SNAS187D February 2003 – January 2016 LMX2430 , LMX2433 , LMX2434
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description continued
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Control Register Content Map
- 9.6.2
R0 Register
- 9.6.2.1 RF_R[14:0] - RF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R0[17:3])
- 9.6.2.2 RF_CPP - RF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R0[18])
- 9.6.2.3 RF_CPG - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Current Gain (R0[19])
- 9.6.2.4 RF_CPT - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R0[20])
- 9.6.2.5 RF_RST - RF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R0[21])
- 9.6.3 R1 Register
- 9.6.4
R2 Register
- 9.6.4.1 RF_TOC[0:11] - RF Synthesizer Time-Out Counter (R2[14:3])
- 9.6.4.2
R3 Register
- 9.6.4.2.1 IF_R[14:0] - IF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R3[17:3])
- 9.6.4.2.2 IF_CPP - IF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R3[18])
- 9.6.4.2.3 IF_CPG - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Current Gain (R3[19])
- 9.6.4.2.4 IF_CPT - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R3[20])
- 9.6.4.2.5 IF_RST - IF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R3[21])
- 9.6.5 R4 Register
- 9.6.6 R5 Register
- 9.6.7 MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22])
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9 Detailed Description
9.1 Overview
The basic phase-lock-loop (PLL) configuration consists of a high-stability crystal reference oscillator, a frequency synthesizer such as the LMX243x, a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), and a passive loop filter. The frequency synthesizer includes a phase detector, current-mode charge pump, programmable reference R and feedback N frequency dividers. The VCO frequency is established by dividing the crystal reference signal down through the reference divider to obtain a comparison reference frequency. This reference signal, fr, is then presented to the input of a phase / frequency detector and compared with the feedback signal, fp, which was obtained by dividing the VCO frequency down by way of the feedback divider. The phase and frequency detector (PFD) measures the phase error between the fr and fp signals and outputs control signals that are directly proportional to the phase error. The charge pump then pumps charge into or out of the loop filter based on the magnitude and direction of the phase error. The loop filter converts the charge into a stable control voltage for the VCO. The function of the PFD is to adjust the voltage presented to the VCO until the frequency of the feedback signal and phase match that of the reference signal. When this phase-locked condition exists, the VCO frequency is N times that of the comparison frequency, where N is the feedback divider ratio.
9.2 Functional Block Diagram
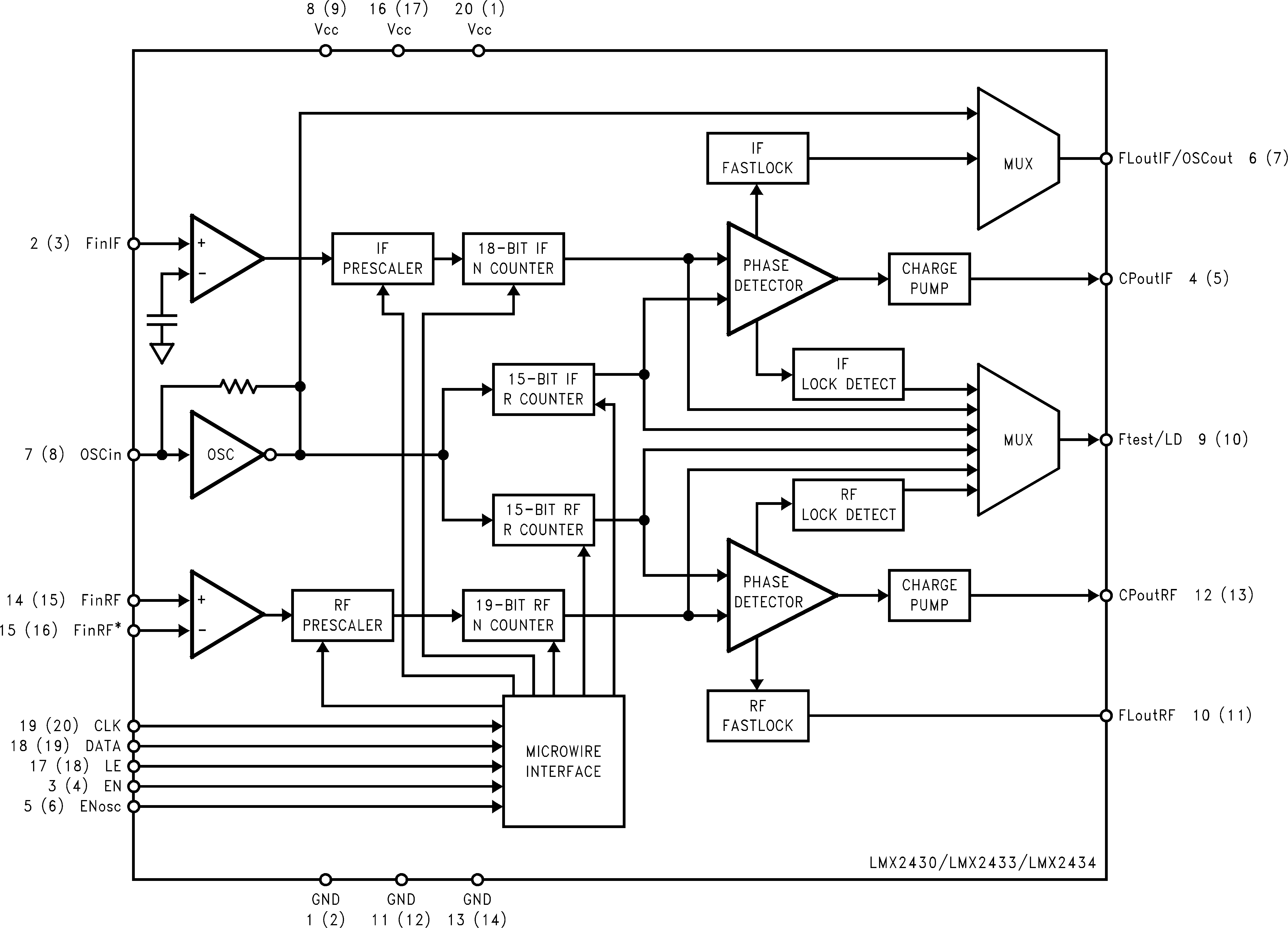
9.3 Feature Description
9.3.1 Reference Oscillator Input
The reference oscillator frequency for both the RF and IF PLLs is provided from an external reference through the OSCin pin. The reference buffer circuit supports input frequencies from 5 to 40 MHz with a minimum input sensitivity of 0.5 VPP. The reference buffer circuit has an approximate Vcc/2 input threshold and can be driven from an external AC-coupled source. Typically, the OSCin pin is connected to the output of a crystal oscillator.
