ZHCSCK8G May 2014 – October 2017 LP8860-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 器件比较表
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Boost Converter Characteristics
- 7.8 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.9 VIN Undervoltage Protection (VIN_UVLO)
- 7.10 VDD Undervoltage Protection (VDD_UVLO)
- 7.11 VIN Overvoltage Protection (VIN_OVP)
- 7.12 VIN Overcurrent Protection (VIN_OCP)
- 7.13 Power-Line FET Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.14 External Temp Sensor Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.15 I2C Serial Bus Timing Parameters (SDA, SCLK)
- 7.16 SPI Timing Requirements
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
- 8.6.1.1 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.2 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.3 Display/Cluster1 Output Current MSB
- 8.6.1.4 Display/Cluster1 Output Current LSB
- 8.6.1.5 Cluster2 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.6 Cluster2 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.7 Cluster2 Output Current
- 8.6.1.8 Cluster3 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.9 Cluster3 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.10 Cluster3 Output Current
- 8.6.1.11 Cluster4 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.12 Cluster4 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.13 Cluster4 Output Current
- 8.6.1.14 Configuration
- 8.6.1.15 Status
- 8.6.1.16 Fault
- 8.6.1.17 LED Fault
- 8.6.1.18 Fault Clear
- 8.6.1.19 Identification
- 8.6.1.20 Temp MSB
- 8.6.1.21 Temp LSB
- 8.6.1.22 Display LED Current MSB
- 8.6.1.23 Display LED Current LSB
- 8.6.1.24 Display LED PWM MSB
- 8.6.1.25 Display LED PWM LSB
- 8.6.1.26 EEPROM Control
- 8.6.1.27 EEPROM Unlock Code
- 8.6.2
EEPROM Bit Explanations
- 8.6.2.1 EEPROM Register 0
- 8.6.2.2 EEPROM Register 1
- 8.6.2.3 EEPROM Register 2
- 8.6.2.4 EEPROM Register 3
- 8.6.2.5 EEPROM Register 4
- 8.6.2.6 EEPROM Register 5
- 8.6.2.7 EEPROM Register 6
- 8.6.2.8 EEPROM Register 7
- 8.6.2.9 EEPROM Register 8
- 8.6.2.10 EEPROM Register 9
- 8.6.2.11 EEPROM Register 10
- 8.6.2.12 EEPROM Register 11
- 8.6.2.13 EEPROM Register 12
- 8.6.2.14 EEPROM Register 13
- 8.6.2.15 EEPROM Register 14
- 8.6.2.16 EEPROM Register 15
- 8.6.2.17 EEPROM Register 16
- 8.6.2.18 EEPROM Register 17
- 8.6.2.19 EEPROM Register 18
- 8.6.2.20 EEPROM Register 19
- 8.6.2.21 EEPROM Register 20
- 8.6.2.22 EEPROM Register 21
- 8.6.2.23 EEPROM Register 22
- 8.6.2.24 EEPROM Register 23
- 8.6.2.25 EEPROM Register 24
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.6 Diode
- 9.2.1.2.7 Boost Converter Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.9 Power Line Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.11 Filter Component Values
- 9.2.1.3 Application Performance Plots
- 9.2.2 Low VDD Voltage and Combined Output Mode Application
- 9.2.3 High Output Voltage Application
- 9.2.4 High Output Current Application
- 9.2.5 Three-Channel Configuration Without Serial Interface
- 9.2.6 Solution With Minimum External Components
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.3 LED Output Modes and Phase Shift PWM (PSPWM) Scheme
The PSPWM scheme allows delaying the time when each LED output is active. When the LED outputs are not activated simultaneously, the peak load current from the boost output is greatly decreased. This reduces the ripple seen on the boost output and allows smaller output capacitors. Reduced ripple also reduces the output ceramic capacitor audible ringing. The PSPWM scheme also increases the load frequency seen on boost output up to 4 times, therefore transferring possible audible noise to a frequency above human hearing range. In addition, “optical ripple” through the LCD panel is reduced helping in waterfall noise reduction.
Figure 18 shows the available LED output modes. The number of LED outputs used can be one to four; outputs can be tied together to increase current for one string or all four strings can be independently controlled in the cluster mode.
In <LED_STRING_CONF[2:0]> = 000 the phase difference between channels is 90 degrees. This mode is intended for application in Figure 53. When <LED_STRING_CONF[2:0] > = 001 the phase difference between 3 channels in display mode is 120 degrees. This mode is intended for application shown in Figure 63. When <LED_STRING_CONF[2:0]> = 010 the phase difference between 2 channels in display mode is 180 degrees, channels 3 and 4 in cluster mode, intended for application illustrated by Figure 60. LED strings not used in Display mode can be used for Cluster mode, or not used. When <LED_STRING_CONF[2:0]> = 111 all strings are in cluster mode.
