ZHCSHU0C March 2018 – October 2021 LM51501-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Enable (EN Pin)
- 8.3.2 High Voltage VCC Regulator (PVCC, AVCC Pin)
- 8.3.3 Power-On Voltage Selection (VSET Pin)
- 8.3.4 Switching Frequency (RT Pin)
- 8.3.5 Clock Synchronization (SYNC Pin in SS Configuration)
- 8.3.6 Current Sense, Slope Compensation, and PWM (CS Pin)
- 8.3.7 Current Limit (CS Pin)
- 8.3.8 Feedback and Error Amplifier (COMP Pin)
- 8.3.9 Automatic Wake-Up and Standby
- 8.3.10 Boost Status Indicator (STATUS Pin)
- 8.3.11 Maximum Duty Cycle Limit and Minimum Input Supply Voltage
- 8.3.12 MOSFET Driver (LO Pin)
- 8.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.2.2 RSET Resistor
- 9.2.2.3 RT Resistor
- 9.2.2.4 Inductor Selection (LM)
- 9.2.2.5 Current Sense (RS)
- 9.2.2.6 Slope Compensation Ramp (RSL)
- 9.2.2.7 Output Capacitor (COUT)
- 9.2.2.8 Loop Compensation Component Selection and Maximum ESR
- 9.2.2.9 PVCC Capacitor, AVCC Capacitor, and AVCC Resistor
- 9.2.2.10 VOUT Filter (CVOUT, RVOUT)
- 9.2.2.11 Input Capacitor
- 9.2.2.12 MOSFET Selection
- 9.2.2.13 Diode Selection
- 9.2.2.14 Efficiency Estimation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 System Examples
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.5 Clock Synchronization (SYNC Pin in SS Configuration)
In SS configuration, the switching frequency of the LM51501-Q1 can be synchronized to an external clock by directly applying a pulse signal to the SYNC pin. The internal clock of the LM51501-Q1 is synchronized at the rising edge of the external clock. The device ignores the rising edge input during forced off-time.
The external synchronization pulse must be greater than the 2.4 V in the high logic state and must be less than 0.4 V in the low logic state. The duty cycle of the external synchronization pulse is not limited, but the minimum pulse width should be greater than 100 ns. Because the maximum duty cycle limit and the peak current limit threshold are affected by synchronizing the switching frequency to an external synchronization pulse, take extra care when using the clock synchronization function. See Section 8.3.11 and Section 8.3.7 for more detailed information.
If the minimum input supply voltage of the boost converter is greater than ¼ of the VOUT regulation target (VVOUT-REG), the frequency of the external synchronization pulse (FSYNC) should be within +15% and –15% of the typical free-running switching frequency (FSW(TYPICAL)) as shown in Equation 2:
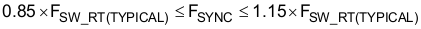
In this range, a maximum 1:4 (VSUPPLY:VLOAD) step-up ratio is allowed.
A higher step-up ratio can be achieved by supplying a lower frequency synchronization pulse. 1:5 step-up ratio can be achieved by selecting FSYNC within –25% and –15% of the FSW_RT(TYPICAL).

In this range, a maximum 1:5 (VSUPPLY:VLOAD) step-up ratio is allowed.