9.3.2 Reference Dividers (R Counters)
The reference dividers divide the reference input signal, OSCin, by a factor of R. The output of the reference divider circuits feeds the reference input of the phase detector. This reference input to the phase detector is often referred to as the comparison frequency. The divide ratio must be chosen such that the maximum phase comparison frequency (fCOMPRF or fCOMPIF) of 10 MHz is not exceeded.
The RF and IF reference dividers are each comprised of 15-bit CMOS binary counters that support a continuous integer divide ratio from 3 to 32,767. The RF and IF reference divider circuits are clocked by the output of the reference buffer circuit which is common to both. Refer to RF_R[14:0] - RF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R0[17:3]) and IF_R[14:0] - IF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R3[17:3]) for details on how to program the RF_R and IF_R counters.
9.3.3 Prescalers
The FinRF and FinIF input pins drive the input of a differential-pair amplifier. The output of the differential-pair amplifier drives a chain of D-type flip-flops in a dual modulus configuration. The output of the prescaler is used to clock the subsequent feedback dividers. The RF PLL complementary inputs can be driven differentially, or the negative input can be AC-coupled to ground through an external capacitor for single-ended configuration. A 16/17 or a 32/33 prescale ratio can be selected for the 5-GHz LMX2434 RF synthesizer. An 8/9 or a 16/17 prescale ratio can be selected for both the LMX2430 and LMX2433 RF synthesizers. The IF PLL is single-ended, and an 8/9 or a 16/17 prescale ratio can be selected for the IF synthesizer.
9.3.4 Programmable Feedback Dividers (N Counters)
The programmable feedback dividers operate in concert with the prescalers to divide the input signal, Fin, by a factor of N. The output of the programmable reference divider is provided to the feedback input of the phase detector circuit. The divide ratio must be chosen so that the maximum phase comparison frequency (fCOMPRF or fCOMPIF) of 10 MHz is not exceeded.
The programmable feedback divider circuit is comprised of an A counter (swallow counter) and a B counter (programmble binary counter). For both the LMX2430 and LMX2433, the RF_A counter is a 4-bit swallow counter, programmable from 0 to 15. The LMX2434 RF_A counter is a 5-bit swallow counter, programmable from 0 to 31. The LMX243x IF_A counter is a 4-bit swallow counter, programmable from 0 to 15. For both the LMX2430 and LMX2433, the RF_B counter is a 15-bit binary counter, programmable from 3 to 32,767. The LMX2434 RF_B counter is a 14-bit binary counter, programmable from 3 to 16,383. The LMX243x IF_B is a 14-bit binary counter programmable from 3 to 16,383. A continuous integer divide ratio is achieved if N ≥ P × (P−1), where P is the value of the prescaler selected.
Divide ratios less than the minimum continuous divide ratio are achievable as long as the binary programmable counter value is greater than the swallow counter value (B ≥ A). Refer to RF_A[3:0] - LMX2430/33 RF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R1[6:3]), RF_A[4:0] - LMX2434 RF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R1[7:3]), RF_B[14:0] - LMX2430/33 RF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R1[21:7]), RF_B[13:0] - LMX2434 RF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R1[21:8]), IF_A[3:0] - IF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R4[6:3]), and IF_B[13:0] - IF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R4[20:7]) for details on how to program the A and B counters. Equation 4 and Equation 5 are useful in determining and programming a particular value of N:
9.3.5 Phase / Frequency Detectors
The RF and IF PFDs are driven from their respective N and R counter outputs. The maximum frequency for both the RF and IF phase detector inputs is 10 MHz. The PFD outputs control the respective charge pumps. The polarity of the pump-up or pump-down control signals are programmed using the RF_CPP or IF_CPP control bits, depending on whether the RF or IF VCO characteristics are positive or negative. Refer to RF_CPP - RF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R0[18]) and IF_CPP - IF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R3[18]) for more details. The PFDs have a detection range of −2π to +2π. The PFDs also receive a feedback signal from the charge pump in order to eliminate dead zone.
