ZHCSPJ6A October 2022 – November 2022 LMK04832-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Register Map for Device Programming
- 8.6.2
Device Register Descriptions
- 8.6.2.1 System Functions
- 8.6.2.2
(0x100 - 0x138) Device Clock and SYSREF Clock Output Controls
- 8.6.2.2.1 DCLKX_Y_DIV
- 8.6.2.2.2 DCLKX_Y_DDLY
- 8.6.2.2.3 CLKoutX_Y_PD, CLKoutX_Y_ODL, CLKoutX_Y_IDL, DCLKX_Y_DDLY_PD, DCLKX_Y_DDLY[9:8], DCLKX_Y_DIV[9:8]
- 8.6.2.2.4 CLKoutX_SRC_MUX, DCLKX_Y_PD, DCLKX_Y_BYP, DCLKX_Y_DCC, DCLKX_Y_POL, DCLKX_Y_HS
- 8.6.2.2.5 CLKoutY_SRC_MUX, SCLKX_Y_PD, SCLKX_Y_DIS_MODE, SCLKX_Y_POL, SCLKX_Y_HS
- 8.6.2.2.6 SCLKX_Y_ADLY_EN, SCLKX_Y_ADLY
- 8.6.2.2.7 SCLKX_Y_DDLY
- 8.6.2.2.8 CLKoutY_FMT, CLKoutX_FMT
- 8.6.2.3
SYSREF, SYNC, and Device Config
- 8.6.2.3.1 VCO_MUX, OSCout_MUX, OSCout_FMT
- 8.6.2.3.2 SYSREF_REQ_EN, SYNC_BYPASS, SYSREF_MUX
- 8.6.2.3.3 SYSREF_DIV
- 8.6.2.3.4 SYSREF_DDLY
- 8.6.2.3.5 SYSREF_PULSE_CNT
- 8.6.2.3.6 PLL2_RCLK_MUX, PLL2_NCLK_MUX, PLL1_NCLK_MUX, FB_MUX, FB_MUX_EN
- 8.6.2.3.7 PLL1_PD, VCO_LDO_PD, VCO_PD, OSCin_PD, SYSREF_GBL_PD, SYSREF_PD, SYSREF_DDLY_PD, SYSREF_PLSR_PD
- 8.6.2.3.8 DDLYdSYSREF_EN, DDLYdX_EN
- 8.6.2.3.9 DDLYd_STEP_CNT
- 8.6.2.3.10 SYSREF_CLR, SYNC_1SHOT_EN, SYNC_POL, SYNC_EN, SYNC_PLL2_DLD, SYNC_PLL1_DLD, SYNC_MODE
- 8.6.2.3.11 SYNC_DISSYSREF, SYNC_DISX
- 8.6.2.3.12 PLL1R_SYNC_EN, PLL1R_SYNC_SRC, PLL2R_SYNC_EN, FIN0_DIV2_EN, FIN0_INPUT_TYPE
- 8.6.2.4
(0x146 - 0x149) CLKIN Control
- 8.6.2.4.1 CLKin_SEL_PIN_EN, CLKin_SEL_PIN_POL, CLKin2_EN, CLKin1_EN, CLKin0_EN, CLKin2_TYPE, CLKin1_TYPE, CLKin0_TYPE
- 8.6.2.4.2 CLKin_SEL_AUTO_REVERT_EN, CLKin_SEL_AUTO_EN, CLKin_SEL_MANUAL, CLKin1_DEMUX, CLKin0_DEMUX
- 8.6.2.4.3 CLKin_SEL0_MUX, CLKin_SEL0_TYPE
- 8.6.2.4.4 SDIO_RDBK_TYPE, CLKin_SEL1_MUX, CLKin_SEL1_TYPE
- 8.6.2.5 RESET_MUX, RESET_TYPE
- 8.6.2.6
(0x14B - 0x152) Holdover
- 8.6.2.6.1 LOS_TIMEOUT, LOS_EN, TRACK_EN, HOLDOVER_FORCE, MAN_DAC_EN, MAN_DAC[9:8]
- 8.6.2.6.2 MAN_DAC
- 8.6.2.6.3 DAC_TRIP_LOW
- 8.6.2.6.4 DAC_CLK_MULT, DAC_TRIP_HIGH
- 8.6.2.6.5 DAC_CLK_CNTR
- 8.6.2.6.6 CLKin_OVERRIDE, HOLDOVER_EXIT_MODE, HOLDOVER_PLL1_DET, LOS_EXTERNAL_INPUT, HOLDOVER_VTUNE_DET, CLKin_SWITCH_CP_TRI, HOLDOVER_EN
- 8.6.2.6.7 HOLDOVER_DLD_CNT
- 8.6.2.7 (0x153 - 0x15F) PLL1 Configuration
- 8.6.2.8 (0x160 - 0x16E) PLL2 Configuration
- 8.6.2.9 (0x16F - 0x555) Misc Registers
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.8.4 Holdover Frequency Accuracy and DAC Performance
When in holdover mode, PLL1 runs in open loop and the DAC sets the CPout1 voltage. If fixed CPout1 mode is used, then the output of the DAC is dependent upon the MAN_DAC register. If tracked CPout1 mode is used, then the output of the DAC is approximately the same voltage at the CPout1 pin before holdover mode was entered. When using Tracked mode and MAN_DAC_EN = 1, the DAC value during holdover is loaded with the programmed value in MAN_DAC and not the tracked value.
When in Tracked CPout1 mode, the DAC has a worst-case tracking error of ±2 LSBs once PLL1 tuning voltage is acquired. The step size is approximately 3.2 mV, therefore the VCXO frequency error during holdover mode caused by the DAC tracking accuracy is ±6.4 mV × Kv, where Kv is the tuning sensitivity of the VCXO in use. Therefore, the accuracy of the system when in holdover mode in ppm is:
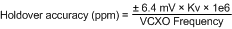
As an example, consider a system with a 19.2-MHz clock input, a 153.6-MHz VCXO with a Kv of 17 kHz/V. The accuracy of the system in holdover in ppm is:
It is important to account for this frequency error when determining the allowable frequency error window to cause holdover mode to exit.