ZHCS590Q January 2011 – December 2014 LMP90097 , LMP90098 , LMP90099 , LMP90100
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 典型应用电路原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 说明(续)
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 True Continuous Background Calibration
- 9.3.2 Continuous Background Sensor Diagnostics
- 9.3.3 Flexible Input MUX Channels
- 9.3.4 Programmable Gain Amplifiers (FGA and PGA)
- 9.3.5 Excitation Current Sources (IB1 and IB2) - LMP90100/LMP90098
- 9.3.6 Signal Path
- 9.3.7 Calibration
- 9.3.8 Sensor Interface
- 9.3.9 RESET and RESTART
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 General Rules
- 9.5.2 Serial Digital Interface
- 9.5.3 Register Address (ADDR)
- 9.5.4 Register Read/Write Protocol
- 9.5.5 Streaming
- 9.5.6 CSB - Chip Select Bar
- 9.5.7 SPI Reset
- 9.5.8 DRDYB - Data Ready Bar
- 9.5.9 DRDYB Case1: Combining SDO/DRDYB with SDO_DRDYB_DRIVER = 0x00
- 9.5.10 DRDYB Case2: Combining SDO/DRDYB with SDO_DRDYB_DRIVER = 0x03
- 9.5.11 DRDYB Case3: Routing DRDYB to D6
- 9.5.12 Data Only Read Transaction
- 9.5.13 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 9.5.14 Register Read/Write Examples
- 9.5.15 Streaming Examples
- 9.6 Register Maps
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械封装和可订购信息
13 器件和文档支持
13.1 器件支持
13.1.1 器件命名规则
13.1.1.1 具体定义
-
共模抑制比 (CMRR)
= 20 LOG(Δ共模输入 / Δ输出偏移)
-
共模抑制比
测量的是对两个输入引脚同相共模信号的抑制能力。 要计算 CMRR,需测得共模输入电压变化时的输出偏移变化。
-
有效位数 (ENOB) –
表示转换器与理想 ADC 等效的有效位数量 (ENOB)。 LMP90xxx 的 ENOB 是一项 DC ENOB 规格,而不是使用 FFT 和 SINAD 测得的动态 ENOB。 其计算格式如下:
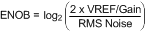
-
增益误差
是与传递函数理想斜率间的偏差。
-
积分非线性 (INL)
测量的是直线通过输入到输出传递函数的每一个代码的偏差。 这条直线上的任何给定代码的偏差都是从代码值的中心测量的。 使用的是端点拟合方法。 根据电气特性表,该米6体育平台手机版_好二三四的 INL 规定在一个有限范围内。
-
负满量程误差
是输出代码转换到负满量程时的差动输入电压与 (-VREF + 1LSB) 之差。
-
负增益误差
是负满量程误差与偏移误差除以(VREF/增益)之差。
-
无噪声分辨率
是指定转换器噪声位数的一种方法。
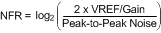
-
ODR
输出数据速率。
-
偏移误差
是输出代码从代码 0000h 转换到 0001h 的差分输入电压与 1LSB 之差。
-
正满量程误差
是输出代码转换到正满量程时的差动输入电压与 (VREF – 1LSB) 之差。
-
正增益误差
是正满量程误差与偏移误差除以(VREF/增益)之差。
-
电源抑制比 (PSRR)
测量的是对模拟电源电压变化的抑制能力。 PSRR 计算的是给定电源电压变化量的偏移误差变化比,单位为 dB。
-
PSRR
= 20 LOG (ΔVA / Δ输出偏移)
13.2 相关链接
以下表格列出了快速访问链接。 范围包括技术文档、支持与社区资源、工具和软件,并且可以快速访问样片或购买链接。
13.3 商标
WEBENCH is a registered trademark of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
13.4 静电放电警告

这些装置包含有限的内置 ESD 保护。 存储或装卸时,应将导线一起截短或将装置放置于导电泡棉中,以防止 MOS 门极遭受静电损伤。