SNIS153D July 2009 – October 2015 LM75B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage Pin (+VS) | −0.3 | 6.5 | V | |
| Voltage at A0, A1and A2 Pins | −0.3 | (+VS + 0.3) and must be ≤ 6.5 | V | |
| Voltage at O.S., SCL and SDA Pins | −0.3 | 6.5 | V | |
| Input Current at any Pin(2) | 5 | mA | ||
| Package Input Current(2) | 20 | mA | ||
| O.S. Output Sink Current | 10 | mA | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. DC and AC electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device beyond its rated operating conditions.
(2) When the input voltage (VI) at any pin exceeds the power supplies (VI < GND or VI > +VS) the current at that pin should be limited to 5 mA. The 20-mA maximum package input current rating limits the number of pins that can safely exceed the power supplies with an input current of 5 mA to four.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LM75B | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(1) | Human-body model (HBM) | ±2500 | V |
| Machine model | ±250 | |||
| LM75C | ||||
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(1) | Human-body model (HBM) | ±1500 | V |
| Machine Model | ±100 | |||
(1) Human body model, 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor. Machine model, 200 pF discharged directly into each pin. The Charged Device Model (CDM) is a specified circuit characterizing an ESD event that occurs when a device acquires charge through some triboelectric (frictional) or electrostatic induction processes and then abruptly touches a grounded object or surface.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Temperature Range | TMIN | TMAX | |
| –55 | 125 | °C | |
| Supply Voltage Range (+VS) LM75B, LM75C | 3 | 5.5 | V |
(1) Soldering process must comply with Texas Instruments Incorporated Reflow Temperature Profile specifications. Refer to
(2) Reflow temperature profiles are different for lead-free and non-lead-free packages.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LM75B | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DGK (VSSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 115.2 | 158.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 62.2 | 52.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 56.4 | 78.8 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 10.2 | 5.3 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 55.8 | 77.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | N/A | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Temperature-to-Digital Converter Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, these specifications apply for: +VS = 5 Vdc for LM75BIM-5, LM75BIMM-5, LM75CIM-5, and LM75CIMM-5; and +VS = 3.3 Vdc for LM75BIM-3, LM75BIMM-3, LM75CIM-3, and LM75CIMM-3(1). TA = TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.(2)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(4) | TYP(3) | MAX(4) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | TA = −25°C to 100°C | –2 | 2 | °C | |||
| TA = −55°C to 125°C | –3 | 3 | |||||
| Resolution | 9 | Bits | |||||
| Temperature Conversion Time | See(5) | 100 | ms | ||||
| See(5), –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 300 | ||||||
| Quiescent Current | LM75B | I2C Inactive | 0.25 | mA | |||
| I2C Inactive, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 0.5 | ||||||
| Shutdown Mode, +VS = 3 V | 4 | μA | |||||
| Shutdown Mode, +VS = 5 V | 6 | ||||||
| LM75C | I2C Inactive | 0.25 | mA | ||||
| I2C Inactive, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 1 | ||||||
| Shutdown Mode, +VS = 3 V | 4 | μA | |||||
| Shutdown Mode, +VS = 5 V | 6 | ||||||
| O.S. Output Saturation Voltage | IOUT = 4.0 mA, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 0.8 | V | ||||
| O.S. Delay | See (6), –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 1 | 6 | Conversions | |||
| TOS Default Temperature | See (7) | 80 | °C | ||||
| THYST Default Temperature | 75 | ||||||
(1) All part numbers of the LM75 will operate properly over the +VS supply voltage range of 3 V to 5.5 V. The devices are tested and specified for rated accuracy at their nominal supply voltage. Accuracy will typically degrade 1°C/V of variation in +VS as it varies from the nominal value.
(2) For best accuracy, minimize output loading. Higher sink currents can affect sensor accuracy with internal heating. This can cause an error of 0.64°C at full rated sink current and saturation voltage based on junction-to-ambient thermal resistance.
(3) Typicals are at TA = 25°C and represent most likely parametric norm.
(4) Limits are specified to AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
(5) The conversion-time specification is provided to indicate how often the temperature data is updated. The LM75 can be accessed at any time and reading the Temperature Register will yield result from the last temperature conversion. When the LM75 is accessed, the conversion that is in process will be interrupted and it will be restarted after the end of the communication. Accessing the LM75 continuously without waiting at least one conversion time between communications will prevent the device from updating the Temperature Register with a new temperature conversion result. Consequently, the LM75 should not be accessed continuously with a wait time of less than 300 ms.
(6) O.S. Delay is user programmable up to 6 “over limit” conversions before O.S. is set to minimize false tripping in noisy environments.
(7) Default values set at power up.
