ZHCSH29B April 2017 – December 2018 LP87524B-Q1 , LP87524J-Q1 , LP87524P-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Descriptions
- 7.3.1 DC-DC Converters
- 7.3.2 Sync Clock Functionality
- 7.3.3 Power-Up
- 7.3.4 Regulator Control
- 7.3.5 Enable and Disable Sequences
- 7.3.6 Device Reset Scenarios
- 7.3.7 Diagnosis and Protection Features
- 7.3.8 GPIO Signal Operation
- 7.3.9 Digital Signal Filtering
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.1.1 OTP_REV
- 7.6.1.2 BUCK0_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.3 BUCK1_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.4 BUCK2_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.5 BUCK3_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.6 BUCK0_VOUT
- 7.6.1.7 BUCK0_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.8 BUCK1_VOUT
- 7.6.1.9 BUCK1_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.10 BUCK2_VOUT
- 7.6.1.11 BUCK2_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.12 BUCK3_VOUT
- 7.6.1.13 BUCK3_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.14 BUCK0_DELAY
- 7.6.1.15 BUCK1_DELAY
- 7.6.1.16 BUCK2_DELAY
- 7.6.1.17 BUCK3_DELAY
- 7.6.1.18 GPIO2_DELAY
- 7.6.1.19 GPIO3_DELAY
- 7.6.1.20 RESET
- 7.6.1.21 CONFIG
- 7.6.1.22 INT_TOP1
- 7.6.1.23 INT_TOP2
- 7.6.1.24 INT_BUCK_0_1
- 7.6.1.25 INT_BUCK_2_3
- 7.6.1.26 TOP_STAT
- 7.6.1.27 BUCK_0_1_STAT
- 7.6.1.28 BUCK_2_3_STAT
- 7.6.1.29 TOP_MASK1
- 7.6.1.30 TOP_MASK2
- 7.6.1.31 BUCK_0_1_MASK
- 7.6.1.32 BUCK_2_3_MASK
- 7.6.1.33 SEL_I_LOAD
- 7.6.1.34 I_LOAD_2
- 7.6.1.35 I_LOAD_1
- 7.6.1.36 PGOOD_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.37 PGOOD_CTRL2
- 7.6.1.38 PGOOD_FLT
- 7.6.1.39 PLL_CTRL
- 7.6.1.40 PIN_FUNCTION
- 7.6.1.41 GPIO_CONFIG
- 7.6.1.42 GPIO_IN
- 7.6.1.43 GPIO_OUT
- 7.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.5.1.2 Start and Stop Conditions
The LP87524B/J/P-Q1 is controlled via an I2C-compatible interface. START and STOP conditions classify the beginning and end of the I2C session. A START condition is defined as SDA transitions from HIGH to LOW while SCL is HIGH. A STOP condition is defined as SDA transition from LOW to HIGH while SCL is HIGH. The I2C master always generates the START and STOP conditions.
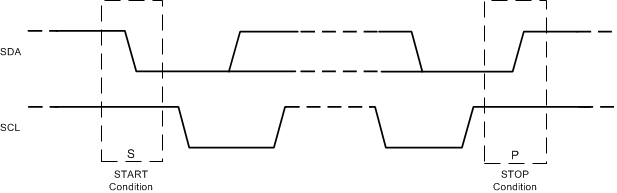 Figure 17. Start and Stop Sequences
Figure 17. Start and Stop Sequences The I2C bus is considered busy after a START condition and free after a STOP condition. During data transmission the I2C master can generate repeated START conditions. A START and a repeated START condition are equivalent function-wise. The data on SDA must be stable during the HIGH period of the clock signal (SCL). In other words, the state of SDA can only be changed when SCL is LOW. Figure 18 shows the SDA and SCL signal timing for the I2C-compatible bus. See the Figure 1 for timing values.
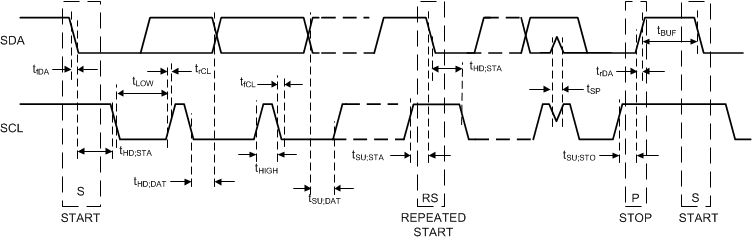 Figure 18. I2C-Compatible Timing
Figure 18. I2C-Compatible Timing