ZHCSHY8 March 2018 LP87561-Q1 , LP87562-Q1 , LP87563-Q1 , LP87564-Q1 , LP87565-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Descriptions
- 8.3.1 Multi-Phase DC/DC Converters
- 8.3.2 Sync Clock Functionality
- 8.3.3 Power-Up
- 8.3.4 Regulator Control
- 8.3.5 Enable and Disable Sequences
- 8.3.6 Device Reset Scenarios
- 8.3.7 Diagnosis and Protection Features
- 8.3.8 GPIO Signal Operation
- 8.3.9 Digital Signal Filtering
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 OTP_REV
- 8.6.1.2 BUCK0_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.3 BUCK0_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.4 BUCK1_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.5 BUCK1_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.6 BUCK2_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.7 BUCK2_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.8 BUCK3_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.9 BUCK3_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.10 BUCK0_VOUT
- 8.6.1.11 BUCK0_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.12 BUCK1_VOUT
- 8.6.1.13 BUCK1_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.14 BUCK2_VOUT
- 8.6.1.15 BUCK2_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.16 BUCK3_VOUT
- 8.6.1.17 BUCK3_FLOOR_VOUT
- 8.6.1.18 BUCK0_DELAY
- 8.6.1.19 BUCK1_DELAY
- 8.6.1.20 BUCK2_DELAY
- 8.6.1.21 BUCK3_DELAY
- 8.6.1.22 GPIO2_DELAY
- 8.6.1.23 GPIO3_DELAY
- 8.6.1.24 RESET
- 8.6.1.25 CONFIG
- 8.6.1.26 INT_TOP1
- 8.6.1.27 INT_TOP2
- 8.6.1.28 INT_BUCK_0_1
- 8.6.1.29 INT_BUCK_2_3
- 8.6.1.30 TOP_STAT
- 8.6.1.31 BUCK_0_1_STAT
- 8.6.1.32 BUCK_2_3_STAT
- 8.6.1.33 TOP_MASK1
- 8.6.1.34 TOP_MASK2
- 8.6.1.35 BUCK_0_1_MASK
- 8.6.1.36 BUCK_2_3_MASK
- 8.6.1.37 SEL_I_LOAD
- 8.6.1.38 I_LOAD_2
- 8.6.1.39 I_LOAD_1
- 8.6.1.40 PGOOD_CTRL1
- 8.6.1.41 PGOOD_CTRL2
- 8.6.1.42 PGOOD_FLT
- 8.6.1.43 PLL_CTRL
- 8.6.1.44 PIN_FUNCTION
- 8.6.1.45 GPIO_CONFIG
- 8.6.1.46 GPIO_IN
- 8.6.1.47 GPIO_OUT
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13"机械、封装和可订购信息
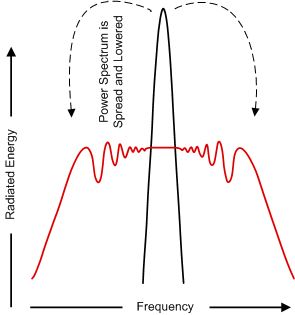
8.3.1.6 Spread-Spectrum Mode
Systems with periodic switching signals may generate a large amount of switching noise in a set of narrowband frequencies (the switching frequency and its harmonics). The usual solution to decrease noise coupling is to add EMI filters and shields to the boards. The LP8756x-Q1 device has register-selectable spread-spectrum mode which minimizes the need for output filters, ferrite beads, or chokes. In spread-spectrum mode, the switching frequency varies around the center frequency, reducing the EMI emissions radiated by the converter and associated passive components and PCB traces (see Figure 12). This feature is available only when internal RC oscillator is used (PLL_MODE[1:0] = 00 in PLL_CTRL register), and it is enabled with the EN_SPREAD_SPEC bit (PIN_FUNCTION register), and it affects all the buck cores.