ZHCSCK8G May 2014 – October 2017 LP8860-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 器件比较表
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Boost Converter Characteristics
- 7.8 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.9 VIN Undervoltage Protection (VIN_UVLO)
- 7.10 VDD Undervoltage Protection (VDD_UVLO)
- 7.11 VIN Overvoltage Protection (VIN_OVP)
- 7.12 VIN Overcurrent Protection (VIN_OCP)
- 7.13 Power-Line FET Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.14 External Temp Sensor Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.15 I2C Serial Bus Timing Parameters (SDA, SCLK)
- 7.16 SPI Timing Requirements
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
- 8.6.1.1 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.2 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.3 Display/Cluster1 Output Current MSB
- 8.6.1.4 Display/Cluster1 Output Current LSB
- 8.6.1.5 Cluster2 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.6 Cluster2 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.7 Cluster2 Output Current
- 8.6.1.8 Cluster3 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.9 Cluster3 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.10 Cluster3 Output Current
- 8.6.1.11 Cluster4 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.12 Cluster4 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.13 Cluster4 Output Current
- 8.6.1.14 Configuration
- 8.6.1.15 Status
- 8.6.1.16 Fault
- 8.6.1.17 LED Fault
- 8.6.1.18 Fault Clear
- 8.6.1.19 Identification
- 8.6.1.20 Temp MSB
- 8.6.1.21 Temp LSB
- 8.6.1.22 Display LED Current MSB
- 8.6.1.23 Display LED Current LSB
- 8.6.1.24 Display LED PWM MSB
- 8.6.1.25 Display LED PWM LSB
- 8.6.1.26 EEPROM Control
- 8.6.1.27 EEPROM Unlock Code
- 8.6.2
EEPROM Bit Explanations
- 8.6.2.1 EEPROM Register 0
- 8.6.2.2 EEPROM Register 1
- 8.6.2.3 EEPROM Register 2
- 8.6.2.4 EEPROM Register 3
- 8.6.2.5 EEPROM Register 4
- 8.6.2.6 EEPROM Register 5
- 8.6.2.7 EEPROM Register 6
- 8.6.2.8 EEPROM Register 7
- 8.6.2.9 EEPROM Register 8
- 8.6.2.10 EEPROM Register 9
- 8.6.2.11 EEPROM Register 10
- 8.6.2.12 EEPROM Register 11
- 8.6.2.13 EEPROM Register 12
- 8.6.2.14 EEPROM Register 13
- 8.6.2.15 EEPROM Register 14
- 8.6.2.16 EEPROM Register 15
- 8.6.2.17 EEPROM Register 16
- 8.6.2.18 EEPROM Register 17
- 8.6.2.19 EEPROM Register 18
- 8.6.2.20 EEPROM Register 19
- 8.6.2.21 EEPROM Register 20
- 8.6.2.22 EEPROM Register 21
- 8.6.2.23 EEPROM Register 22
- 8.6.2.24 EEPROM Register 23
- 8.6.2.25 EEPROM Register 24
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.6 Diode
- 9.2.1.2.7 Boost Converter Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.9 Power Line Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.11 Filter Component Values
- 9.2.1.3 Application Performance Plots
- 9.2.2 Low VDD Voltage and Combined Output Mode Application
- 9.2.3 High Output Voltage Application
- 9.2.4 High Output Current Application
- 9.2.5 Three-Channel Configuration Without Serial Interface
- 9.2.6 Solution With Minimum External Components
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.6 Boost Controller
The LP8860-Q1 boost controller generates a 16-V to 48-V supply voltage for the LEDs. Output voltage can be increased by an external resistive voltage divider connected to the FB pin, but voltage lower than 16 V is not supported.
