ZHCSKM9F May 2011 – December 2019 LM5050-1 , LM5050-1-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Typical Application With Input and Output Transient Protection
- 8.2.2 Using a Separate VS Supply for Low Vin Operation
- 8.2.3 ORing of Two Power Sources
- 8.2.4 Reverse Input Voltage Protection With IQ Reduction
- 8.2.5 Basic Application With Input Transient Protection
- 8.2.6 48-V Application With Reverse Input Voltage (VIN = –48 V) Protection
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.1.2 Short Circuit Failure of an Input Supply
An abrupt 0-Ω short circuit across the input supply will cause the highest possible reverse current to flow while the internal LM5050-1 control circuitry discharges the gate of the MOSFET. During this time, the reverse current is limited only by the RDS(ON) of the MOSFET, along with parasitic wiring resistances and inductances. Worst case instantaneous reverse current would be limited to:
The internal Reverse Comparator will react, and will start the process of discharging the Gate, when the reverse current reaches:
When the MOSFET is finally switched off, the energy stored in the parasitic wiring inductances will be transferred to the rest of the circuit. As a result, the LM5050-1 IN pin will see a negative voltage spike while the OUT pin will see a positive voltage spike. The IN pin can be protected by diode clamping the pin to GND in the negative direction. The OUT pin can be protected with a TVS protection diode, a local bypass capacitor, or both. In low voltage applications, the MOSFET drainto- source breakdown voltage rating may be adequate to protect the OUT pin (that is, VIN + V(BR)DSS(MAX) < 75 V ), but most MOSFET data sheets do not ensure the maximum breakdown rating, so this method should be used with caution.
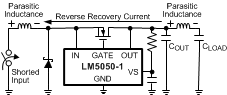 Figure 23. Reverse Recovery Current Generates Inductive Spikes at VIN and VOUT pins.
Figure 23. Reverse Recovery Current Generates Inductive Spikes at VIN and VOUT pins.