SNVS372G August 2005 – October 2016 LM4132 , LM4132-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-1.8 (VOUT = 1.8 V)
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-2 (VOUT = 2.048 V)
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-2.5 (VOUT = 2.5 V)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-3 (VOUT = 3 V)
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-3.3 (VOUT = 3.3 V)
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-3.3-Q1(VOUT = 3.3 V)
- 6.11 Electrical Characteristics LM4132-4.1 (VOUT = 4.096 V)
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
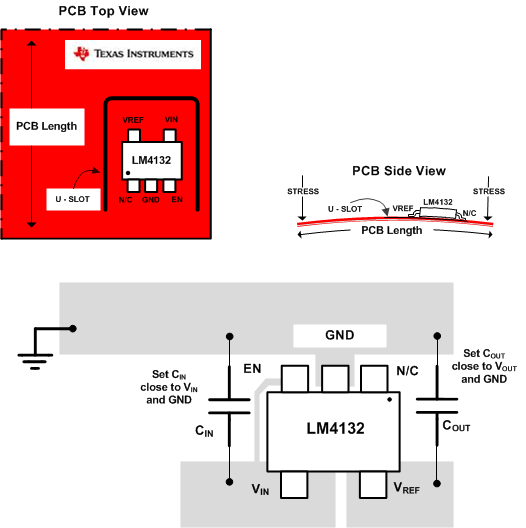
The mechanical stress due to PCB mounting can cause the output voltage to shift from its initial value. The center of a PCB generally has the highest mechanical and thermal expansion stress. Mounting the device near the edges or the corners of the board where mechanical stress is at its minimum. References in SOT-23 packages are generally less prone to assembly stress than devices in small outline (SOIC) packages.
A mechanical isolation of the device by creating an island by cutting a U shape slot (U - SLOT) on the PCB while mounting the device helps in reducing the impact of the PCB stresses on the output voltage of the reference. This approach would also provide some thermal isolation from the rest of the circuit.
Figure 54 shows a recommended printed board layout for LM4132 along with an in-set diagram, which exhibits a slot cut on three sides of the reference device.
Bypass capacitors must be mounted close to the device. Mounting bypass capacitors close to the device reduces the parasitic trace components, thereby improving performance.