ZHCSCW7D October 2014 – February 2018 LMH5401
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: VS = 5 V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: VS = 3.3 V
- 6.7 Typical Characteristics: 5 V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: 3.3 V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: 3.3-V to 5-V Supply Range
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
6.7 Typical Characteristics: 5 V
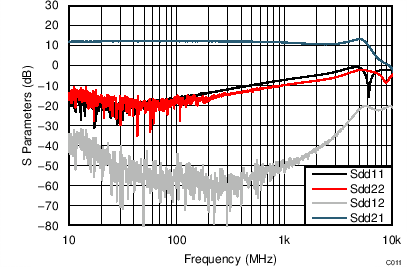
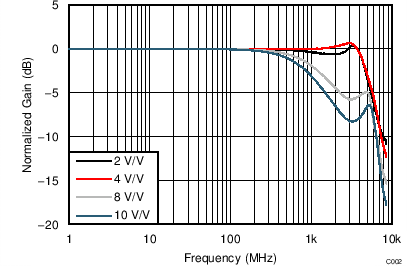
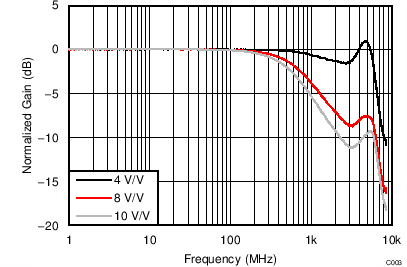
at TA = 25°C, split supplies, VCM = 0 V, RL = 200-Ω differential (RO = 40 Ω each), G = 12 dB (4 V/V), single-ended input and differential output, and input and output pins referenced to midsupply, (unless otherwise noted.) Measured using an EVM as discussed in the section (see Figure 56 to Figure 59).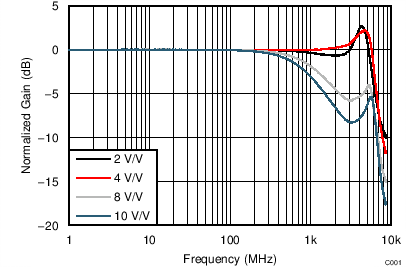
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 0.2 VPP, RL = 200 Ω |
| VOUT_AMP = 0.2 VPP, RL = 200 Ω |
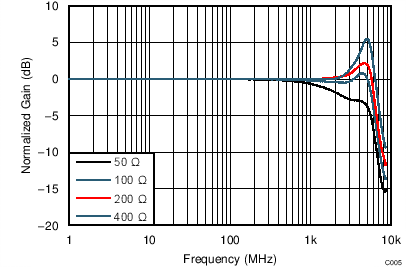
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, G = 12 dB, SE-DE |
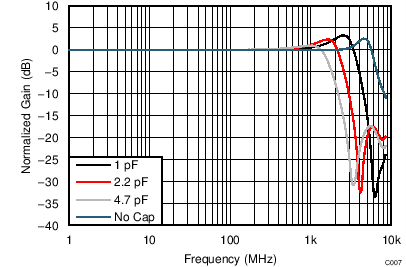
