ZHCSMJ6B November 2020 – March 2021 LMK5C33216
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Oscillator Input (XO)
- 9.3.2 Reference Inputs
- 9.3.3 Clock Input Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.4 Reference Input Mux Selection
- 9.3.5 Hitless Switching
- 9.3.6 Gapped Clock Support on Reference Inputs
- 9.3.7 Input Clock and PLL Monitoring, Status, and Interrupts
- 9.3.8
PLL Relationships
- 9.3.8.1 PLL Frequency Relationships
- 9.3.8.2 Analog PLLs (APLL1, APLL2, APLL3)
- 9.3.8.3 APLL Reference Paths
- 9.3.8.4 APLL Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and Charge Pump
- 9.3.8.5 APLL Feedback Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.6 APLL Loop Filters (LF1, LF2, LF3)
- 9.3.8.7 APLL Voltage Controlled Oscillators (VCO1, VCO2, VCO3)
- 9.3.8.8 APLL VCO Clock Distribution Paths
- 9.3.8.9 DPLL Reference (R) Divider Paths
- 9.3.8.10 DPLL Time-to-Digital Converter (TDC)
- 9.3.8.11 DPLL Loop Filter (DLF)
- 9.3.8.12 DPLL Feedback (FB) Divider Path
- 9.3.9 Output Clock Distribution
- 9.3.10 Output Channel Muxes
- 9.3.11 Output Dividers (OD)
- 9.3.12 SYSREF
- 9.3.13 Output Delay
- 9.3.14 Clock Outputs (OUTx_P/N)
- 9.3.15 Glitchless Output Clock Start-Up
- 9.3.16 Clock Output Interfacing and Termination
- 9.3.17 Output Synchronization (SYNC)
- 9.3.18 Zero-Delay Mode (ZDM) Synchronization
- 9.3.19 Time of Day (ToD) Counter
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Application
- 10.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
3 说明
LMK5C33216 是一款高性能网络时钟发生器、同步器和抖动衰减器,具有高级参考时钟选择和无中断切换功能,可满足通信基础设施应用的严格要求。
LMK5C33216 集成了 3 个 DPLL,具有可编程环路带宽且无外部环路滤波器,尽可能提升了灵活性和易用性。每个 DPLL 相位将配对的 APLL 锁定到 DPLL 基准输入。APLL 基准决定了长期频率精度。
3 个 APLL 可以独立于其配对的 DPLL 运行,并从另一个 APLL 级联从而提供可编程频率转换。APLL3 采用使用 TI 专有的体声波 (BAW) VCBO 技术的超高性能 PLL,可生成具有 40fs RMS 抖动的输出时钟,而不受 XO 和基准输入的抖动和频率的影响。APLL1 和 APLL2 提供用于其他频域的选项。
该器件可通过 I2C 或 SPI 接口进行全面编程。板载 EEPROM 可用于自定义系统启动时钟。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | IN | OUT | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMK5C33216 | 2 | 16 | VQFN (64) | 9.00mm x 9.00mm |
(1) 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购米6体育平台手机版_好二三四附录。
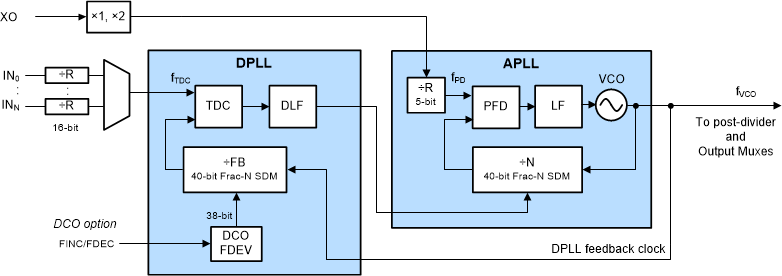 图 3-1 配对的 DPLL 和 APLL 方框图。
图 3-1 配对的 DPLL 和 APLL 方框图。