ZHCSLQ5D October 2007 – August 2020 LM5067
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.6.2 Fault Timeout Period
- During turn-on of the output voltage, or upon detection of a fault condition where the current limit and/or power limit circuits regulate the current through Q1, CT is charged by the fault timer current source (85 µA). The Fault Timeout Period is the time required for the TIMER pin voltage to reach 4.0V above VEE, at which time Q1 is switched off. The required capacitor value for the desired Fault Timeout Period tFAULT is calculated from:
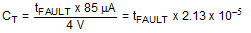
For example, if the desired Fault Timeout Period is 16 ms, CT calculates to 0.34 µF. After a fault timeout, if the LM5067-1 is in use, CT must be allowed to discharge to < 0.3 V by the 2.5 µA current sink, after which a power up sequence can be initiated by external circuitry. See Fault Timer and Restart and Latched Fault Restart Control. If the LM5067-2 is in use, after the Fault Timeout Period expires a restart sequence begins as described below (Restart Timing).
Since the LM5067 normally operates in power limit and/or current limit during a power up sequence, the Fault Timeout Period MUST be longer than the time required for the output voltage to reach its final value. See Turn-On Time.