SNAS605AS March 2013 – May 2020 LMK04821 , LMK04826 , LMK04828
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1
Overview
- 9.1.1 Jitter Cleaning
- 9.1.2 JEDEC JESD204B Support
- 9.1.3 Three PLL1 Redundant Reference Inputs
- 9.1.4 VCXO/Crystal Buffered Output
- 9.1.5 Frequency Holdover
- 9.1.6 PLL2 Integrated Loop Filter Poles
- 9.1.7 Internal VCOs
- 9.1.8 External VCO Mode
- 9.1.9 Clock Distribution
- 9.1.10 Zero-Delay
- 9.1.11 Status Pins
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 9.7
Device Register Descriptions
- 9.7.1 System Functions
- 9.7.2
(0x100 - 0x138) Device Clock and SYSREF Clock Output Controls
- 9.7.2.1 CLKoutX_Y_ODL, CLKoutX_Y_IDL, DCLKoutX_DIV
- 9.7.2.2 DCLKoutX_DDLY_CNTH, DCLKoutX_DDLY_CNTL
- 9.7.2.3 DCLKoutX_ADLY, DCLKoutX_ADLY_MUX, DCLKout_MUX
- 9.7.2.4 DCLKoutX_HS, SDCLKoutY_MUX, SDCLKoutY_DDLY, SDCLKoutY_HS
- 9.7.2.5 SDCLKoutY_ADLY_EN, SDCLKoutY_ADLY
- 9.7.2.6 DCLKoutX_DDLY_PD, DCLKoutX_HSg_PD, DCLKout_ADLYg_PD, DCLKout_ADLY_PD, DCLKoutX_Y_PD, SDCLKoutY_DIS_MODE, SDCLKoutY_PD
- 9.7.2.7 SDCLKoutY_POL, SDCLKoutY_FMT, DCLKoutX_POL, DCLKoutX_FMT
- 9.7.3
SYSREF, SYNC, and Device Config
- 9.7.3.1 VCO_MUX, OSCout_MUX, OSCout_FMT
- 9.7.3.2 SYSREF_CLKin0_MUX, SYSREF_MUX
- 9.7.3.3 SYSREF_DIV[12:8], SYSREF_DIV[7:0]
- 9.7.3.4 SYSREF_DDLY[12:8], SYSREF_DDLY[7:0]
- 9.7.3.5 SYSREF_PULSE_CNT
- 9.7.3.6 PLL2_NCLK_MUX, PLL1_NCLK_MUX, FB_MUX, FB_MUX_EN
- 9.7.3.7 PLL1_PD, VCO_LDO_PD, VCO_PD, OSCin_PD, SYSREF_GBL_PD, SYSREF_PD, SYSREF_DDLY_PD, SYSREF_PLSR_PD
- 9.7.3.8 DDLYdSYSREF_EN, DDLYdX_EN
- 9.7.3.9 DDLYd_STEP_CNT
- 9.7.3.10 SYSREF_CLR, SYNC_1SHOT_EN, SYNC_POL, SYNC_EN, SYNC_PLL2_DLD, SYNC_PLL1_DLD, SYNC_MODE
- 9.7.3.11 SYNC_DISSYSREF, SYNC_DISX
- 9.7.3.12 Fixed Registers (0x145, 0x171 - 0x172)
- 9.7.4 (0x146 - 0x149) CLKin Control
- 9.7.5 RESET_MUX, RESET_TYPE
- 9.7.6
(0x14B - 0x152) Holdover
- 9.7.6.1 LOS_TIMEOUT, LOS_EN, TRACK_EN, HOLDOVER_FORCE, MAN_DAC_EN, MAN_DAC[9:8]
- 9.7.6.2 MAN_DAC[9:8], MAN_DAC[7:0]
- 9.7.6.3 DAC_TRIP_LOW
- 9.7.6.4 DAC_CLK_MULT, DAC_TRIP_HIGH
- 9.7.6.5 DAC_CLK_CNTR
- 9.7.6.6 CLKin_OVERRIDE, HOLDOVER_PLL1_DET, HOLDOVER_LOS_DET, HOLDOVER_VTUNE_DET, HOLDOVER_HITLESS_SWITCH, HOLDOVER_EN
- 9.7.6.7 HOLDOVER_DLD_CNT[13:8], HOLDOVER_DLD_CNT[7:0]
- 9.7.7
(0x153 - 0x15F) PLL1 Configuration
- 9.7.7.1 CLKin0_R[13:8], CLKin0_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.2 CLKin1_R[13:8], CLKin1_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.3 CLKin2_R[13:8], CLKin2_R[7:0]
- 9.7.7.4 PLL1_N
- 9.7.7.5 PLL1_WND_SIZE, PLL1_CP_TRI, PLL1_CP_POL, PLL1_CP_GAIN
- 9.7.7.6 PLL1_DLD_CNT[13:8], PLL1_DLD_CNT[7:0]
- 9.7.7.7 PLL1_R_DLY, PLL1_N_DLY
- 9.7.7.8 PLL1_LD_MUX, PLL1_LD_TYPE
- 9.7.8
(0x160 - 0x16E) PLL2 Configuration
- 9.7.8.1 PLL2_R[11:8], PLL2_R[7:0]
- 9.7.8.2 PLL2_P, OSCin_FREQ, PLL2_XTAL_EN, PLL2_REF_2X_EN
- 9.7.8.3 PLL2_N_CAL
- 9.7.8.4 PLL2_FCAL_DIS, PLL2_N
- 9.7.8.5 PLL2_WND_SIZE, PLL2_CP_GAIN, PLL2_CP_POL, PLL2_CP_TRI
- 9.7.8.6 SYSREF_REQ_EN, PLL2_DLD_CNT