9.3.5.1 Phase Comparator and Internal Charge-Pump Characteristics
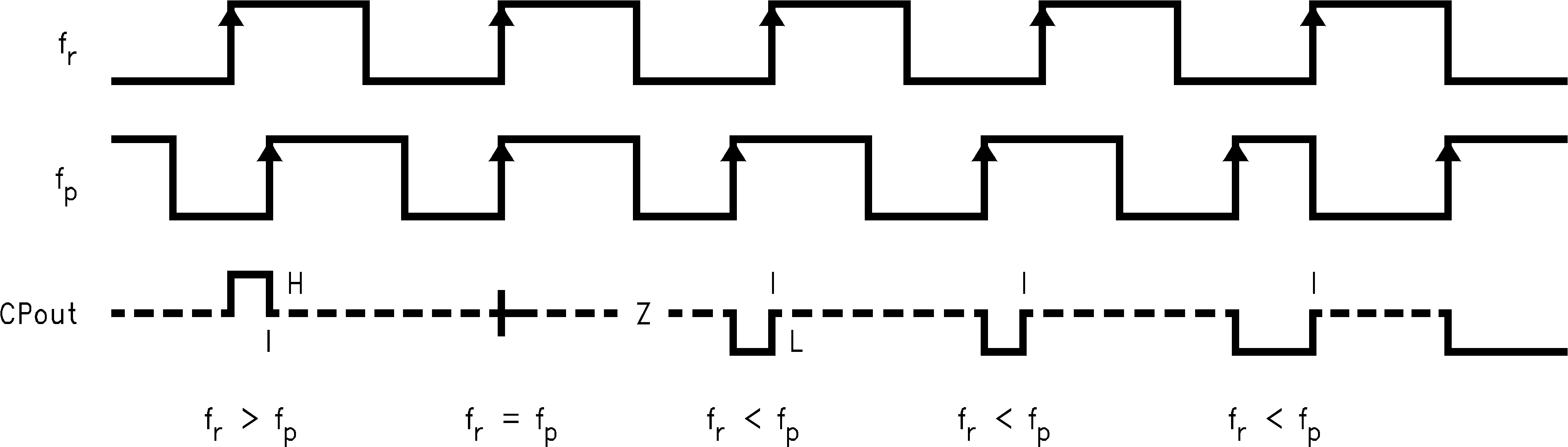
1. The minimum width of the pump-up and pump-down current pulses occur at the CPoutRF or CPoutIF pins when the loop is phase locked.
2. The diagram assumes positive VCO characteristic that is, RF_CPP or IF_CPP = 1.
3. fr is the PFD input from the reference divider (R counter).
4. fp is the PFD input from the programmable feedback divider (N counter).
5. CPout refers to either the RF or IF charge-pump output
9.3.6 Charge Pumps
The charge pump directs charge into or out of an external loop filter. The loop filter converts the charge into a stable control voltage which is applied to the tuning input of the VCO. The charge pump steers the VCO control voltage towards VCC during pump-up events and towards GND during pump-down events. When locked, CPoutRF or CPoutIF are primarily in a tri-state mode with small corrections occurring at the phase comparator rate. The charge-pump output current magnitude can be selected by toggling the RF_CPG or IF_CPG control bits.
9.3.7 Microwire Serial Interface
The programmable register set is accessed through the MICROWIRE serial interface. A low voltage logic interface allows direct connection to 1.8-V devices. The interface is comprised of three signal pins: CLK, DATA and LE. Serial data is clocked into the 24-bit shift register on the rising edge of CLK. The last two bits decode the internal control register address. When LE transitions HIGH, DATA stored in the shift register is loaded into one of four control registers depending on the state of the address bits. The MSB of DATA is loaded in first. The synthesizers can be programmed even in power-down mode. A complete programming description is provided in Programming.
9.3.8 Multi-Function Outputs
The Ftest/LD output pin of the LMX243x device is a multi-function output that can be configured as a general-purpose CMOS tri-state output, push-pull analog lock-detect output, open-drain analog lock-detect output, digital filtered lock-detect output, or used to monitor the output of the various reference divider (R counter) or feedback divider (N counter) circuits. The Ftest/LD control word is used to select the desired output function. When the PLL is in power-down mode, the Ftest/LD output is disabled and is in a high-impedance state. A complete programming description of the multi-function output is provided in MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22]).
9.3.8.1 Push-Pull Analog Lock-Detect Output
An analog lock-detect status generated from the phase detector is available on the Ftest/LD output pin if selected. A push-pull configuration can be selected for the lock-detect output signal. With this configuration, the lock-detect output goes HIGH when the charge pump is inactive. It goes LOW when the charge pump is active during a comparison cycle. Narrow low-going pulses are observed when the charge pump turns on.
There are three separate push-pull analog lock-detect signals that are routed to the multiplexer. Two of these monitor the lock status of the individual synthesizers. The third detects the condition when both the RF and IF synthesizers are in a locked state. External circuitry is required to provide a steady DC signal to indicate when the PLL is in a locked state. Refer to MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22]) for details on how to program the different push-pull analog lock-detect options.
9.3.8.2 Open-Drain Analog Lock-Detect Output
The lock-detect output can be an open-drain configuration. In this configuration, the lock-detect output goes to a high impedance state when the charge pump is inactive. It goes LOW when the charge pump is active during a comparison cycle. When a pullup resistor is used, narrow low-going pulses are observed when the charge pump turns on.
Similarly, three separate open-drain analog lock-detect signals are routed to the multiplexer. Two of these monitor the lock status of the individual synthesizers. The third detects the condition when both the RF and IF synthesizers are in a locked state. External circuitry is required to provide a steady DC signal to indicate when the PLL is in a locked state. Refer to MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22]) for details on how to program the different open-drain analog lock-detect options.
9.3.8.3 Digital Filtered Lock-Detect Output
A digital filtered lock-detect status generated from the phase detector is also available on the Ftest/LD output pin if selected. The lock-detect digital filter compares the difference between the phases of the inputs to the PFD to an RC-generated delay of approximately 15 ns. If the phase error is less than the 15-ns RC delay for 5 consecutive reference cycles, the PLL enters a locked state (HIGH). Once in lock, the RC delay is changed to approximately 30 ns. Once the phase error becomes greater than the 30-ns RC delay, the PLL falls out of lock (LOW). When the PLL is in power-down mode, the Ftest/LD output is forced LOW. A flow chart of the digital filtered lock-detect output is shown in Figure 30.
