SNVSBP2 February 2020 LP8758-E3
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.1.1 OTP_REV
- 7.6.1.2 BUCK0_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.3 BUCK0_CTRL2
- 7.6.1.4 BUCK1_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.5 BUCK1_CTRL2
- 7.6.1.6 BUCK2_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.7 BUCK2_CTRL2
- 7.6.1.8 BUCK3_CTRL1
- 7.6.1.9 BUCK3_CTRL2
- 7.6.1.10 BUCK0_VOUT
- 7.6.1.11 BUCK0_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.12 BUCK1_VOUT
- 7.6.1.13 BUCK1_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.14 BUCK2_VOUT
- 7.6.1.15 BUCK2_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.16 BUCK3_VOUT
- 7.6.1.17 BUCK3_FLOOR_VOUT
- 7.6.1.18 BUCK0_DELAY
- 7.6.1.19 BUCK1_DELAY
- 7.6.1.20 BUCK2_DELAY
- 7.6.1.21 BUCK3_DELAY
- 7.6.1.22 RESET
- 7.6.1.23 CONFIG
- 7.6.1.24 INT_TOP
- 7.6.1.25 INT_BUCK_0_1
- 7.6.1.26 INT_BUCK_2_3
- 7.6.1.27 TOP_STAT
- 7.6.1.28 BUCK_0_1_STAT
- 7.6.1.29 BUCK_2_3_STAT
- 7.6.1.30 TOP_MASK
- 7.6.1.31 BUCK_0_1_MASK
- 7.6.1.32 BUCK_2_3_MASK
- 7.6.1.33 SEL_I_LOAD
- 7.6.1.34 I_LOAD_2
- 7.6.1.35 I_LOAD_1
- 7.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3 Application Curves
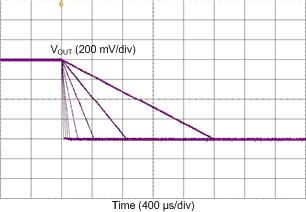
Measurements are done using typical application set up with connections shown in Figure 19. Graphs may not reflect the OTP default settings. Unless otherwise specified: VIN = 3.7 V, V(NRST) = 1.8 V, TA = 25 °C, ƒSW = 3 MHz, L = 470 nH (TDK VLS252010HBX-R47M), ILIM FWD set to maximum 5 A.
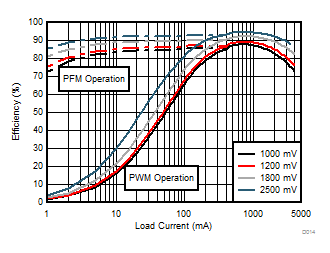
| VIN = 3.7 V | ||
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | ||
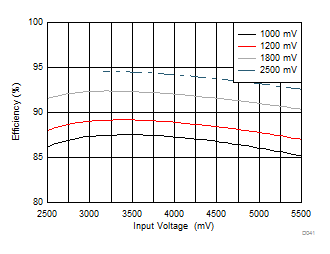
| Load = 1A | |||
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | |||
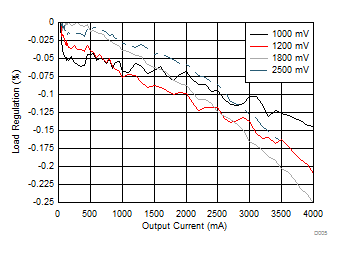
| Change in Output Voltage from Zero Load (%) | ||