6.6 Digital DC Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, these specifications apply for +VS = 5 Vdc for LM75BIM-5, LM75BIMM-5, LM75CIM-5, and LM75CIMM-5; and +VS = 3.3 Vdc for LM75BIM-3, LM75BIMM-3, LM75CIM-3, and LM75CIMM-3(1). TA = TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(3) | TYP(2) | MAX(3) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN(1) | Logical “1” Input Voltage | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | +VS × 0.7 | +VS + 0.3 | V | ||
| VIN(0) | Logical “0” Input Voltage | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | −0.3 | +VS × 0.3 | V | ||
| IIN(1) | Logical “1” Input Current | VIN = +VS | 0.005 | μA | |||
| VIN = +VS, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 1 | ||||||
| IIN(0) | Logical “0” Input Current | VIN = 0 V | −0.005 | μA | |||
| VIN = 0 V, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | −1 | ||||||
| CIN | All Digital Inputs | 5 | pF | ||||
| IOH | High Level Output Current | LM75B | VOH = 5 V, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 10 | μA | ||
| LM75C | VOH = 5 V, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 100 | μA | ||||
| VOL | Low Level Output Voltage | IOL = 3 mA, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 0.4 | V | |||
| tOF | Output Fall Time | CL = 400 pF IO = 3 mA, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 250 | ns | |||
