ZHCSNW4 October 2022 LM5012-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Control Architecture
- 8.3.2 Internal VCC Regulator and Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.3.3 Regulation Comparator
- 8.3.4 Internal Soft Start
- 8.3.5 On-Time Generator
- 8.3.6 Current Limit
- 8.3.7 N-Channel Buck Switch and Driver
- 8.3.8 Schottky Diode Selection
- 8.3.9 Enable/Undervoltage Lockout (EN/UVLO)
- 8.3.10 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 8.3.11 Thermal Protection
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.3 Buck Inductor (LO)
Use Equation 10 and Equation 11 to calculate the inductor ripple current (assuming CCM operation) and peak inductor current, respectively.
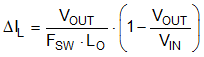
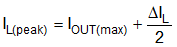
For most applications, choose an inductance such that the inductor ripple current, ΔIL, is between 30% and 50% of the rated load current at nominal input voltage. Use Equation 12 to calculate the inductance.
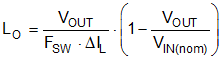
For applications in which the device must support input transients exceeding 72 V, TI advises to select the inductor to be at least 22 μH. This action ensures that excessive current rise does not occur in the power stage due to the large inductor current slew that can occur during an output short-circuit condition.
Choosing a 33-μH inductor in this design results in 909-mA peak-to-peak ripple current at a nominal input voltage of 48 V, equivalent to 36% of the 2.5-A rated load current. For designs that must operate up to the maximum input voltage at the full-rated load current of 2.5 A, the inductance must increase to ensure current limit (IPEAK current limit) is not hit.
Check the inductor data sheet to make sure the saturation current of the inductor is well above the current limit setting of the LM5012-Q1. TI recommends that the saturation current be greater than 4.5 A. Ferrite-core inductors have relatively lower core losses and are preferred at high switching frequencies, but exhibit a hard saturation characteristic — the inductance collapses abruptly when the saturation current is exceeded. This results in an abrupt increase in inductor ripple current, higher output voltage ripple, and reduced efficiency, in turn compromising reliability. Note that inductor saturation current levels generally decrease as the core temperature increases.