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | ||
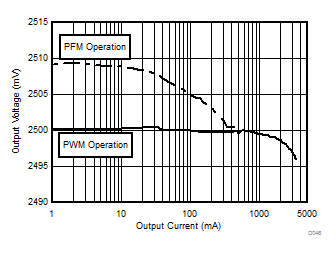
| VOUT setting = 2500 mV | ||
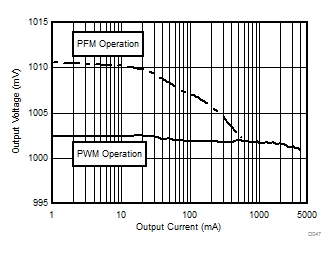
PWM-PFM Mode
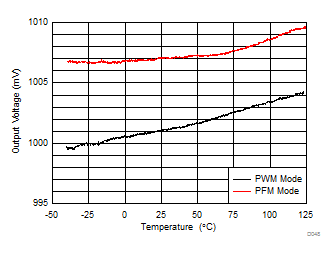
| VOUT setting = 1000 mV | ||
| Load = 1 A (PWM Mode) and 100 mA (PFM Mode) | ||
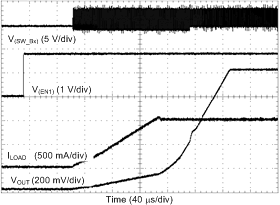
| Load = 1 A |
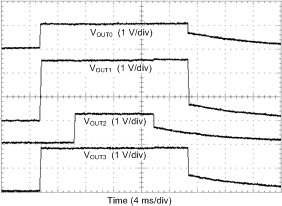
| Load = 0 A | Enable and disable delays = default | |
| VOUT settings = default | ||
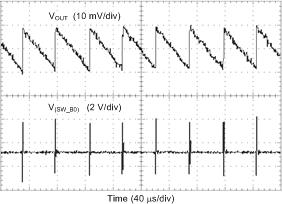
| Load = 10 mA |
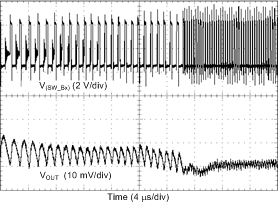
| Load = 4 A | VOUT = 1000 mV | |
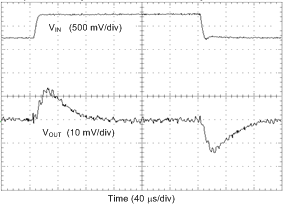
| VIN stepping 3.3 V ↔ 3.8 V, TR = TF = 10 µs | ||
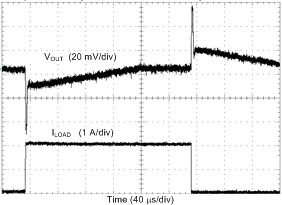
| Load = 0 A → 2 A → 0 A | TR = TF = 400 ns | VOUT = 1 V |
Forced PWM Mode
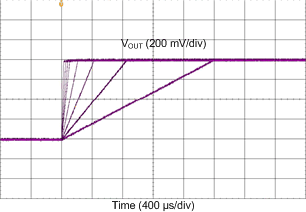
| Load = 100 mA | ||
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | ||
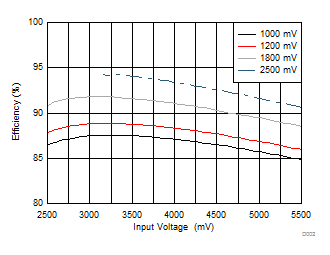
| Load = 3A | ||
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | ||
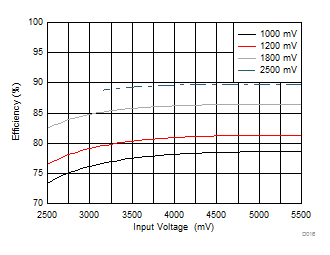
| VOUT setting = 1000 mV | ||
PWM-PFM Mode
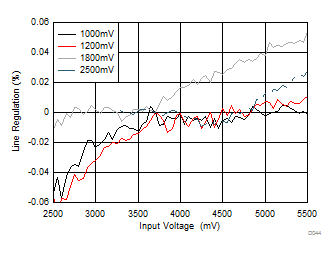
| Change in Output Voltage from VIN = 3.7 V (%) | Load = 1 A | |
| VOUT settings = 1000 mV, 1200 mV, 1800 mV, and 2500 mV | ||
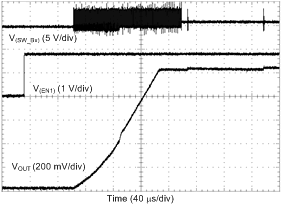
| Load = 0 A | ||
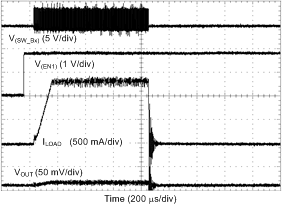
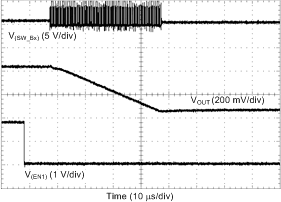
| Load = 0 A | ||
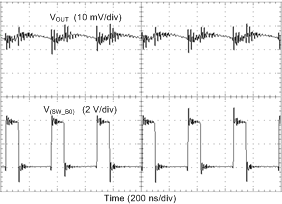
| Load = 200 mA |
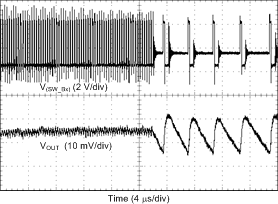
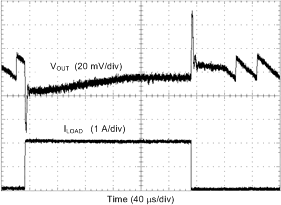
| Load = 0 A → 2 A → 0 A | TR = TF = 400 ns | VOUT = 1 V |
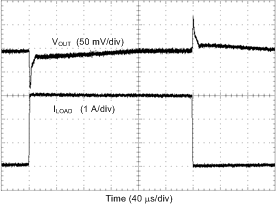
| Load = 1A → 4 A → 1A | TR = TF = 1 µs | VOUT = 1 V |
Forced PWM Mode