ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.4 Set Fault Timer
The fault timer runs when the hot swap is in power limit or current limit, which is the case during start-up. Thus the timer has to be sized large enough to prevent a time-out during start-up. If the part starts directly into current limit (ILIM × VDS < PLIM) the maximum start time can be computed with Equation 11.
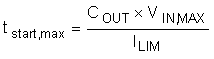
For most designs (including this example), ILIM × VDS > PLIM, so the hot swap starts in power limit and transition into current limit. In that case, the estimated start time can be computed with Equation 12.
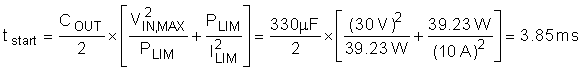
Note that the above start-time assumes constant, typical current limit and power limit values. The actual startup time is slightly longer, as the power limit is a function of Vds and decreases as the output voltage increases. To ensure that the timer never times out during start-up, TI recommends setting the minimum fault time (tflt) to be greater than the start time (tstart) by adding an additional margin of 50% of the fault time. This accounts for the variation in power limit, timer current, and timer capacitance. Thus CTIMER can be computed with Equation 13.
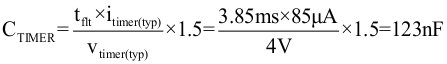
The next largest available CTIMER is chosen as 150 nf. Once the CTIMER is chosen the actual programmed fault time can be computed with Equation 14.
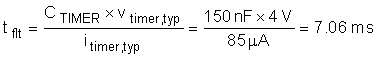
This is the typical time that the LM5069 shuts off the CSD19536KTT MOSFET.