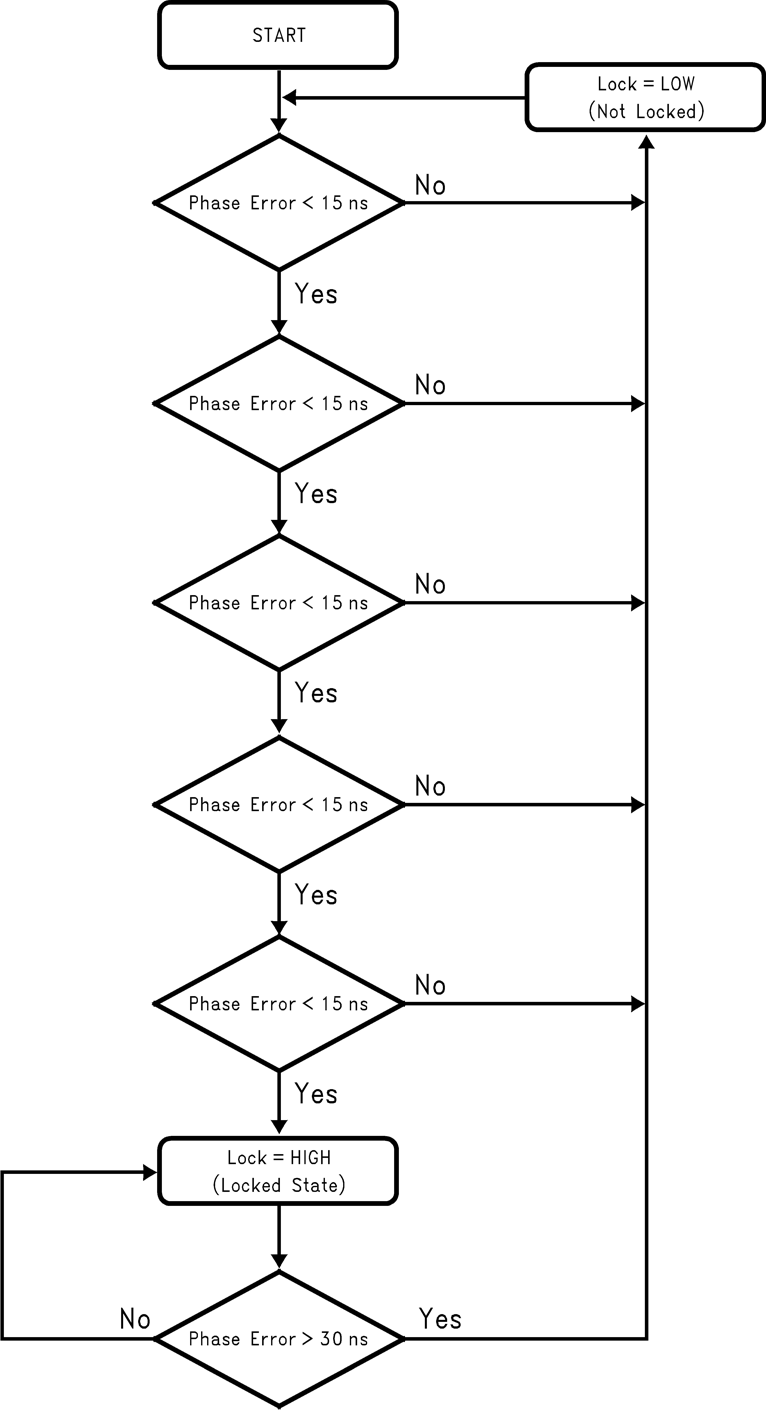 Figure 30. Digital Lock-Detect Operation
Figure 30. Digital Lock-Detect Operation
Similarly, three separate digital filtered lock-detect signals are routed to the multiplexer. Two of these monitor the lock status of the individual synthesizers. The third detects the condition when both the RF and IF synthesizers are in a locked state. External circuitry is not required when the digital filtered lock-detect option is selected. Refer to MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22]) for details on how to program the different digital filtered lock-detect options.
9.3.8.4 Reference Divider and Feedback Divider Output
The outputs of the various N and R dividers can be monitored by selecting the appropriate Ftest/LD word. This is essential when performing OSCin or Fin sensitivity measurements. Refer to the LMX243x FinRF Sensitivity Test Setup or LMX243x OSCin Sensitivity Test Setup sections for more details.
NOTE
The R and N outputs that are routed to the Ftest/LD are R/2 and N/2, respectively. The internal /2 circuit is used to provide a 50% duty cycle. Refer to MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22]) for more details on how to route the appropriate divider output to the Ftest/LD pin.
9.3.9 Fastlock Output
The LMX243x fastlock feature allows a faster loop response time during lock aquisition. The loop response time (lock time) can be approximately halved if the loop bandwidth is doubled. In order to achieve this, the same gain / phase relationship must be maintained when the loop bandwidth is doubled. When the FLoutRF or OSCout/ FLoutIF pins are configured as fastLock outputs, an open-drain device is enabled. The open-drain device switches in a resistor parallel, and of equal value, to R2 of the external loop filter.
The loop bandwidth is effectively doubled and stability is maintained. Once locked to the correct frequency, the PLL returns to a steady-state condition. The LMX243x offers two methods to achieve fastlock: manual and automatic. Manual fastlock is achieved by increasing the charge pump current from 1 mA (RF_CPG/ IF_CPG Bit = 0) in the steady-state mode, to 4 mA (RF_CPG/ IF_CPG Bit = 1) in fastlock mode. Automatic fastlock is achieved by programming the time-out counter register (RF_TOC/ IF_TOC) with the appropriate number of phase comparison cycles that the RF/ IF synthesizer spends in the fastlock state. Refer to R2 Register and R5 Register for details on how to configure the FLoutRF or OSCout/ FLoutIF output to an open-drain fastlock output.
9.3.10 Counter Reset
When the RF_RST/ IF_RST bit is enabled, both the feedback divider (RF_N/ IF_N) and reference divider (RF_R/ IF_R) are held at their load point. When the device is programmed to normal operation, both the feedback divider and reference divider are enabled and resume counting in close alignment to each other. Refer to RF_RST - RF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R0[21]) and IF_RST - IF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R3[21]) for more details.
9.4 Device Functional Modes
9.4.1 Power Control
The LMX243x device can be asynchronously powered down when the EN pin is set LOW, independent of the state of the power-down bits.
