ZHCS587H July 2011 – January 2016 LMP90077 , LMP90078 , LMP90079 , LMP90080
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.6 Timing Requirements
- 8.7 Timing Requirements - CSB Timing
- 8.8 Timing Requirements - SCLK and SDI Timing
- 8.9 Timing Requirements - SDO Timing With DOD1
- 8.10 Timing Requirements - SDO Timing with DOD2
- 8.11 Timing Requirements - SDO and DRDYB Timing
- 8.12 Typical Characteristics
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Calibration
- 9.3.2 True Continuous Background Calibration
- 9.3.3 Continuous Background Sensor Diagnostics
- 9.3.4 Flexible Input MUX Channels
- 9.3.5 Programmable Gain Amplifiers (FGA & PGA)
- 9.3.6 Excitation Current Sources (IB1 & IB2) - LMP90080/LMP90078
- 9.3.7 Signal Path
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 Serial Digital Interface
- 9.5.2 RESET and RESTART
- 9.5.3 Register Read/Write Examples
- 9.5.4 Streaming Examples
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
13 器件和文档支持
13.1 器件支持
13.1.1 器件命名规则
共模抑制比 测量两个输入引脚对于同相共模信号的抑制能力。要计算 CMRR,需测得共模输入电压变化时的输出偏移变化。
CMRR = 20 LOG (Δ共模输入 / Δ输出偏移)
有效位数量(ENOB 或有效位)– 表示转换器等效于理想 ADC 时的有效位数量 (ENOB)。LMP90080 的 ENOB 是一项直流 ENOB 规范,而非使用快速傅立叶变换 (FFT) 和信纳比 (SINAD) 测得的动态 ENOB。其计算格式如下:
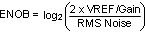
增益误差是与传递函数理想斜率间的偏差。
积分非线性 (INL) 测量通过输入到输出传递函数的直线上每一个代码的偏差。这条直线上的任何给定代码的偏差都是从代码值的中心测量的。使用的是端点拟合方法。根据电气特性表,该米6体育平台手机版_好二三四的 INL 规定在一个有限范围内。
负满量程误差是输出代码转换到负满量程时的差动输入电压与 (-VREF + 1 LSB) 之差。
负增益误差 是负满量程误差与偏移误差除以 (VREF / 增益) 之差。
无噪声分辨率 是指定转换器噪声位数的一种方法。
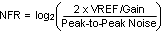
ODR 输出数据速率。
偏移误差 是输出代码由 0000h 转换至 0001h 的差分输入电压与 1 LSB 之差。
正满量程误差是输出代码转换至正满量程时的差动输入电压与 (VREF – 1 LSB) 之差。
正增益误差 是正满量程误差与偏移误差除以 (VREF / 增益) 之差。
电源抑制比 (PSRR) 测量对模拟电源电压变化的抑制能力。PSRR 计算的是给定电源电压变化量的偏移误差变化比,单位为 dB。
PSRR = 20 LOG (ΔVA / Δ输出偏移)
13.2 相关链接
以下表格列出了快速访问链接。范围包括技术文档、支持与社区资源、工具和软件,并且可以快速访问样片或购买链接。
13.3 社区资源
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
Design Support TI's Design Support Quickly find helpful E2E forums along with design support tools and contact information for technical support.
13.4 商标
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
WEBENCH is a registered trademark of TI.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
13.5 静电放电警告

这些装置包含有限的内置 ESD 保护。 存储或装卸时,应将导线一起截短或将装置放置于导电泡棉中,以防止 MOS 门极遭受静电损伤。
13.6 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.