(1) All part numbers of the LM75 will operate properly over the +VS supply voltage range of 3 V to 5.5 V. The devices are tested and specified for rated accuracy at their nominal supply voltage. Accuracy will typically degrade 1°C/V of variation in +VS as it varies from the nominal value.
(2) Typicals are at TA = 25°C and represent most likely parametric norm.
(3) Limits are specified to AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
6.7 I2C Digital Switching Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted, these specifications apply for VS = 5 Vdc for LM75BIM-5, LM75BIMM-5, LM75CIM-5, and LM75CIMM-5; and +VS = 3.3 Vdc for LM75BIM-3, LM75BIMM-3, LM75CIM-3, and LM75CIMM-3, CL (load capacitance) on output lines = 80 pF unless otherwise specified. TA = TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(2)(3) | TYP(1) | MAX(2)(3) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 | SCL (Clock) Period, See Figure 1 | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 2.5 | µs | |||
| t2 | Data in Set-Up Time to SCL High, See Figure 1 | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 100 | ns | |||
| t3 | Data Out Stable after SCL Low, See Figure 1 | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 0 | ns | |||
| t4 | SDA Low Set-Up Time to SCL Low (Start Condition), See Figure 1 | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 100 | ns | |||
| t5 | SDA High Hold Time after SCL High (Stop Condition), See Figure 1 | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 100 | ns | |||
| tTIMEOUT | SDA Time Low for Reset of Serial Interface(4) | LM75B | –55°C ≤ TA ≤ 125°C | 75 | 325 | ms | |
| LM75C | Not Applicable | ||||||
(1) Typicals are at TA = 25°C and represent most likely parametric norm.
(2) Limits are specified to AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level).
(3) Timing specifications are tested at the bus input logic levels (Vin(0)=0.3xVA for a falling edge and Vin(1)=0.7xVA for a rising edge) when the SCL and SDA edge rates are similar.
(4) Holding the SDA line low for a time greater than tTIMEOUT will cause the LM75B to reset SDA to the IDLE state of the serial bus communication (SDA set High).