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 0.2 VPP, capacitance at DUT output pins, G = 12 dB, SE-DE |
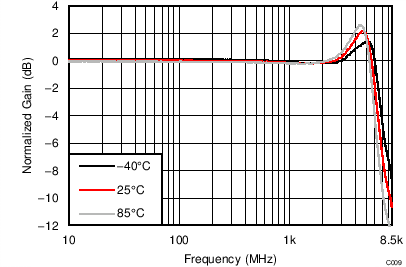
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, G = 12 dB, SE-DE |
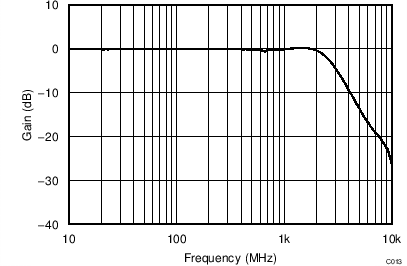
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 200 mVPP |
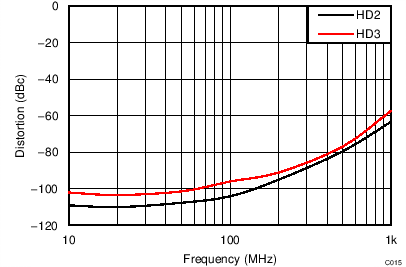
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP | ||
| (Differential to Differential, RL = 200 Ω) |
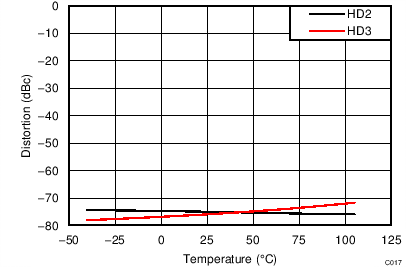
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, RL = 200 Ω, f = 500 MHz |
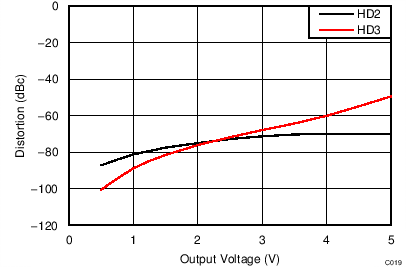
| VS = ±2.5 V, f = 500 MHz |
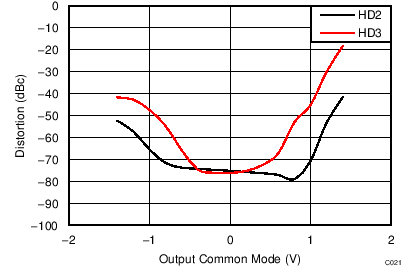
| VS = ±2.5 V, f = 500 MHz , VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP |
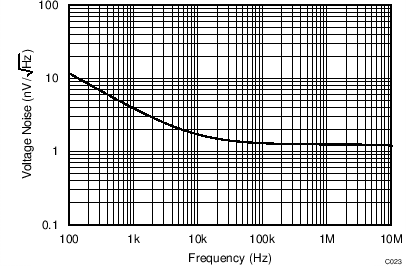
| VS = ±2.5 V |
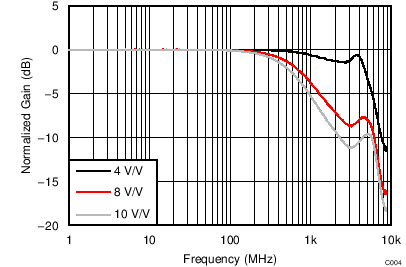
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP |
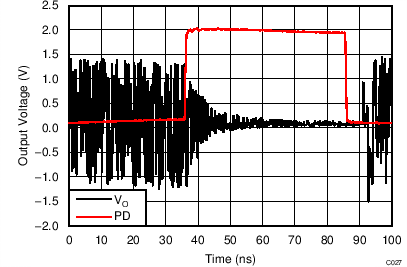
| VS = ±2.5 V |
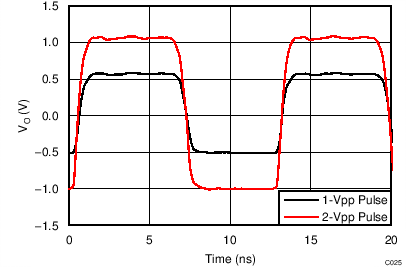
| VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, RL = 200 Ω |
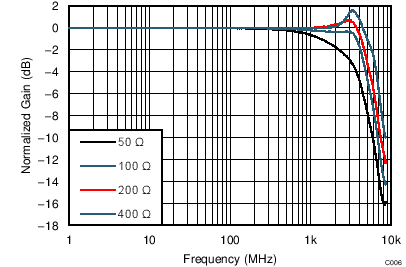
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, G = 12 dB, SE-DE |
