ZHCSKF5C October 2019 – November 2020 LMR33640
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.2 Dropout
The dropout performance of any buck regulator is affected by the RDSON of the power MOSFETs, the DC resistance of the inductor, and the maximum duty cycle that the controller can achieve. As the input voltage level approaches the output voltage, the off-time of the high-side MOSFET starts to approach the minimum value. Beyond this point, the switching can become erratic, and the output voltage can fall out of regulation. To avoid this problem, the LMR33640 automatically reduces the switching frequency to increase the effective duty cycle and maintain regulation. In this data sheet, the dropout voltage is defined as the difference between the input and output voltage when the output has dropped by 1% of its nominal value. Under this condition, the switching frequency has dropped to its minimum value of about 140 kHz. Note that the 0.4 V short circuit detection threshold is not activated when in dropout mode. Typical dropout characteristics can be found in Figure 8-10, Figure 8-11, and Figure 8-12.
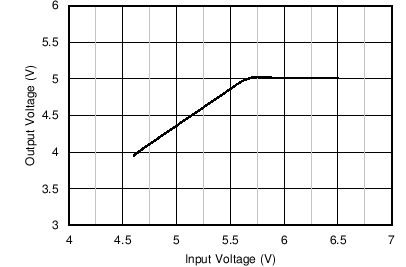 Figure 8-10 Overall Dropout Characteristic VOUT = 5 V, IOUT = 4 A
Figure 8-10 Overall Dropout Characteristic VOUT = 5 V, IOUT = 4 A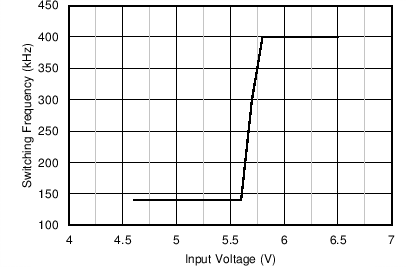 Figure 8-12 Typical Switching Frequency in Dropout Mode VOUT = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz
Figure 8-12 Typical Switching Frequency in Dropout Mode VOUT = 5 V, fSW = 400 kHz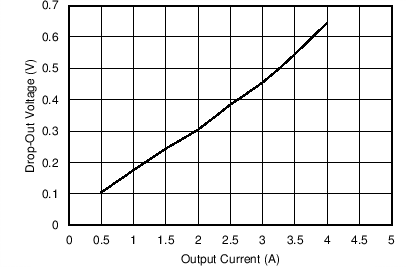 Figure 8-11 Typical Dropout Voltage vs Output Current in Frequency Fold-back ƒSW = 140 kHz
Figure 8-11 Typical Dropout Voltage vs Output Current in Frequency Fold-back ƒSW = 140 kHz