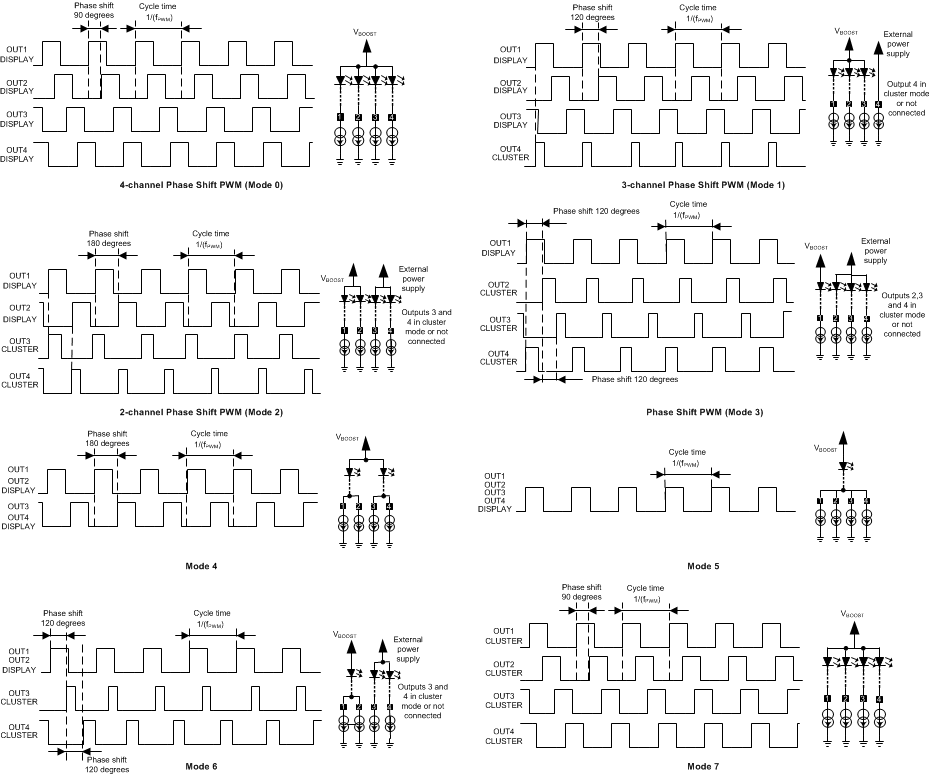 Figure 18. Phase Shift Modes
Figure 18. Phase Shift Modes
Table 9. Description of the LED Output Modes
| MODE | LED_STRING_CONF[2:0] | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 000 | 4 separate LED strings with 90° phase shift |
| 1 | 001 | 3 separate LED strings with 120° phase shift (String 4 in cluster mode or not used) |
| 2 | 010 | 2 separate LED strings with 180° phase shift (Strings 3 and 4 in cluster mode or not used) |
| 3 | 011 | 1 LED string. (Strings 2,3 and 4 in cluster mode or not used) |
| 4 | 100 | 2 LED strings (1+2, 3+4) with 180° phase shift. Strings with same phase can be connected together. |
| 5 | 101 | 1 LED string (1+2+3+4). All strings with same phase (can be tied together). |
| 6 | 110 | 1 LED string (1+2). 1st and 2nd strings tied with same phase, strings 3 and 4 are in cluster mode or not used |
| 7 | 111 | All strings are used in cluster mode with 90° phase shift |
Table 10. Output Mode Configuration
| LED_STRING_CONF[2:0] | 000 | 001 | 010 | 011 | 100 | 101 | 110 | 111 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SETUP | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings | No. of Displ. Strings | No. of Cluster Strings |
| 4 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1+1 | 1 | 1+1+1 | 2+2 | 0 | same phase/
4 tied |
0 | same phase/
2 tied |
1+1 | 0 | 1+1+1+1 | |
| Adaptive voltage control | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | ||||
| FAULT DETECTION | ||||||||||||||||
| Open LED string | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| Short LED string | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y/N | Y/N | Y | Y | ||||
| OPTIONS | ||||||||||||||||
| Sloper | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | ||||
| Dithering | ||||||||||||||||
| Int. temp. current dimming | ||||||||||||||||
| Ext. temp. current limit | ||||||||||||||||
| Ext. temp. current dimming | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||
| Brightness modes | All | All | Reg. only | All | Reg. only | All | Reg. only | All | All | All | Reg. only | Reg. only | ||||
| PMW dimming | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| Hybrid PWM and Current Dimming | N | N | N | N | N | |||||||||||
| LED OUTPUT PARAMETERS (PLL Frequency 40 MHz) | ||||||||||||||||
| ƒLED PWM min | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | |||||||||||
| Resolution at min ƒLED PWM | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 | |||||||||||
| fLED PWM max | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 4.9 kHz | |||||||||||
| Resolution at max ƒLED PWM | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Additional Dither for Display | 4 | 4 | N | 4 | N | 4 | N | 4 | 4 | 4 | N | N | ||||
| LED OUTPUT PARAMETERS (PLL Frequency 5 MHz/off | ||||||||||||||||
| fLED PWM min | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 4.9 kHz | 610 Hz | |||||||||||
| Resolution at min ƒLED PWM | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 13 | |||||||||||
| ƒLED PWM Max | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 39 kHz | 610 Hz | |||||||||||
| Resolution at max ƒLED PWM | 7 | 7 | 7 | 13 | ||||||||||||
| Additional bits with dither | 4 | 4 | N | 4 | N | 4 | N | 4 | 4 | 4 | N | N | ||||