The output voltage can be controlled either with EEPROM register bits <BOOST_INITIAL_VOLTAGE[5:0]>, or automatic adaptive boost control can be used. During start-up the output voltage is ramped to default start-up voltage <BOOST_INITIAL_VOLTAGE[5:0]> where it then adapts to the required voltage based on LED output headroom voltage (if adaptive mode has been enabled in EEPROM). Initial voltage for adaptive voltage control mode must be higher than LED string voltage — otherwise the system may generate a boost overvoltage fault during VDDIO/EN pin toggling if the output boost capacitor is not discharged below the initial voltage before the next boost start-up. A different option is to set <MASK_BOOST_OVP_STATUS> bit high to prevent a boost overvoltage fault.
The converter is a magnetic switching PWM mode DC-DC converter with a current limit. The topology of the magnetic boost converter is called Current Programmed Mode (CPM) control, where the inductor current is measured and controlled with the feedback. Switching frequency is selectable from 100 kHz and 2.2 MHz with EEPROM bits <BOOST_FREQ_SEL[2:0]>. In most cases lower frequency has the highest system efficiency.
In adaptive mode the boost output voltage is adjusted automatically based on LED current sink headroom voltage. Boost output voltage control step size is, in this case, 125 mV to ensure as small as possible current sink headroom and high efficiency. The adaptive mode is enabled with the <EN_ADAP EEPROM> bit. If boost is started with adaptive mode enabled, then the initial boost output voltage value is defined with the <BOOST_INITIAL_VOLTAGE[5:0]> EEPROM register bits in order to eliminate long output voltage iteration time when boost is started after VDDIO/EN toggling or power-on reset.
Boost can be clocked by an external SYNC signal (100 kHz to 2.2 MHz); minimum pulse length for the signal is 200 ns. If an external SYNC disappears, boost uses internal frequency defined by <BOOST_FREQ_SEL[2:0]> EEPROM bits. The boost frequency with external SYNC and EEPROM bits-defined frequency need to be close to each other; maximum frequency mismatch is ±25%. The boost controller has optional spread-spectrum switching operation (±3% from central frequency, 1.875-kHz modulation frequency) which reduces spectrum spikes around the switching frequency and its harmonic frequencies.
Further EMI reduction can be achieved by limiting the rise and fall times of the FET with an additional external resistor on the GD pin.
The boost gate driver is powered directly from VDD voltage or from the charge pump which multiplies VDD voltage by 2. If the charge pump is disabled, the VDD and CPUMP pins must be tied together.
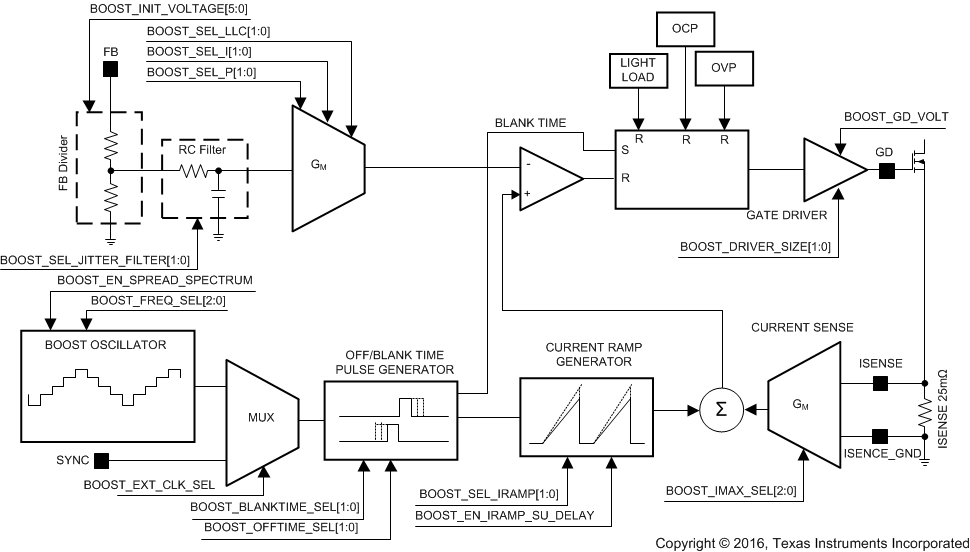 Figure 21. Boost Converter Topology
Figure 21. Boost Converter Topology