Soft-Start
- 8.2.1.2.16 PWM Dimming Method
- 8.2.1.2.17 Analog Dimming Method
- 8.2.2
Buck-Boost Application
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Operating Point
- 8.2.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.3 Average LED Current
- 8.2.2.2.4 Thermal Foldback
- 8.2.2.2.5 Inductor Ripple Current
- 8.2.2.2.6 Output Capacitance
- 8.2.2.2.7 Peak Current Limit
- 8.2.2.2.8 Slope Compensation
- 8.2.2.2.9 Loop Compensation
- 8.2.2.2.10 Input Capacitance
- 8.2.2.2.11 NFET
- 8.2.2.2.12 Diode
- 8.2.2.2.13 Input UVLO
- 8.2.2.2.14 Output OVLO
- 8.2.2.2.15 Soft-Start
- 8.2.2.3 Application Curve
- 8.2.3 Boost Application
- 8.2.4 Buck-Boost Application
- 8.2.5 Boost Application
- 8.2.6 Buck-Boost Application
- 8.2.7 Buck Application
- 8.2.8 Buck-Boost Application
- 8.2.9 SEPIC Application
- 8.2.1
Basic Topology Schematics
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.1 Current Regulators
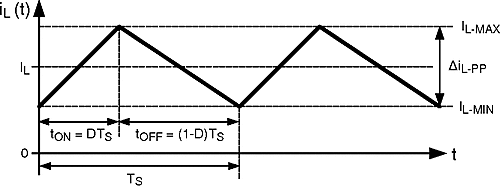 Figure 17. Ideal CCM Regulator Inductor Current iL(t)
Figure 17. Ideal CCM Regulator Inductor Current iL(t) Current regulators can be designed to accomplish three basic functions: buck, boost, and buck-boost. All three topologies in their most basic form contain a main switching MOSFET, a recirculating diode, an inductor and capacitors. The LM3424-Q1 is designed to drive a ground referenced NFET which is perfect for a standard boost regulator. Buck and buck-boost regulators, on the other hand, usually have a high-side switch. When driving an LED load, a ground referenced load is often not necessary, therefore a ground referenced switch can be used to drive a floating load instead. The LM3424-Q1 can then be used to drive all three basic topologies as shown in the Basic Topology Schematics section. Other topologies such as the SEPIC and flyback converter (both derivatives of the buck-boost) can be implemented as well.
Looking at the buck-boost design, the basic operation of a current regulator can be analyzed. During the time that the NFET (Q1) is turned on (tON), the input voltage source stores energy in the inductor (L1) while the output capacitor (CO) provides energy to the LED load. When Q1 is turned off (tOFF), the re-circulating diode (D1) becomes forward biased and L1 provides energy to both CO and the LED load. Figure 17 shows the inductor current (iL(t)) waveform for a regulator operating in CCM.
The average output LED current (ILED) is proportional to the average inductor current (IL) , therefore if IL is tightly controlled, ILED will be well regulated. As the system changes input voltage or output voltage, the ideal duty cycle (D) is varied to regulate IL and ultimately ILED. For any current regulator, D is a function of the conversion ratio:
Buck
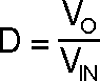
Boost
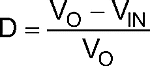
Buck-Boost