NOTE
The OSCout/ FLoutIF pin can still be enabled if the ENosc pin is set HIGH, independent of the state of the EN pin. This capability allows the oscillator buffer to be used as a crystal oscillator.
When EN is set HIGH, power down is controlled through the MICROWIRE. The power-down word is comprised of the RF_PD/ IF_PD bit, in conjunction with the RF_CPT/ IF_CPT bit. The power-down control word is used to set the operating mode of the device. Refer to RF_CPT - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R0[20]), RF_PD - RF Synthesizer Power Down (R1[23]), IF_CPT - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R3[20]), and IF_PD - IF Synthesizer Power Down (R4[23]) for details on how to program the RF or IF power-down bits.
When either synthesizer is powered down, the respective prescaler, phase detector, and charge-pump circuit is disabled. The CPoutRF/ CPoutIF, FinRF/ FinIF, and FinRF* pins are all forced to a high impedance state. The reference divider and feedback divider circuits are held at the load point during power down. The oscillator buffer is disabled when the ENosc pin is set LOW. The OSCin pin is forced to a HIGH state through an approximate 100-kΩ resistance when this condition exists. When either synthesizer is activated, the respective prescaler, phase detector, charge-pump circuit, and the oscillator buffer are all powered up. The feedback divider and reference divider are held at their load point. This allows the reference oscillator, feedback divider, reference divider, and prescaler circuitry to reach proper bias levels. After a finite delay, the feedback and reference dividers are enabled and resume counting in close alignment (the maximum error is one prescaler cycle). The MICROWIRE control register remains active and capable of loading and latching data while in power-down mode.
9.4.1.1 Synchronous Power-Down Mode
In this mode, the power-down function is gated by the charge pump. When the device is configured for synchronous power down, the device enters the power-down mode upon completion of the next charge-pump pulse event.
9.4.1.2 Asynchronous Power-Down Mode
In the asynchronous power-down mode, the power-down function is NOT gated by the completion of a charge-pump pulse event. When the device is configured for asynchronous power down, the part goes into power-down mode immediately.
Table 7. Power-Down Modes
| EN PIN | RF_CPT / IF_CPT BIT | RF_PD / IF_PD BIT |
OPERATING MODE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | X(1) | X(1) | Asynchronous Power Down |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | PLL Active. Normal Operation |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | PLL Active. Charge-Pump Output in High-Impedance State |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Synchronous Power Down |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Asynchronous Power Down |
9.5 Programming
9.5.1 Microwire Interface
The 24-bit shift register is loaded through the MICROWIRE interface. The shift register consists of a 21-bit DATA[20:0] FIELD and a 3-bit ADDRESS[2:0] FIELD as shown in Table 8. The ADDRESS FIELD is used to decode the internal control register address. When LE transitions HIGH, DATA stored in the shift register is loaded into one of 6 control registers depending on the state of the ADDRESS bits. The MSB of DATA is loaded into the shift register first. The DATA FIELD assignments are shown in Control Register Content Map.
Table 8. Register Structure
| MSB | LSB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] | ADDRESS[2:0] | ||||
| 23 | 3 | 2 | 0 | ||
9.5.2 Control Register Location
The ADDRESS[2:0] bits decode the internal register address. The Table 9 shows how the ADDRESS bits are mapped into the target control register.
Table 9. Control Register Locations
| ADDRESS[2:0] | TARGET | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FIELD | REGISTER | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | R0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | R1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | R2 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | R3 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | R4 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | R5 |
9.6 Register Maps
9.6.1 Control Register Content Map
The control register content map describes how the bits within each control register are allocated to specific control functions. The bits that are marked 0 must be programmed as such to ensure proper device operation.
Table 10. Control Register Content Map
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R0 | MUX[3:2] | RF_ RST |
RF_ CPT |
RF_ CPG |
RF_ CPP |
RF_R[14:0] | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||
| R1 | RF_ PD |
RF_ P |
LMX2430/33 RF_B[14:0] |
LMX2430/33 RF_A[3:0] |
0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| R1 | RF_ PD |
RF_ P |
LMX2434 RF_B[13:0] |
LMX2434 RF_A[4:0] |
0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| R2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RF_TOC[11:0] | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||||||||
| R3 | MUX[1:0] | IF_ RST |
IF_ CPT |
IF_ CPG |
IF_ CPP |
IF_R[14:0] | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| R4 | IF_ PD |
IF_ P |
0 | IF_B[13:0] | IF_A[3:0] | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| R5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | IF_TOC[11:0] | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||
9.6.2 R0 Register
The R0 register contains the RF_R, RF_CPP, RF_CPG, RF_CPT, and RF_RST control words, in addition to two of the four bits that compose the MUX control word. The detailed descriptions and programming information for each control word is discussed in the following sections.
Table 11. R0 Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R0 | MUX[3:2] | RF_ RST |
RF_ CPT |
RF_ CPG |
RF_ CPP |
RF_R[14:0] | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||
9.6.2.1 RF_R[14:0] - RF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R0[17:3])
The RF reference divider (RF_R) can be programmed to support divide ratios from 3 to 32,767. Divide ratios less than 3 are prohibited.
Table 12. PLL R Divider
| DIVIDE RATIO | RF_R[14:0] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 32767 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.2.2 RF_CPP - RF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R0[18])
The RF_CPP bit is used to control the PFD polarity of the RF synthesizer based on the VCO tuning characteristics.
Table 13. Phase Detector Polarity
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_CPP | R0[18] | RF Phase and Frequency Detector Polarity | RF VCO Negative Tuning Characteristics | RF VCO Positive Tuning Characteristics |
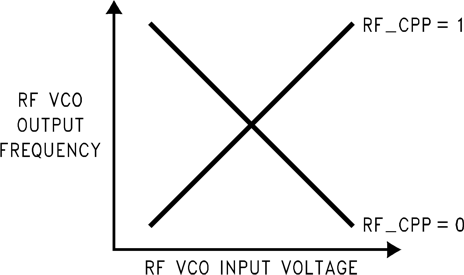 Figure 31. RF VCO Characteristics
Figure 31. RF VCO Characteristics
9.6.2.3 RF_CPG - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Current Gain (R0[19])
The RF_CPG bit controls the charge-pump gain of the RF synthesizer. Two gain levels are available.