- 9.7.8.7 PLL2_LF_R4, PLL2_LF_R3
- 9.7.8.8 PLL2_LF_C4, PLL2_LF_C3
- 9.7.8.9 PLL2_LD_MUX, PLL2_LD_TYPE
- 9.7.9
(0x16F - 0x1FFF) Misc Registers
- 9.7.9.1 PLL2_PRE_PD, PLL2_PD
- 9.7.9.2 VCO1_DIV
- 9.7.9.3 OPT_REG_1
- 9.7.9.4 OPT_REG_2
- 9.7.9.5 RB_PLL1_LD_LOST, RB_PLL1_LD, CLR_PLL1_LD_LOST
- 9.7.9.6 RB_PLL2_LD_LOST, RB_PLL2_LD, CLR_PLL2_LD_LOST
- 9.7.9.7 RB_DAC_VALUE(MSB), RB_CLKinX_SEL, RB_CLKinX_LOS
- 9.7.9.8 RB_DAC_VALUE
- 9.7.9.9 RB_HOLDOVER
- 9.7.9.10 SPI_LOCK
- 9.1
Overview
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- NKD|64
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- NKD|64
订购信息
8.2 Differential Voltage Measurement Terminology
The differential voltage of a differential signal can be described by two different definitions, which can cause confusion when reading data sheets or communicating with other engineers. This section addresses the measurement and description of a differential signal, so that the reader can understand and distinguish between the two different definitions.
The first definition used to describe a differential signal is the absolute value of the voltage potential between the inverting and non-inverting signal. The symbol for this first measurement is typically VID or VOD, depending on if an input or output voltage is being described.
The second definition used to describe a differential signal is to measure the potential of the non-inverting signal with respect to the inverting signal. The symbol for this second measurement is VSS, and is a calculated parameter. This signal does not exist in the IC with respect to ground; it only exists in reference to its differential pair. VSS can be measured directly by oscilloscopes with floating references; otherwise this value can be calculated as twice the value of VOD, as described in the first description.
Figure 8 illustrates the two different definitions side-by-side for inputs, and Figure 9 illustrates the two different definitions side-by-side for outputs. The VID and VOD definitions show VA and VB DC levels that the non-inverting and inverting signals toggle between with respect to ground. VSS input and output definitions show that if the inverting signal is considered the voltage potential reference, the non-inverting signal voltage potential is now increasing and decreasing above and below the non-inverting reference. Thus, the peak-to-peak voltage of the differential signal can be measured.
VID and VOD are often defined as volts (V) and VSS is often defined as volts peak-to-peak (VPP).
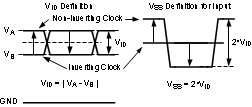 Figure 8. Two Different Definitions for
Figure 8. Two Different Definitions for
Differential Input Signals
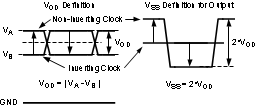 Figure 9. Two Different Definitions for
Figure 9. Two Different Definitions for
Differential Output Signals
Refer to application note AN-912 Common Data Transmission Parameters and their Definitions (SNLA036) for more information.