SNOSA40K November 2002 – December 2016 LP2996-N , LP2996A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DDA|8
订购信息
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVIN to GND | −0.3 | 6 | V | |
| PVIN to GND | –0.3 | AVIN | V | |
| Input voltage (VDDQ)(3) | −0.3 | 6 | V | |
| Junction temperature, TJ | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
(3) VDDQ voltage must be less than 2 × (AVIN – 1) or 6 V, whichever is smaller.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±1000 | V |
(1) The human body model is a 100-pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5-kΩ resistor into each pin.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVIN to GND | 2.2 | 5.5 | V | |
| PVIN supply voltage | 0 | AVIN | V | |
| SD input voltage | 0 | AVIN | V | |
| TJ | Junction temperature(1) | 0 | 125 | °C |
(1) At elevated temperatures, devices must be derated based on thermal resistance.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC | LP2996-N, LP2996A | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DDA (SO) | NHP (WQFN) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 119.5 | 56.5 | 52.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 65.3 | 65.1 | 50.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 59.8 | 36.5 | 30.1 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 16.7 | 15.9 | 0.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 59.3 | 36.5 | 30.2 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | — | 8.4 | 9.8 | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
Minimum and maximum limits apply over the full operating temperature range (TJ = 0°C to 125°C) and are specified through test, design, or statistical correlation. Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm (TJ = 25°C), and are provided for reference purposes only. Unless otherwise specified, AVIN = PVIN = 2.5 V and VDDQ = 2.5 V.(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VREF | VREF voltage (DDR I) | VDD = VDDQ = 2.3 V | 1.135 | 1.158 | 1.185 | V | |
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.5 V | 1.235 | 1.258 | 1.285 | ||||
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.7 V | 1.335 | 1.358 | 1.385 | ||||
| VREF voltage (DDR II) | PVIN = VDDQ = 1.7 V | 0.837 | 0.86 | 0.887 | V | ||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.8 V | 0.887 | 0.91 | 0.937 | ||||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.9 V | 0.936 | 0.959 | 0.986 | ||||
| VREF voltage (DDR III) | PVIN = VDDQ = 1.35 V | 0.669 | 0.684 | 0.699 | V | ||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.5 V | 0.743 | 0.758 | 0.773 | ||||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.6 V | 0.793 | 0.808 | 0.823 | ||||
| ZVREF | VREF output impedance | IREF = –30 to 30 µA | 2.5 | kΩ | |||
| VTT | VTT output voltage (DDR I)(2) | IOUT = 0 A | VDD = VDDQ = 2.3 V | 1.12 | 1.159 | 1.19 | V |
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.5 V | 1.21 | 1.259 | 1.29 | ||||
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.7 V | 1.32 | 1.359 | 1.39 | ||||
| IOUT = ±1.5 A | VDD = VDDQ = 2.3 V | 1.125 | 1.159 | 1.19 | |||
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.5 V | 1.225 | 1.259 | 1.29 | ||||
| VDD = VDDQ = 2.7 V | 1.325 | 1.359 | 1.39 | ||||
| VTT output voltage (DDR II)(2) | IOUT = 0 A, AVIN = 2.5 V | PVIN = VDDQ = 1.7 V | 0.822 | 0.856 | 0.887 | V | |
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.8 V | 0.874 | 0.908 | 0.939 | ||||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.9 V | 0.923 | 0.957 | 0.988 | ||||
| IOUT = ±0.5 A, AVIN = 2.5 V | PVIN = VDDQ = 1.7 V | 0.82 | 0.856 | 0.89 | |||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.8 V | 0.87 | 0.908 | 0.94 | ||||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.9 V | 0.92 | 0.957 | 0.99 | ||||
| VTT output voltage (DDR III)(2) | IOUT = 0 A, AVIN = 2.5 V | PVIN = VDDQ = 1.35 V | 0.656 | 0.677 | 0.698 | V | |
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.5 V | 0.731 | 0.752 | 0.773 | ||||
| PVIN = VDDQ = 1.6 V | 0.781 | 0.802 | 0.823 | ||||
| IOUT = 0.2 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.35 V | 0.667 | 0.688 | 0.71 | ||||
| IOUT = –0.2 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.35 V | 0.641 | 0.673 | 0.694 | ||||
| IOUT = 0.4 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.5 V | 0.74 | 0.763 | 0.786 | ||||
| IOUT = –0.4 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.5 V | 0.731 | 0.752 | 0.773 | ||||
| IOUT = 0.5 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.6 V | 0.79 | 0.813 | 0.836 | ||||
| IOUT = –0.5 A, AVIN = 2.5 V, PVIN = VDDQ = 1.6 V | 0.781 | 0.802 | 0.823 | ||||
| VOSVtt | VTT output voltage offset (VREF – VTT) for DDR I(2) |
IOUT = 0 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | mV | |
| IOUT = –1.5 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| IOUT = 1.5 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| VTT output voltage offset (VREF – VTT) for DDR II(2) |
IOUT = 0 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | mV | ||
| IOUT = –0.5 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| IOUT = 0.5 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| VTT output voltage offset (VREF – VTT) for DDR III(2) |
IOUT = 0 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | mV | ||
| IOUT = ±0.2 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| IOUT = ±0.4 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| IOUT = ±0.5 A | –30 | 0 | 30 | ||||
| IQ | Quiescent current(3) | IOUT = 0 A | 320 | 500 | µA | ||
| ZVDDQ | VDDQ input impedance | 100 | kΩ | ||||
| ISD | Quiescent current in shutdown(3) | SD is low | 115 | 150 | µA | ||
| IQ_SD | Shutdown leakage current | SD is low | 2 | 5 | µA | ||
| VIH | Minimum shutdown, high level | 1.9 | V | ||||
| VIL | Maximum shutdown, low level | 0.8 | V | ||||
| IV | VTT leakage current in shutdown | SD is low, VTT = 1.25 V | 1 | 10 | µA | ||
| ISENSE | VSENSE input current | 13 | nA | ||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown | 165 | °C | ||||
| TSD_HYS | Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 10 | °C | ||||
(1) VDD is defined as VDD = AVIN = PVIN.