Table 14. Charge-Pump Polarity
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_CPG | R0[19] | RF Charge-Pump Current Gain | LOW 1 mA |
HIGH 4 mA |
9.6.2.4 RF_CPT - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R0[20])
The RF_CPT bit allows the charge pump to be switched between a normal operating mode and a high-impedance output state. This happens asynchronously with the change in the RF_CPT bit.
Furthermore, the RF_CPT bit operates in conjuction with the RF_PD bit to set a synchronous or an asynchronous power-down mode. Refer to RF_PD - RF Synthesizer Power Down (R1[23]) for more details on how to program the RF_PD bit.
Table 15. Charge-Pump Tri-State
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_CPT | R0[20] | RF Charge-Pump tri-state | RF Charge Pump Normal Operation | RF Charge-Pump Output in High Impedance State |
9.6.2.5 RF_RST - RF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R0[21])
The RF_RST bit resets the RF_A, RF_B and RF_R counters. After removing the reset, the RF_A and RF_B counters resume counting in close alignment with the RF_R counter. The maximum error is one prescaler cycle.
Table 16. N Counter Reset
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_RST | R0[21] | RF Counter Reset | RF_A, RF_B and RF_R Normal Operation |
RF_A, RF_B and RF_R Reset |
9.6.3 R1 Register
The R1 register contains the RF_A, RF_B, RF_P, and RF_PD control words. The RF_A and RF_B control words are used to set up the programmable feedback divider. The detailed descriptions and programming information for each control word is discussed in the following sections.
Table 17. RI Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R1 | RF_ PD |
RF_ P |
LMX2430/33 RF_B[14:0] |
LMX2430/33 RF_A[3:0] |
0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| R1 | RF_ PD |
RF_ P |
LMX2434 RF_B[13:0] |
LMX2434 RF_A[4:0] |
0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
9.6.3.1 LMX243x RF Synthesizer Swallow Counter
9.6.3.1.1 RF_A[3:0] - LMX2430/33 RF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R1[6:3])
The RF_A control word is used to set up the A counter of the RF synthesizer. For both the LMX2430 and LMX2433, the A counter is a 4-bit swallow counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The RF_A control word can be programmed to values ranging from 0 to 15.
Table 18. RF_A Divider for LMX2430/33
| DIVIDE RATIO | LMX2430/33 RF_A[3:0] |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| • | • | • | • | • |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.3.1.2 RF_A[4:0] - LMX2434 RF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R1[7:3])
The LMX2434 A counter is a 5-bit swallow counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The RF_A control word can be programmed to values ranging from 0 to 31.
Table 19. RF A Divider for LMX2434
| DIVIDE RATIO | LMX2434 RF_A[4:0] |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 31 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.3.2 LMX243x RF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter
9.6.3.2.1 RF_B[14:0] - LMX2430/33 RF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R1[21:7])
The RF_B control word is used to set up the B counter of the RF synthesizer. For both the LMX2430 and LMX2433, the B counter is a 15-bit programmable binary counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The RF_B control word can be programmed to values ranging from 3 to 32,767. Divide ratios less than 3 are prohibited.
Table 20. RF B Divider for LMX2430/33
| DIVIDE RATIO | LMX2430/33 RF_B[14:0] |
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 32767 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.3.2.2 RF_B[13:0] - LMX2434 RF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R1[21:8])
The LMX2434 B counter is a 14-bit programmable binary counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The RF_B control word can be programmed to values ranging from 3 to 16,383. Divide ratios less than 3 are prohibited.
Table 21. RF B Divider for LMX2434
| DIVIDE RATIO | LMX2434 RF_B[13:0] |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 16383 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.3.3 LMX243x RF Synthesizer Prescaler Select
9.6.3.3.1 RF_P - LMX2430/33 RF Synthesizer Prescaler Select (R1[22])
Both the LMX2430 and LMX2433 RF synthesizers use a selectable dual-modulus prescaler. An 8/9 or a 16/17 prescale ratio can be selected.
Table 22. Prescaler Select Bit for LMX2430/33
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_P | R1[22] | LMX2430/33 RF Prescaler Select |
8/9 Prescaler Selected | 16/17 Prescaler Selected |
9.6.3.3.2 RF_P - LMX2434 RF Synthesizer Prescaler Select (R1[22])
The LMX2434 RF synthesizer uses a selectable dual-modulus prescaler. A 16/17 or a 32/33 prescale ratio can be selected.
Table 23. Prescaler Select Bit for LMX2434
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_P | R1[22] | LMX2434 RF Prescaler Select |
16/17 Prescaler Selected | 32/33 Prescaler Selected |
9.6.3.4 RF_PD - RF Synthesizer Power Down (R1[23])
The RF_PD bit is used to switch the RF PLL between a powered-up and powered-down mode.
Furthermore, the RF_PD bit operates in conjunction with the RF_CPT bit to set a synchronous or an asynchronous power-down mode. Refer to RF_CPT - RF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R0[20]) for more details on how to program the RF_CPT bit.
Table 24. Power Down Bit
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| RF_PD | R1[23] | RF Power down | RF PLL Active | RF PLL Power down |
9.6.4 R2 Register
The R2 Register contains the RF_TOC control word. The RF_TOC is used to set up the fastlock circuitry of the RF synthesizer. The RF_TOC is a 12-bit binary counter programmable from 0 to 4095.
