ZHCSLQ5D October 2007 – August 2020 LM5067
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.7.2 Option B:
If all four thresholds must be accurately defined, the configuration in Figure 9-7 can be used.
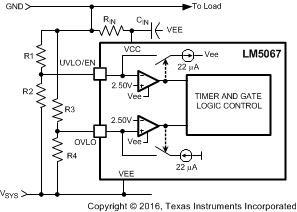 Figure 9-7 Programming the Four Thresholds
Figure 9-7 Programming the Four ThresholdsThe four resistor values are calculated as follows:
- Determine the upper UVLO threshold (VUVH) to enable Q1, and the lower UVLO threshold (VUVL) to disable Q1.
Equation 14.
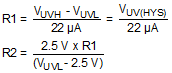
- Determine the upper OVLO threshold (VOVH) to disable Q1, and the lower OVLO threshold (VOVL) to enable Q1.
Equation 15.
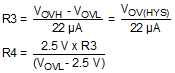
As an example, assume the application requires the following thresholds: VUVH = –22 V, VUVL = –17 V, VOVH = –60 V, and VOVL = –58 V. Therefore VUV(HYS) = 5 V, and VOV(HYS) = 2 V. The resistor values are:
R1 = 227 kΩ, R2 = 39.1 kΩ
R3 = 90.9 kΩ, R4 = 3.95 kΩ
Where the R1-R4 resistor values are known, the threshold voltages and hysteresis are calculated from the following:
Equation 16. 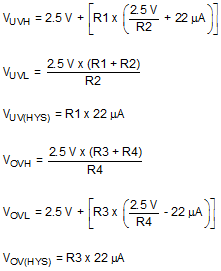
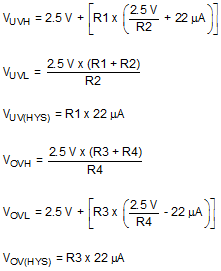
Note:
Ensure the voltages at the UVLO and OVLO pins do not exceed the Absolute Maximum ratings for those pins when the system voltage is at maximum.