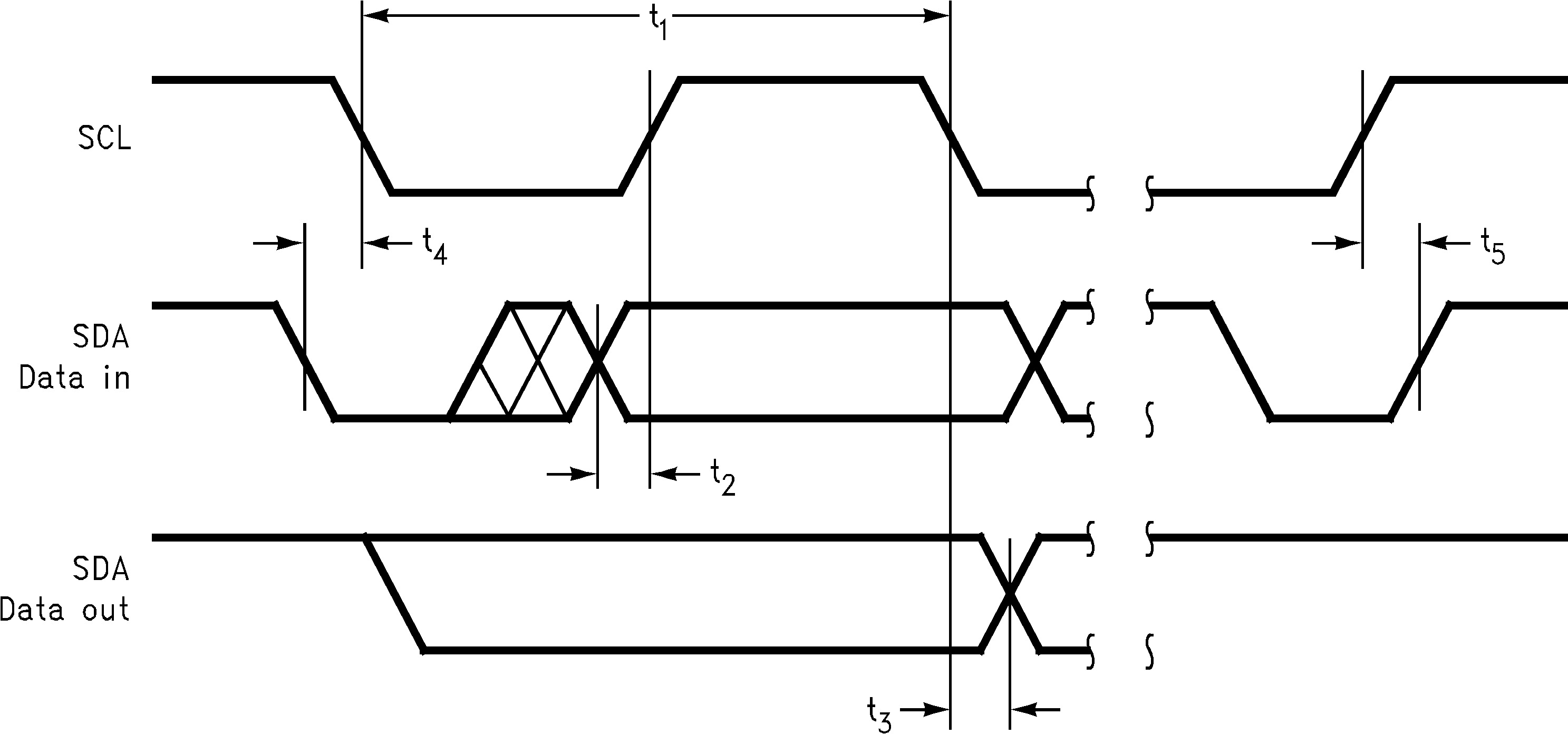 Figure 1. Timing Diagram
Figure 1. Timing Diagram
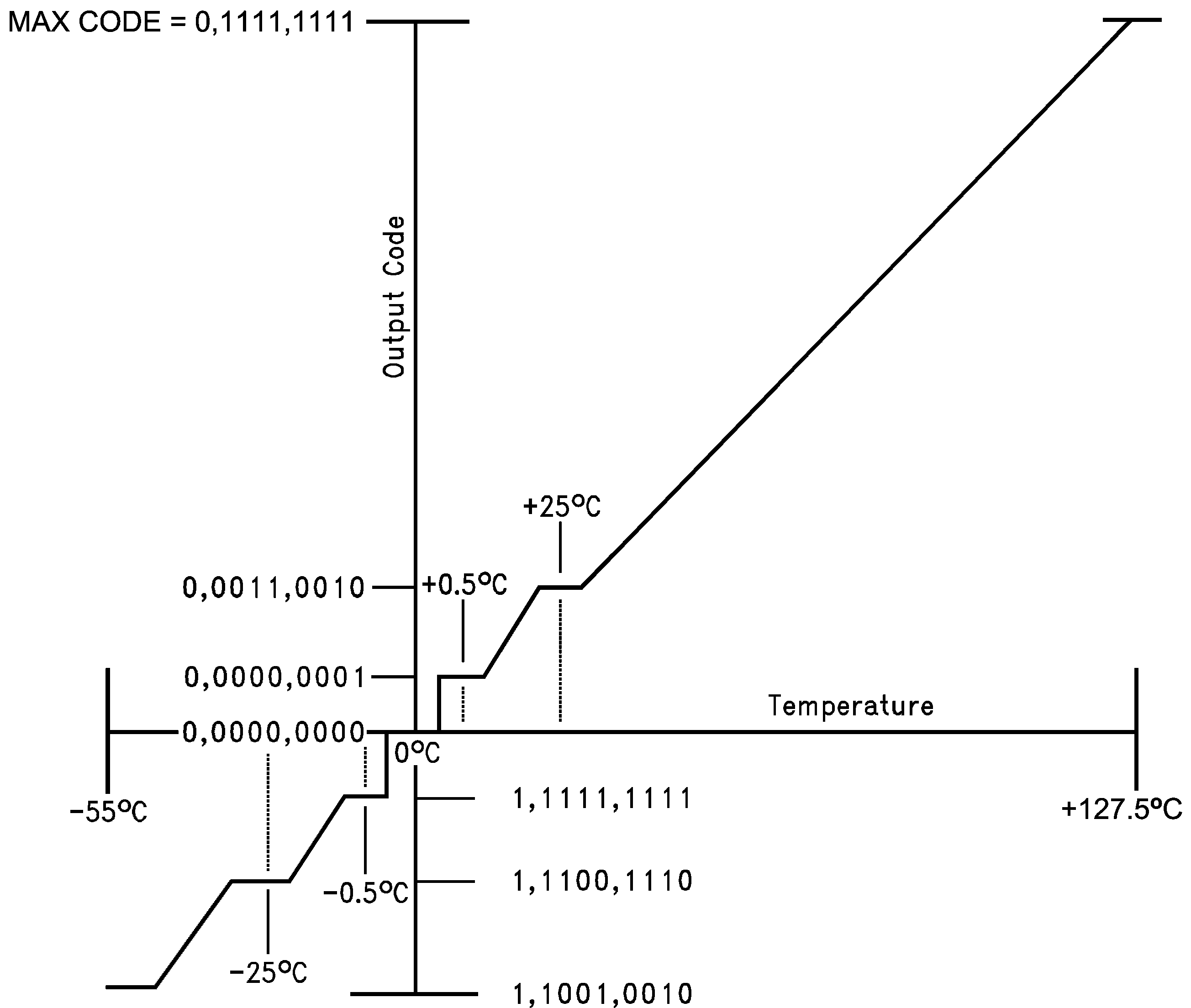 Figure 2. Temperature-to-Digital Transfer Function (Non-Linear Scale for Clarity)
Figure 2. Temperature-to-Digital Transfer Function (Non-Linear Scale for Clarity)
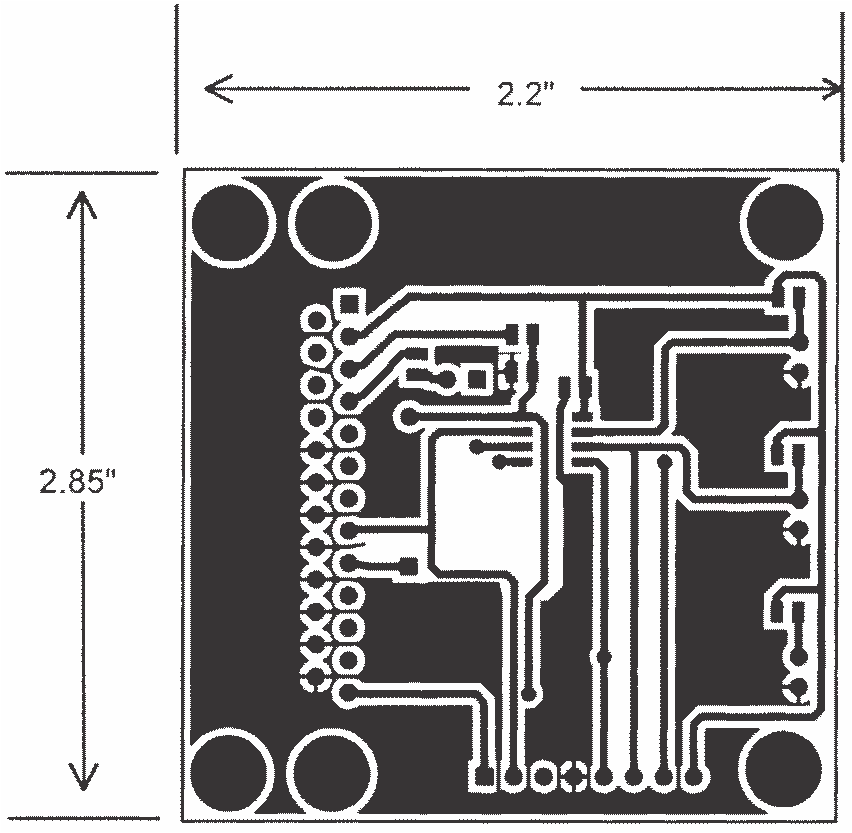
LM75C θJA (thermal resistance, junction-to-ambient) when attached to a printed circuit board with 2 oz. foil similar to the one shown. Summarized below:
| Device Number | Package Number | Thermal Resistance (θJA) |
| LM75BIM-3, LM75BIM-5, LM75CIM-3, LM75CIM-5 | D (R-PDSO-G8) | 200°C/W |
| LM75BIMM-3, LM75BIMM-5, LM75CIMM-3, LM75CIMM-5 | DGK (S-PDSO-G8) | 250°C/W |