Table 25. R2 Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | RF_TOC[11:0] | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||||||||||
9.6.4.1 RF_TOC[0:11] - RF Synthesizer Time-Out Counter (R2[14:3])
The FLoutRF pin can be configured as a general-purpose CMOS tri-state output or as a fastlock output by programming the RF_TOC appropriately. When the RF_TOC is programmed from 0 to 3, automatic fastlock is disabled, and the FLoutRF pin is either configured as a general-purpose CMOS tri-state output or manual fastlock is enabled. When the RF_TOC is programmed to 0, the FLoutRF pin is in tri-state (high impedance) mode. The charge-pump current is then the value specified by RF_CPG (R0[19]). When the RF_TOC is programmed to 1, the FLoutRF pin is pulled to a LOW state. The charge-pump current is then set to a HIGH gain state (RF_CPG bit = 1). This condition is known as the manual fastlock. When the RF_TOC is programmed to 2, the FLout_RF pin is again pulled to a LOW state, but this time the charge-pump current is the value specified by RF_CPG (R0[19]). When the RF_TOC is programmed to 3, the FLoutRF pin is pulled to a HIGH state. Again, the charge-pump current is the value specified by RF_CPG (R0[19]). When the RF_TOC is programmed from 4 to 4095, fastlock is enabled, and the FLoutRF pin is pulled to a LOW state. Fastlock time outs after the specified number of PFD events. At this time, the FLoutRF pin switches to tri-state (high impedance) mode. The value programmed into RF_TOC represents the number of PFD events that the RF synthesizer spends in the fastlock state.
NOTE
Any write to the RF_TOC requires a PFD event on the RF synthesizer to latch the contents. This means that writes to the RF_TOC take effect synchronously with the next PFD event.
Table 26. Fastlock Time-Out Counter
| RF_TOC[11:0] | FASTLOCK MODE | FASTLOCK PERIOD [PFD EVENTS] |
FLoutRF PIN FUNCTIONALITY / STATE | ICPoutRF MAGNITUDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. High Impedance State |
ICPoutRF magnitude controlled by R0[19] |
| 1 | Enabled Manual Fastlock |
N/A | General-Purpose. Logic LOW State |
ICPoutRF = 4 mA |
| 2 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. Logic LOW State |
ICPoutRF magnitude controlled by R0[19] |
| 3 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. Logic HIGH State |
ICPoutRF magnitude controlled by R0[19] |
| 4 | Enabled Automatic Fastlock |
4 | FastLock. Logic LOW State. Switches to High Impedance after 4 PFD events |
ICPoutRF = 4 mA Switches to 1 mA after 4 PFD events |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 4095 | Enabled Automatic Fastlock |
4095 | FastLock. Logic LOW State. Switches to High Impedance after 4095 PFD events |
ICPoutRF = 4 mA Switches to 1 mA after 4095 PFD events |
9.6.4.2 R3 Register
The R3 register contains the IF_R, IF_CPP, IF_CPG, IF_CPT, and IF_RST control words, in addition to two of the four bits that compose the MUX control word. The detailed descriptions and programming information for each control word is discussed in the following sections.
Table 27. R3 Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R3 | MUX[1:0] | IF_ RST |
IF_ CPT |
IF_ CPG |
IF_ CPP |
IF_R[14:0] | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
9.6.4.2.1 IF_R[14:0] - IF Synthesizer Programmable Reference Divider (R Counter) (R3[17:3])
The IF reference divider (IF_R) can be programmed to support divide ratios from 3 to 32,767. Divide ratios less than 3 are prohibited.
Table 28. IF R Divider
| DIVIDE RATIO | IF_R[14:0] | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 32767 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.4.2.2 IF_CPP - IF Synthesizer Phase Detector Polarity (R3[18])
The IF_CPP bit is used to control the PFD polarity of the IF synthesizer based on the VCO tuning characteristics.
Table 29. IF PLL Charge-Pump Polarity
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_CPP | R3[18] | IF PFD Polarity | IF VCO Negative Tuning Characteristics | IF VCO Positive Tuning Characteristics |
 Figure 32. IF VCO Characteristics
Figure 32. IF VCO Characteristics
9.6.4.2.3 IF_CPG - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Current Gain (R3[19])
The IF_CPG bit controls the charge-pump gain of the IF synthesizer. Two gain levels are available.
Table 30. IF PLL Phase Detector Polarity Bit
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_CPG | R3[19] | IF Charge-Pump Current Gain | LOW 1 mA |
HIGH 4 mA |
9.6.4.2.4 IF_CPT - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R3[20])
The IF_CPT bit allows the charge pump to be switched between a normal operating mode and a high impedance output state. This happens asynchronously with the change in the IF_CPT bit.
Furthermore, the IF_CPT bit operates in conjuction with the IF_PD bit to set a synchronous or an asynchronous power-down mode. Refer to IF_PD - IF Synthesizer Power Down (R4[23]) for more details on how to program the IF_PD bit.
Table 31. IF PLL Charge-Pump Polarity Bit
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_CPT | R3[20] | IF Charge-Pump Tri-State | IF Charge Pump Normal Operation | IF Charge-Pump Output in High Impedance State |
9.6.4.2.5 IF_RST - IF Synthesizer Counter Reset (R3[21])
The IF_RST bit resets of the IF_A, IF_B and IF_R counters. After removing the reset, the IF_A and IF_B counters resume counting in close alignment with the IF_R counter. The maximum error is one prescaler cycle.
Table 32. IF PLL Counter Reset
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_RST | R3[21] | IF Counter Reset | IF_A, IF_B and IF_R Normal Operation |
IF_A, IF_B and IF_R Reset |
9.6.5 R4 Register
The R4 register contains the IF_A, IF_B, IF_P, and IF_PD control words. The IF_A and IF_B control words are used to set up the programmable feedback divider. The detailed descriptions and programming information for each control word is discussed in the following sections. R4[21] is always set to 0.
Table 33. R4 Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R4 | IF_ PD |
IF_ P |
0 | IF_B[13:0] | IF_A[3:0] | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||
9.6.5.1 IF_A[3:0] - IF Synthesizer Swallow Counter (A Counter) (R4[6:3])
The IF_A control word is used to set up the A counter of the IF synthesizer. The A counter is a 4-bit swallow counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The IF_A control word can be programmed to values ranging from 0 to 15.