(2) VTT load regulation is tested by using a 10-ms current pulse and measuring VTT.
(3) Quiescent current defined as the current flow into AVIN.
6.6 Typical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, AVIN = PVIN = 2.5 V.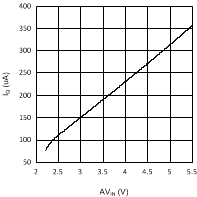 Figure 1. IQ vs AVIN In Shutdown
Figure 1. IQ vs AVIN In Shutdown
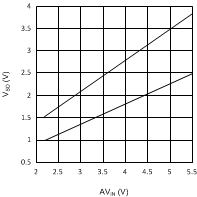 Figure 3. VIH and VIL
Figure 3. VIH and VIL
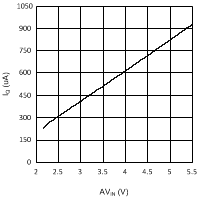 Figure 2. IQ vs AVIN
Figure 2. IQ vs AVIN
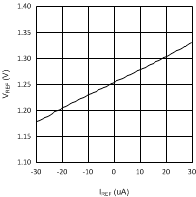 Figure 4. VREF vs IREF
Figure 4. VREF vs IREF
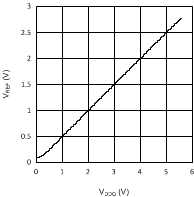 Figure 5. VREF vs VDDQ
Figure 5. VREF vs VDDQ
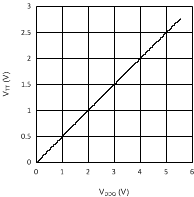 Figure 7. VTT vs VDDQ
Figure 7. VTT vs VDDQ
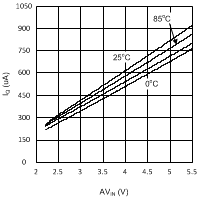 Figure 9. IQ vs AVIN Temperature
Figure 9. IQ vs AVIN Temperature
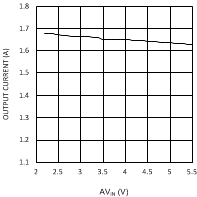
| VDDQ = 2.5 V | PVIN = 2.5 V |
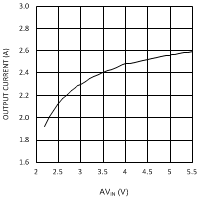
| VDDQ = 2.5 V |
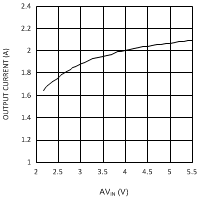
| VDDQ = 1.8 V |
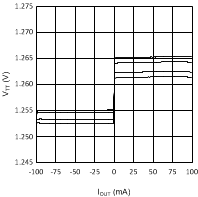 Figure 6. VTT vs IOUT
Figure 6. VTT vs IOUT
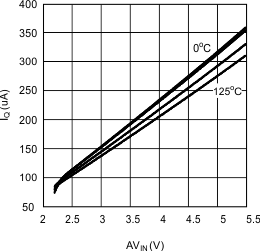 Figure 8. IQ vs AVIN in Shutdown Temperature
Figure 8. IQ vs AVIN in Shutdown Temperature
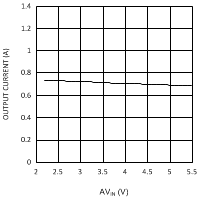
| VDDQ = 2.5 V | PVIN = 1.8 V |
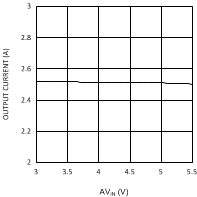
| VDDQ = 2.5 V | PVIN = 3.3 V |
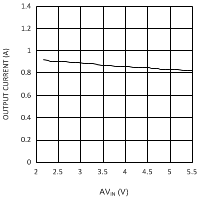
| VDDQ = 1.8 V | PVIN = 1.8 V |
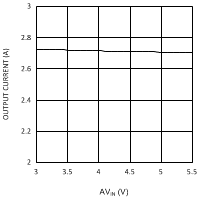
| VDDQ = 1.8 V | PVIN = 3.3 V |