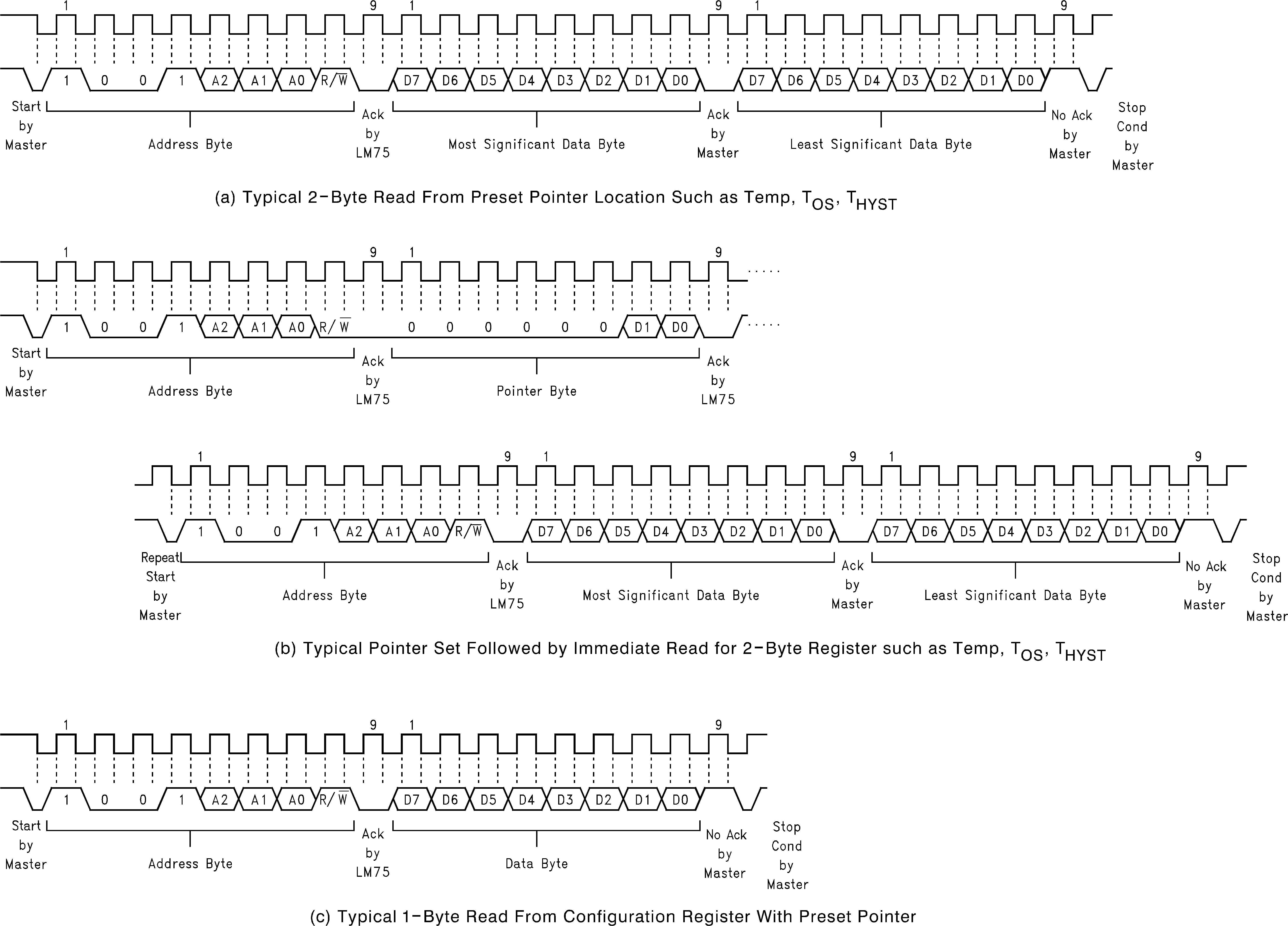 Figure 4. I2C Timing Diagrams
Figure 4. I2C Timing Diagrams
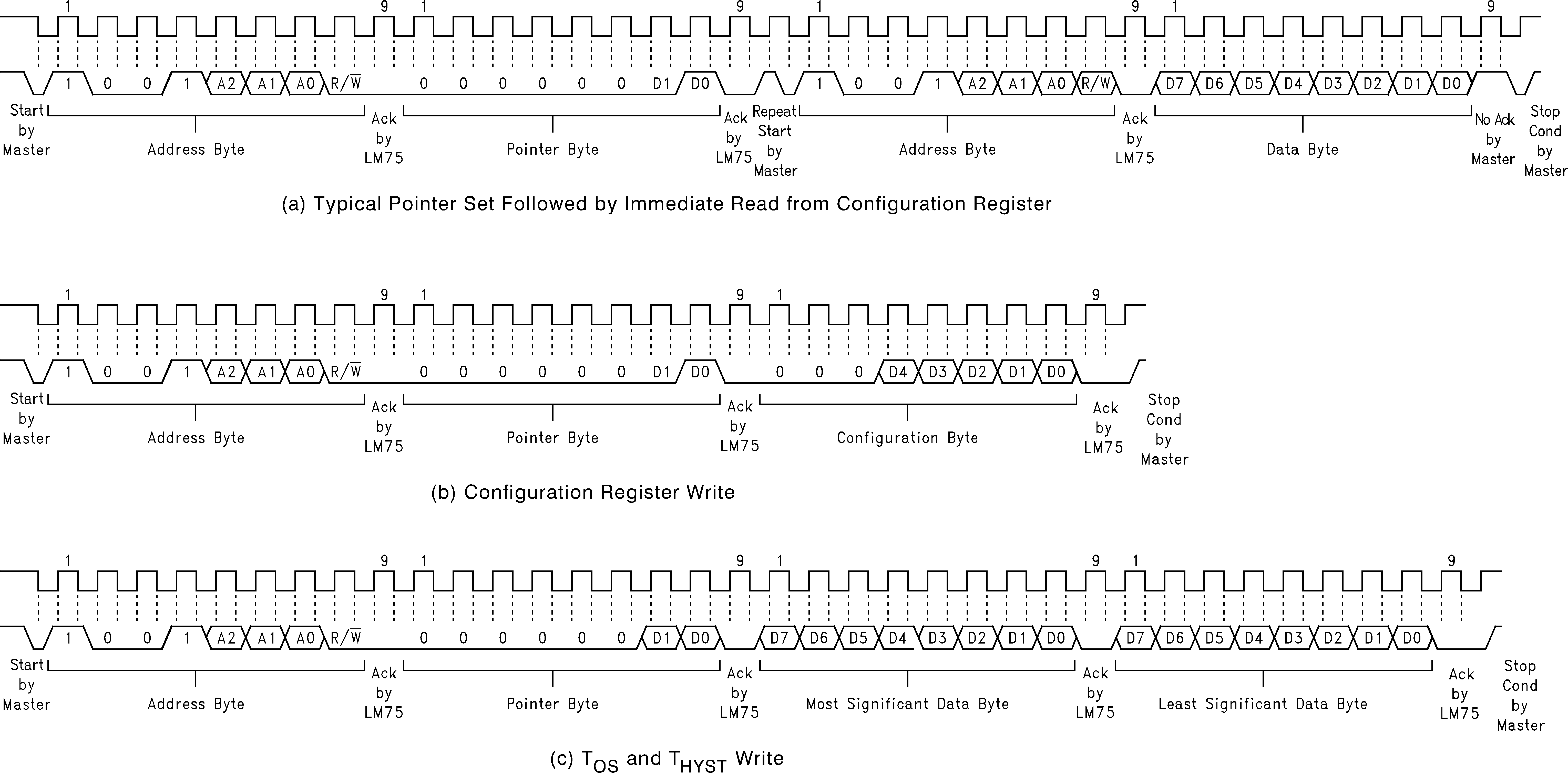 Figure 5. I2C Timing Diagrams (Continued)
Figure 5. I2C Timing Diagrams (Continued)
6.8 Typical Characteristics
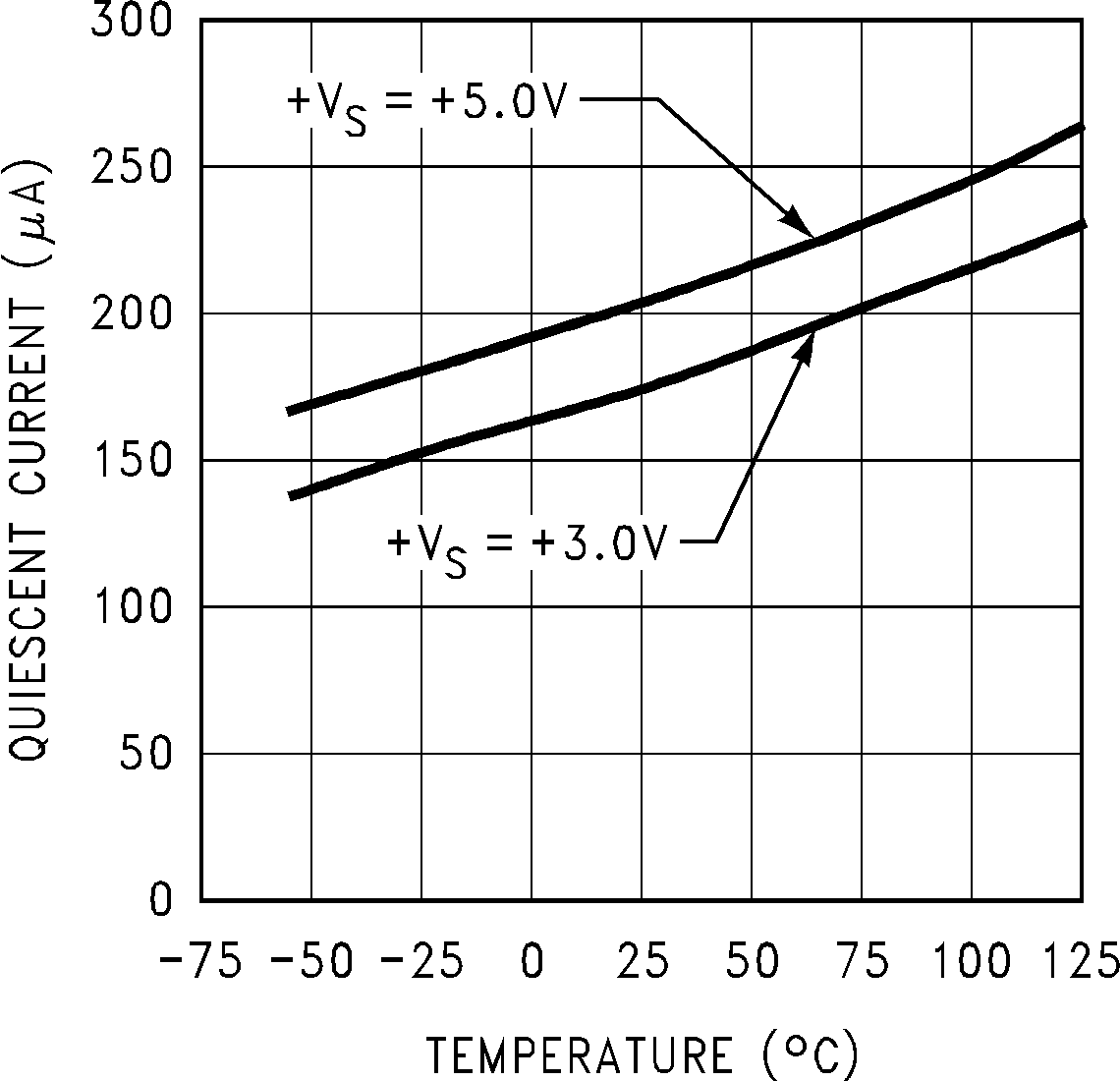 Figure 6. Static Quiescent Current vs Temperature (LM75C)
Figure 6. Static Quiescent Current vs Temperature (LM75C)
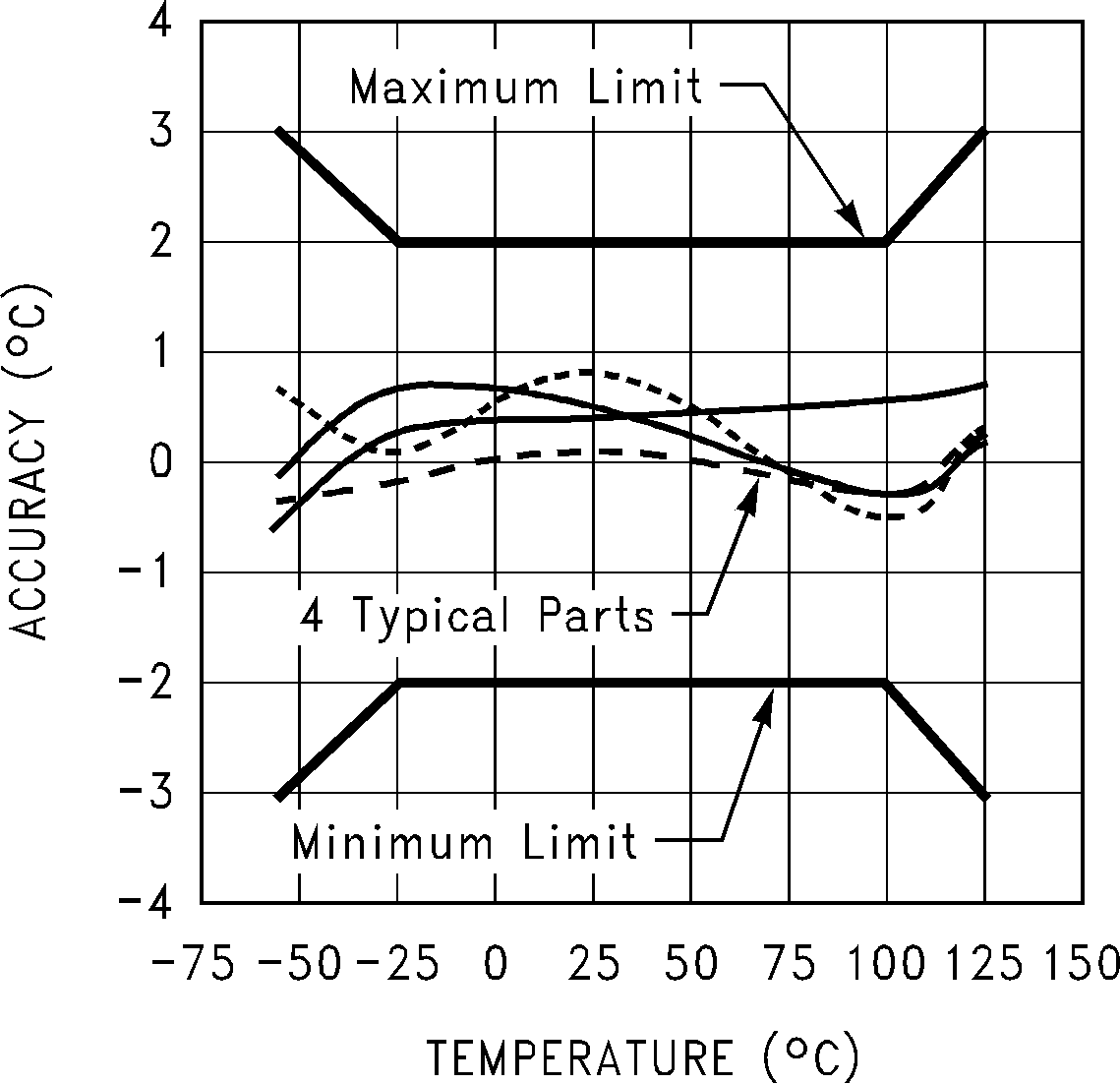 Figure 8. Accuracy vs Temperature (LM75C)
Figure 8. Accuracy vs Temperature (LM75C)
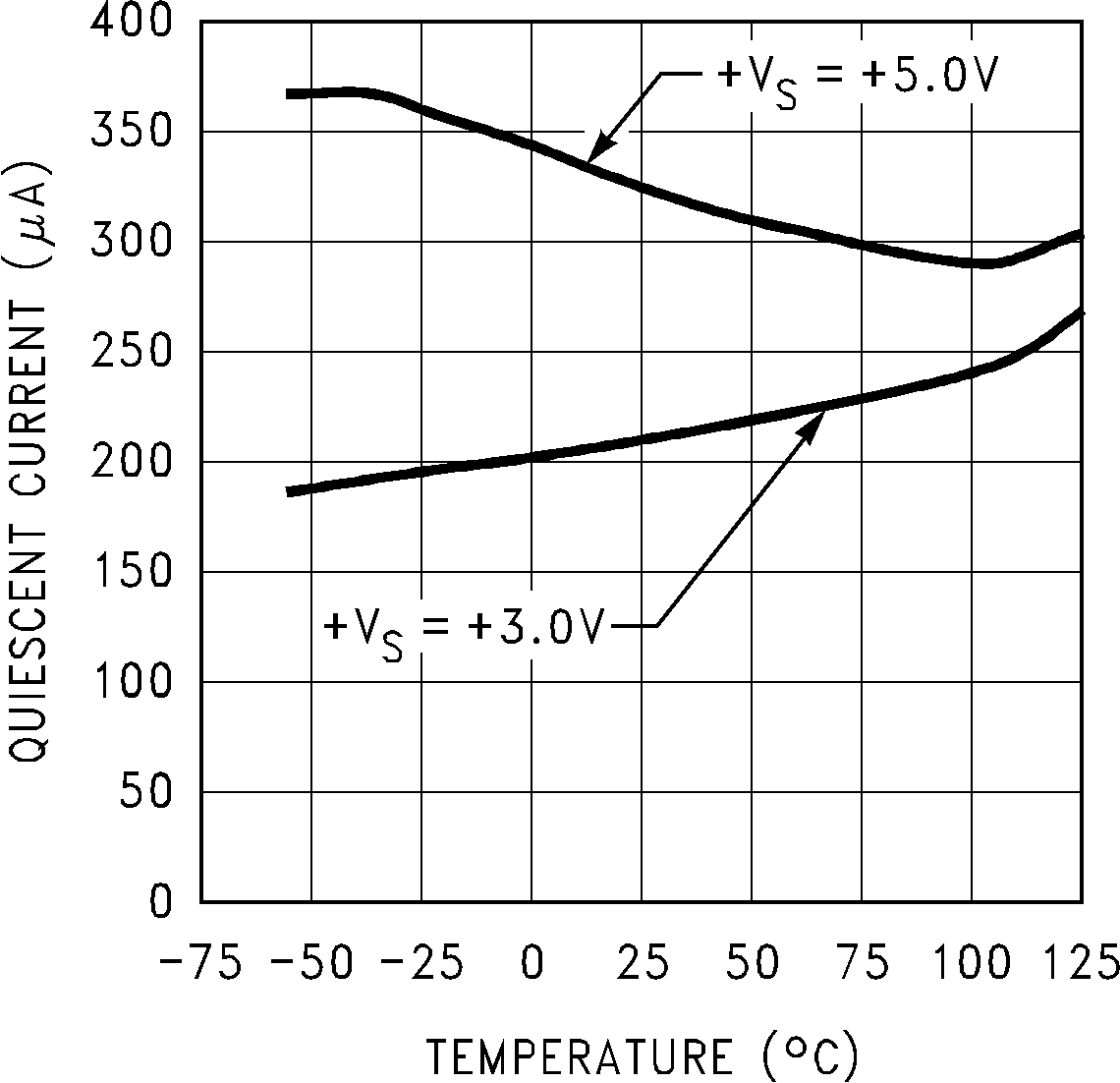 Figure 7. Dynamic Quiescent Current vs Temperature (LM75C)
Figure 7. Dynamic Quiescent Current vs Temperature (LM75C)