Table 34. IF A counter Bit
| DIVIDE RATIO | IF_A[3:0] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| • | • | • | • | • |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.5.2 IF_B[13:0] - IF Synthesizer Programmable Binary Counter (B Counter) (R4[20:7])
The IF_B control word is used to set up the B counter of the IF synthesizer. The B counter is a 14-bit programmable binary counter used in the programmable feedback divider. The IF_B control word can be programmed to values ranging from 3 to 16,383. Divide ratios less than 3 are prohibited.
Table 35. IF B Counter
| DIVIDE RATIO | IF_B[13:0] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • | • |
| 16383 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
9.6.5.2.1 IF_P - IF Synthesizer Prescaler Select (R4[22])
The LMX243x IF synthesizer uses a selectable dual modulus prescaler. An 8/9 or a 16/17 prescale ratio can be selected.
Table 36. IF Prescaler Select Bit
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_P | R4[22] | IF Prescaler Select | 8/9 Prescaler Selected | 16/17 Prescaler Selected |
9.6.5.3 IF_PD - IF Synthesizer Power Down (R4[23])
The IF_PD bit is used to switch the IF PLL between a powered-up and powered-down mode.
Furthermore, the IF_PD bit operates in conjuction with the IF_CPT bit to set a synchronous or an asynchronous power-down mode. Refer to IF_CPT - IF Synthesizer Charge-Pump Tri-State (R3[20]) for more details on how to program the IF_CPT bit.
Table 37. IF PLL Powerdown Bit
| CONTROL BIT | REGISTER LOCATION | DESCRIPTION | FUNCTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |||
| IF_PD | R4[23] | IF Power down | IF PLL Active | IF PLL Power down |
9.6.6 R5 Register
The R5 Register contains the IF_TOC control word. The IF_TOC is used to set up the fastlock circuitry of the IF synthesizer. The IF_TOC is a 12-bit binary counter programmable from 0 to 4095.
Table 38. R5 Register
| REG | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA[20:0] FIELD | ADDRESS [2:0] FIELD |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| R5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | IF_TOC[11:0] | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||
9.6.6.1 IF_TOC[0:11] - IF Synthesizer Time-Out Counter (R5[14:3])
The OSCout/ FLoutIF pin can be configured as a general-purpose CMOS tri-state output or as a fastlock output by programming the IF_TOC appropriately. When the IF_TOC is programmed from 0 to 3, automatic fastlock is disabled, and the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin is configured as a general-purpose CMOS tri-state output or manual fastlock is enabled. When the IF_TOC is programmed to 0, the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin is in tri-state (high impedance) mode. The charge-pump current is then the value specified by IF_CPG (R3[19]). When the IF_TOC is programmed to 1, the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin is pulled to a LOW state. The charge-pump current is then set to a HIGH gain state (IF_CPG bit = 1). This condition is known as the manual fastlock. When the IF_TOC is programmed to 2, the OSCout/ FLout_IF pin is again pulled to a LOW state, but this time the charge-pump current is the value specified by IF_CPG (R3[19]). When the IF_TOC is programmed to 3, the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin is pulled to a HIGH state. Again, the charge-pump current is the value specified by IF_CPG (R3[19]). When the IF_TOC is programmed from 4 to 4095, fastlock is enabled, and the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin is pulled to a LOW state. Fastlock timeouts after the specified number of PFD events. At this time, the OSCout/ FLoutIF pin switches to tri-state (high impedance) mode. The value programmed into IF_TOC represents the number of PFD events that the IF synthesizer spends in the fastlock state.
NOTE
Any write to the IF_TOC requires a PFD event on the IF synthesizer to latch the contents. This means that writes to the IF_TOC take effect synchronously with the next PFD event.
Table 39. IF PLL Fastlock Time-Out Counter
| IF_TOC[11:0] | FASTLOCK MODE | FASTLOCK PERIOD [PFD Events] |
OSCout/ FLoutIF PIN FUNCTIONALITY / STATE | ICPoutIF MAGNITUDE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. High Impedance State |
ICPoutIF magnitude controlled by R3[19] |
| 1 | Enabled Manual Fastlock |
N/A | General-Purpose. Logic LOW State |
ICPoutIF = 4 mA |
| 2 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. Logic LOW State |
ICPoutIF magnitude controlled by R3[19] |
| 3 | Disabled | N/A | General-Purpose. Logic HIGH State |
ICPoutIF magnitude controlled by R3[19] |
| 4 | Enabled Automatic Fastlock |
4 | FastLock. Logic LOW State. Switches to High Impedance after 4 PFD events |
ICPoutIF = 4 mA Switches to 1 mA after 4 PFD events |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 4095 | Enabled Automatic Fastlock |
4095 | FastLock. Logic LOW State. Switches to High Impedance after 4095 PFD events |
ICPoutIF = 4 mA Switches to 1 mA after 4095 PFD events |
9.6.7 MUX[3:0] - Multifunction Output Select (R3[23:22]:R0[23:22])
The MUX control word is used to determine which signal is routed to the Ftest/LD pin.
Table 40. Multifunction Output Select(1)
| MUX[3:0] | MUX OUTPUT STATE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | High Impedance (Tri-state) State Output |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Logic HIGH State Output |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Logic LOW State Output |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | RF PLL and IF PLL Digital Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | RF PLL Digital Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | IF PLL Digital Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | RF PLL and IF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | RF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | IF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Open-Drain Output |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | RF PLL and IF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Push-Pull Output |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | RF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Push-Pull Output |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | IF PLL Analog Lock Detect. Push-Pull Output |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | IF_R/ 2 Frequency |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | IF_N/ 2 Frequency |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | RF_R/ 2 Frequency |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | RF_N/ 2 Frequency |
2. IF_N = (IF_B × IF_P) + IF_A