SNVS628H October 2009 – December 2019 LM5060
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Example Number 1: LM5060EVAL Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 VDS Fault Detection and Selecting Sense Pin Resistor RS
- 8.2.1.2.2 Turn-On Time
- 8.2.1.2.3 Fault Detection Delay Time
- 8.2.1.2.4 MOSFET Selection
- 8.2.1.2.5 Input and Output Capacitors
- 8.2.1.2.6 UVLO, OVP
- 8.2.1.2.7 POWER GOOD Indicator
- 8.2.1.2.8 Input Bypass Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Large Load Capacitance
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Example Number 2: Reverse Polarity Protection With Diodes
- 8.2.3 Example Number 3: Reverse Polarity Protection With Resistor
- 8.2.1
Example Number 1: LM5060EVAL Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.3 Fault Detection Delay Time
To allow the gate of the MOSFET adequate time to change, and to allow the MOSFET to conduct currents beyond the protection threshold for a brief period of time, a fault delay timer function is provided. This feature is important when drive loads which require a surge of current in excess of the normal ON current upon start up, or at any point in time, such as lamps and motors. A single low leakage capacitor (CTIMER) connected from the TIMER (pin 7), to ground sets the delay time interval for both the VGS status detection at start-up and for the subsequent VDS Over-Current fault detection.
When the LM5060 is enabled under normal operating conditions the timer capacitor will begin charging at a 6 μA (typical) rate while simultaneously charging the gate of the external MOSFET at a 24 μA (typical) rate. The gate-to-source voltage (VGS) of the external MOSFET is expected to reach the 5-V (typical) threshold before the timer capacitor has charged to the VTMRH threshold (2 V typical) in order to avoid being shutdown.
While VGS is less than the typical 5-V threshold (VGATE-TH), the VDS start-up fault delay time is calculated from:
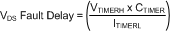
where
- ITMRL is typically 6 μA and VTMRH is typically 2 V
If the CTIMER value is 68 nF (0.068μF) the VGS start-up fault delay time would typically be:
When the LM5060 has successfully completed the start-up sequence by reaching a VGS of 5 V within the fault delay time set by the timer capacitor (CTIMER), the capacitor is quickly discharged to 300 mV (typical) and the charge current is increased to 11 μA (typical) while the gate of the external MOSFET is continued to be charge at a 24 μA (typical) rate. The external MOSFET may not be fully enhanced at this point in time and some additional time may be needed to allow the gate-to-source voltage (VGS) to charge to a higher value. The drain-to-source voltage (VDS) of the external MOSFET must fall below the VDSTH threshold set by RS and ISENSE before the timer capacitor has charged to the VTMRH threshold (2 V typical) to avoid a fault.
When VGS is greater than the typical 5-V threshold (VGATE-TH), the VDS transition fault delay time is calculated from:
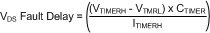
where
- ITMRH is typically 11 μA
- VTMRH is typically 2 V
- VTMRL is typically 300 mV
If the CTIMER value is 68 nF(0.068 μF) the VDS transition fault delay time would typically be:
Should a subsequent load current surge trip the VDS Fault Comparator, the timer capacitor discharge transistor turns OFF and the 11 μA (typical) current source begins linearly charging the timer capacitor. If the surge current, with the detected excessive VDS voltage, lasts long enough for the timer capacitor to charge to the timing comparator threshold (VTMRH) of typically 2 V, the LM5060 will immediately discharge the MOSFET gate and latch the MOSFET off. The VDS fault delay time during an Over-Current event is calculated from:
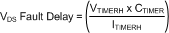
where
- ITMRH is typically 11 μA
- VTMRH is typically 2 V
If the CTIMER value is 68 nF(0.068 μF) the VDS Over-Current fault delay time would typically be:
Since a single capacitor is used to set the delay time for multiple fault conditions, it is likely that some compromise will need to be made between a desired delay time and a practical delay time.