ZHCSHO0C February 2018 – March 2023 LMZM23600
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.4 Current Limit
The LMZM23600 devices features two current limits inside the IC. A coarse high side or peak current limit is provided to protect against faults. The high-side current limit limits the duration of the on-period of the high-side power MOSFET during a given clock cycle. A precision cycle-by-cycle valley current limit prevents excessive average output current. A new switching cycle is not initiated until the inductor current drops below the valley current limit.
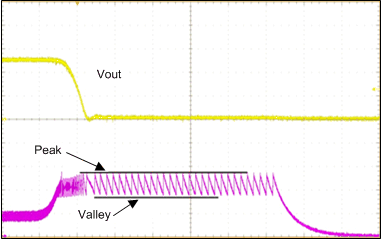 Figure 8-1 Current Limit Operation During Output Short Circuit
Figure 8-1 Current Limit Operation During Output Short CircuitFigure 8-1 shows the response of the LMZM23600 device to a short circuit on the output: The peak current limit prevents excessive peak current while the valley current limit prevents excessive average inductor current. After a small number of cycles, hiccup mode is activated.