SNVSB23 March 2018 LP87521-Q1 , LP87522-Q1 , LP87523-Q1 , LP87524-Q1 , LP87525-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Descriptions
- 8.3.1 Multi-Phase DC/DC Converters
- 8.3.2 Sync Clock Functionality
- 8.3.3 Power-Up
- 8.3.4 Regulator Control
- 8.3.5 Enable and Disable Sequences
- 8.3.6 Device Reset Scenarios
- 8.3.7 Diagnosis and Protection Features
- 8.3.8 GPIO Signal Operation
- 8.3.9 Digital Signal Filtering
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 OTP_REV
- 8.6.1.2 BUCK0_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.3 BUCK1_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.4 BUCK2_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.5 BUCK3_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.6 BUCK0_VOUT
- 8.6.1.7 BUCK0_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.8 BUCK1_VOUT
- 8.6.1.9 BUCK1_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.10 BUCK2_VOUT
- 8.6.1.11 BUCK2_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.12 BUCK3_VOUT
- 8.6.1.13 BUCK3_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.14 BUCK0_DELAY
- 8.6.1.15 BUCK1_DELAY
- 8.6.1.16 BUCK2_DELAY
- 8.6.1.17 BUCK3_DELAY
- 8.6.1.18 GPIO2_DELAY
- 8.6.1.19 GPIO3_DELAY
- 8.6.1.20 RESET
- 8.6.1.21 CONFIG
- 8.6.1.22 INT_TOP1
- 8.6.1.23 INT_TOP2
- 8.6.1.24 INT_BUCK_0_1
- 8.6.1.25 INT_BUCK_2_3
- 8.6.1.26 TOP_STAT
- 8.6.1.27 BUCK_0_1_STAT
- 8.6.1.28 BUCK_2_3_STAT
- 8.6.1.29 TOP_MASK1
- 8.6.1.30 TOP_MASK2
- 8.6.1.31 BUCK_0_1_MASK
- 8.6.1.32 BUCK_2_3_MASK
- 8.6.1.33 SEL_I_LOAD
- 8.6.1.34 I_LOAD_2
- 8.6.1.35 I_LOAD_1
- 8.6.1.36 PGOOD_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.37 PGOOD_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.38 PGOOD_FLT
- 8.6.1.39 PLL_CTRL
- 8.6.1.40 PIN_FUNCTION
- 8.6.1.41 GPIO_CONFIG
- 8.6.1.42 GPIO_IN
- 8.6.1.43 GPIO_OUT
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.6 I2C Serial Bus Timing Requirements
These specifications are ensured by design. VIN_Bx = 3.7 V, unless otherwise noted.| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ƒSCL | Serial clock frequency | Standard mode | 100 | kHz | |
| Fast mode | 400 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 1 | MHz | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 3.4 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 1.7 | ||||
| tLOW | SCL low time | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 1.3 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.5 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 160 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 320 | ||||
| tHIGH | SCL high time | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 0.6 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.26 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 60 | ns | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 120 | ||||
| tSU;DAT | Data setup time | Standard mode | 250 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 100 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 50 | ||||
| High-speed mode | 10 | ||||
| tHD;DAT | Data hold time | Standard mode | 10 | 3450 | ns |
| Fast mode | 10 | 900 | |||
| Fast mode+ | 10 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 70 | ns | ||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 10 | 150 | |||
| tSU;STA | Setup time for a start or a repeated start condition | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 0.6 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.26 | ||||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ns | |||
| tHD;STA | Hold time for a start or a repeated start condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 0.6 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.26 | ||||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ns | |||
| tBUF | Bus free time between a stop and start condition | Standard mode | 4.7 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 1.3 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.5 | ||||
| tSU;STO | Setup time for a stop condition | Standard mode | 4 | µs | |
| Fast mode | 0.6 | ||||
| Fast mode+ | 0.26 | ||||
| High-speed mode | 160 | ns | |||
| trDA | Rise time of SDA signal | Standard mode | 1000 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 20 | 300 | |||
| Fast mode+ | 120 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 80 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 20 | 160 | |||
| tfDA | Fall time of SDA signal | Standard mode | 300 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 20 × (VDD / 5.5 V) | 300 | |||
| Fast mode+ | 20 × (VDD / 5.5 V) | 120 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 80 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 30 | 160 | |||
| trCL | Rise time of SCL signal | Standard mode | 1000 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 20 | 300 | |||
| Fast mode+ | 120 | ||||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 40 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 20 | 80 | |||
| trCL1 | Rise time of SCL signal after a repeated start condition and after an acknowledge bit | High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 80 | ns |
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 20 | 160 | |||
| tfCL | Fall time of a SCL signal | Standard mode | 300 | ns | |
| Fast mode | 20 × (VDD / 5.5 V) | 300 | |||
| Fast mode+ | 20 × (VDD / 5.5 V) | 120 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 100 pF | 10 | 40 | |||
| High-speed mode, Cb = 400 pF | 20 | 80 | |||
| Cb | Capacitive load for each bus line (SCL and SDA) | 400 | pF | ||
| tSP | Pulse width of spike suppressed (SCL and SDA spikes that are less than the indicated width are suppressed) | Standard mode, fast mode and fast mode+ | 50 | ns | |
| High-speed mode | 10 | ||||
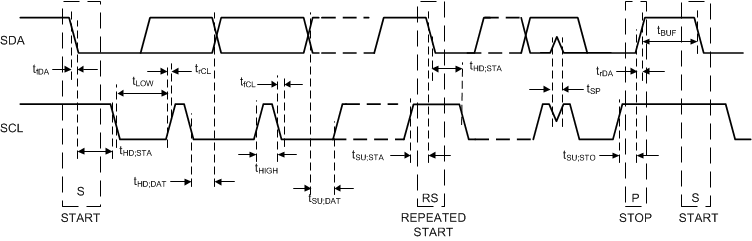 Figure 1. I2C Timing
Figure 1. I2C Timing