ZHCSJW8D October 2011 – June 2019 LMR10515
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
9.2.1.7 Calculating Efficiency, And Junction Temperature
The complete LMR10515 DC/DC converter efficiency can be calculated in the following manner.
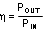
Or
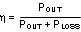
Calculations for determining the most significant power losses are shown below. Other losses totaling less than 2% are not discussed.
Power loss (PLOSS) is the sum of two basic types of losses in the converter: switching and conduction. Conduction losses usually dominate at higher output loads, whereas switching losses remain relatively fixed and dominate at lower output loads. The first step in determining the losses is to calculate the duty cycle (D):
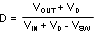
VSW is the voltage drop across the internal PFET when it is on, and is equal to:
VD is the forward voltage drop across the Schottky catch diode. It can be obtained from the diode manufactures Electrical Characteristics section. If the voltage drop across the inductor (VDCR) is accounted for, the equation becomes:
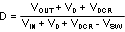
The conduction losses in the free-wheeling Schottky diode are calculated as follows:
Often this is the single most significant power loss in the circuit. Care should be taken to choose a Schottky diode that has a low forward voltage drop.
Another significant external power loss is the conduction loss in the output inductor. The equation can be simplified to:
The LMR10515 conduction loss is mainly associated with the internal PFET:
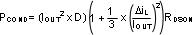
If the inductor ripple current is fairly small, the conduction losses can be simplified to:
Switching losses are also associated with the internal PFET. They occur during the switch on and off transition periods, where voltages and currents overlap resulting in power loss. The simplest means to determine this loss is to empirically measuring the rise and fall times (10% to 90%) of the switch at the switch node.
Switching Power Loss is calculated as follows:
Another loss is the power required for operation of the internal circuitry:
IQ is the quiescent operating current, and is typically around 3.3 mA for the 1.6 MHz frequency option.
Typical Application power losses are:
Table 1. Power Loss Tabulation
| VIN | 5 V | ||
| VOUT | 3.3 V | POUT | 4.125 W |
| IOUT | 1.25 A | ||
| VD | 0.45 V | PDIODE | 188 mW |
| FSW | 1.6 MHz | ||
| IQ | 3.3 mA | PQ | 16.5 mW |
| TRISE | 4 ns | PSWR | 20 mW |
| TFALL | 4 ns | PSWF | 20 mW |
| RDS(ON) | 150 mΩ | PCOND | 156 mW |
| INDDCR | 70 mΩ | PIND | 110 mW |
| D | 0.667 | PLOSS | 511 mW |
| η | 88% | PINTERNAL | 213 mW |