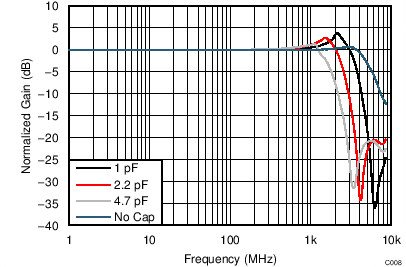
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, capacitance at DUT output pins, G = 12 dB, SE-DE |
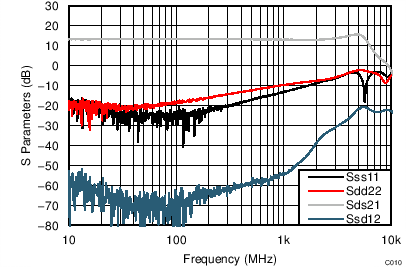
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 200 mVPP, ±2.5-V supply |
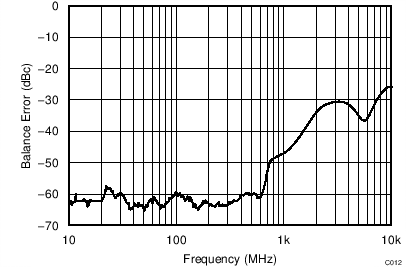
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 200 mVPP |
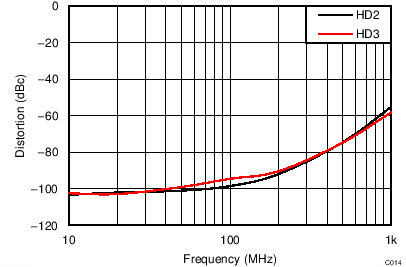
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, SE-DE, RL = 200 Ω |
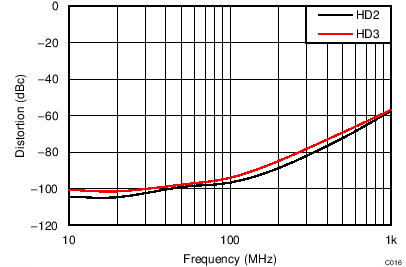
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, (SE-DE, RL = 100 Ω) | ||
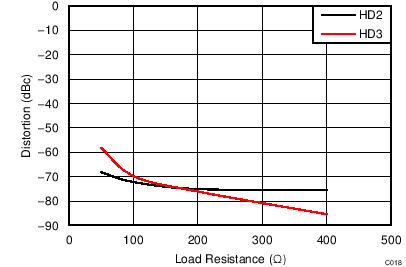
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, f = 500 MHz |
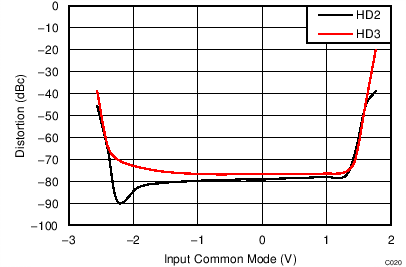
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 2 VPP, f = 500 MHz |
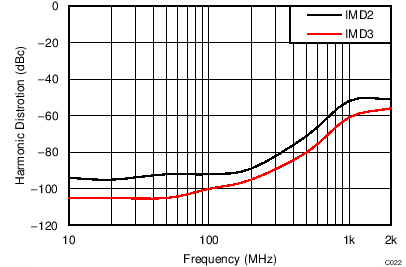
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP = 1 VPP per tone |
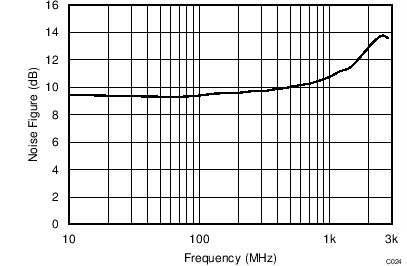
| VS = ±2.5 V |
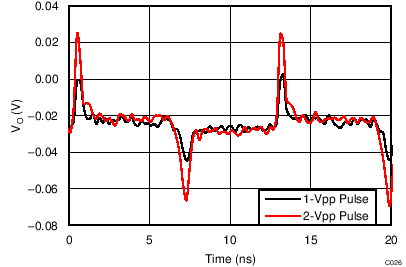
| VS = ±2.5 V, VOUT_AMP, VCM = (VO+ + VO–) / 2 |
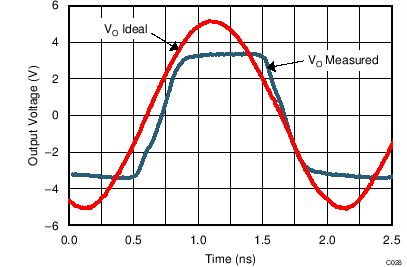
| VS = ±2.5 V |