ZHCSCK8G May 2014 – October 2017 LP8860-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 器件比较表
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Current Sinks Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Boost Converter Characteristics
- 7.8 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.9 VIN Undervoltage Protection (VIN_UVLO)
- 7.10 VDD Undervoltage Protection (VDD_UVLO)
- 7.11 VIN Overvoltage Protection (VIN_OVP)
- 7.12 VIN Overcurrent Protection (VIN_OCP)
- 7.13 Power-Line FET Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.14 External Temp Sensor Control Electrical Characteristics
- 7.15 I2C Serial Bus Timing Parameters (SDA, SCLK)
- 7.16 SPI Timing Requirements
- 7.17 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
- 8.6.1.1 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.2 Display/Cluster1 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.3 Display/Cluster1 Output Current MSB
- 8.6.1.4 Display/Cluster1 Output Current LSB
- 8.6.1.5 Cluster2 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.6 Cluster2 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.7 Cluster2 Output Current
- 8.6.1.8 Cluster3 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.9 Cluster3 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.10 Cluster3 Output Current
- 8.6.1.11 Cluster4 Brightness Control MSB
- 8.6.1.12 Cluster4 Brightness Control LSB
- 8.6.1.13 Cluster4 Output Current
- 8.6.1.14 Configuration
- 8.6.1.15 Status
- 8.6.1.16 Fault
- 8.6.1.17 LED Fault
- 8.6.1.18 Fault Clear
- 8.6.1.19 Identification
- 8.6.1.20 Temp MSB
- 8.6.1.21 Temp LSB
- 8.6.1.22 Display LED Current MSB
- 8.6.1.23 Display LED Current LSB
- 8.6.1.24 Display LED PWM MSB
- 8.6.1.25 Display LED PWM LSB
- 8.6.1.26 EEPROM Control
- 8.6.1.27 EEPROM Unlock Code
- 8.6.2
EEPROM Bit Explanations
- 8.6.2.1 EEPROM Register 0
- 8.6.2.2 EEPROM Register 1
- 8.6.2.3 EEPROM Register 2
- 8.6.2.4 EEPROM Register 3
- 8.6.2.5 EEPROM Register 4
- 8.6.2.6 EEPROM Register 5
- 8.6.2.7 EEPROM Register 6
- 8.6.2.8 EEPROM Register 7
- 8.6.2.9 EEPROM Register 8
- 8.6.2.10 EEPROM Register 9
- 8.6.2.11 EEPROM Register 10
- 8.6.2.12 EEPROM Register 11
- 8.6.2.13 EEPROM Register 12
- 8.6.2.14 EEPROM Register 13
- 8.6.2.15 EEPROM Register 14
- 8.6.2.16 EEPROM Register 15
- 8.6.2.17 EEPROM Register 16
- 8.6.2.18 EEPROM Register 17
- 8.6.2.19 EEPROM Register 18
- 8.6.2.20 EEPROM Register 19
- 8.6.2.21 EEPROM Register 20
- 8.6.2.22 EEPROM Register 21
- 8.6.2.23 EEPROM Register 22
- 8.6.2.24 EEPROM Register 23
- 8.6.2.25 EEPROM Register 24
- 8.6.1
Register Bit Explanations
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.6 Diode
- 9.2.1.2.7 Boost Converter Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.9 Power Line Transistor
- 9.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.11 Filter Component Values
- 9.2.1.3 Application Performance Plots
- 9.2.2 Low VDD Voltage and Combined Output Mode Application
- 9.2.3 High Output Voltage Application
- 9.2.4 High Output Current Application
- 9.2.5 Three-Channel Configuration Without Serial Interface
- 9.2.6 Solution With Minimum External Components
- 9.2.1
Typical Application for Display Backlight
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.9.1 LED Fault Comparators and Adaptive Boost Control
Every LED current sink has 3 comparators for adaptive boost control and fault detection. Each comparator outputs is filtered. Filter control bits <BL_COMP_FILTER_SEL [3:0]> select how many PWM generator clock cycles (5 MHz if PLL disabled or PLL clock) high/mid comparator is filtered before it is used to detect shorted LEDs and boost voltage down-scaling. Usually 1 µs is sufficient; for 5-MHz frequency it means <BL_COMP_FILTER_SEL [3:0]> = 0000b, 10 MHz = 0001b, 20 MHz = 0010b, and 40 MHz = 0011b.
Adaptive boost-control function adjusts the boost output voltage to the minimum sufficient voltage for proper LED current sink operation. The output with the highest VF LED string is detected and the boost output voltage adjusted accordingly. Current sink headroom can be adjusted with EEPROM bits <DRV_HEADR[2:0]>. Boost adaptive control voltage step size is 125 mV. Boost adaptive control operates similarly with and without PSPWM. Additionally, when faster boost response is needed in larger brightness steps, the "jump" command can be used. Jump allows increase of the boost voltage with greater steps. Jump is enabled with the <EN_JUMP> EEPROM bit. The threshold for the magnitude of brightness increase that requires use of jump can be set with the <JUMP_STEP_SIZE[1:0]> EEPROM bits. <BRIGHTNESS_JUMP_THRES[1:0]> EEPROM bits define when the jump command is activated.
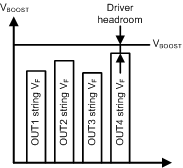 Figure 27. Boost Voltage Adaptation
Figure 27. Boost Voltage Adaptation
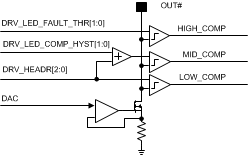 Figure 28. Output Voltage Comparators
Figure 28. Output Voltage Comparators
Figure 29 shows different cases which cause boost voltage increase, decrease, or generate faults.
 Figure 29. Protection and Boost Adaptation Algorithms
Figure 29. Protection and Boost Adaptation Algorithms
NOTE
In the Cluster mode, if voltage of one or more outputs is below LOW_COMP, it causes open LED fault detection.