ZHCSGN5B March 2017 – July 2018 LP8863-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Protection Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 LED Current Sink and LED PWM Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 Power-Line FET and RISENSE Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 Input PWM Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Boost Converter Electrical Characteristics
- 7.11 Oscillator
- 7.12 Charge Pump
- 7.13 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.14 Timing Requirements for SPI Interface
- 7.15 Timing Requirements for I2C Interface
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
FullMap Registers
- 8.6.1.1 BL_MODE Register (Offset = 20h) [reset = 300h]
- 8.6.1.2 DISP_BRT Register (Offset = 28h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.3 GROUPING1 Register (Offset = 30h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.4 GROUPING2 Register (Offset = 32h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.5 USER_CONFIG1 Register (Offset = 40h) [reset = 8B0h]
- 8.6.1.6 USER_CONFIG2 Register (Offset = 42h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.7 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_3 Register (Offset = 4Eh) [reset = 200Ah]
- 8.6.1.8 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_1 Register (Offset = 50h) [reset = A02Ah]
- 8.6.1.9 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_2 Register (Offset = 52h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.6.1.10 INTERRUPT_STATUS_1 Register (Offset = 54h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.11 INTERRUPT_STATUS_2 Register (Offset = 56h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.12 INTERRUPT_STATUS_3 Register (Offset = 58h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.13 JUNCTION_TEMPERATURE Register (Offset = E8h) [reset = 100h]
- 8.6.1.14 TEMPERATURE_LIMIT_HIGH Register (Offset = ECh) [reset = 7Dh]
- 8.6.1.15 TEMPERATURE_LIMIT_LOW Register (Offset = EEh) [reset = 69h]
- 8.6.1.16 CLUSTER1_BRT Register (Offset = 13Ch) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.17 CLUSTER2_BRT Register (Offset = 148h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.18 CLUSTER3_BRT Register (Offset = 154h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.19 CLUSTER4_BRT Register (Offset = 160h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.20 CLUSTER5_BRT Register (Offset = 16Ch) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.21 BRT_DB_CONTROL Register (Offset = 178h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.22 LED0_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C2h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.23 LED1_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C4h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.24 LED2_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C6h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.25 LED3_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C8h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.26 LED4_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1CAh) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.27 LED5_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1CCh) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.28 BOOST_CONTROL Register (Offset = 288h) [reset = 1C0h]
- 8.6.1.29 SHORT_THRESH Register (Offset = 28Ah) [reset = 2882h]
- 8.6.1.30 FSM_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A4h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.31 PWM_INPUT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A6h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.32 PWM_OUTPUT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A8h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.33 LED_CURR_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2AAh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.34 ADAPT_BOOST_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2ACh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.35 AUTO_DETECT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2AEh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1
FullMap Registers
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.6 Output Diode
- 9.2.1.2.7 Switching FET
- 9.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.9 Power-Line FET
- 9.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.11 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 9.2.1.2.12 Critical Components for Design
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Application With Basic/Minimal Operation
- 9.2.3
SEPIC Mode Application
- 9.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.2 Coupling Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.5 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.3.2.6 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.3.2.7 Switching FET
- 9.2.3.2.8 Output Diode
- 9.2.3.2.9 Switching Sense Resistor
- 9.2.3.2.10 Power-Line FET
- 9.2.3.2.11 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.3.2.12 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 9.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
- 9.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.2.1 Boost Adaptive Voltage Control
The LP8863-Q1 boost DC/DC converter generates the bias voltage for the LEDs. During normal operation, boost output voltage is adjusted automatically based on the LED current sink headroom voltages. This is called adaptive boost control. The number of used LED outputs is auto detected and only the active LED outputs are monitored to control the adaptive boost voltage. Any LED strings with open or short faults are also removed from the adaptive voltage control loop. The LED driver pin voltages are periodically monitored by the control loop and the boost voltage is raised if any of the LED outputs falls below the low headroom threshold. The boost voltage is lowered if all the LED outputs are above the high headroom threshold. See Figure 10 for how the low and high headroom thresholds automatically scale based on the LED string current and VSAT level being used.
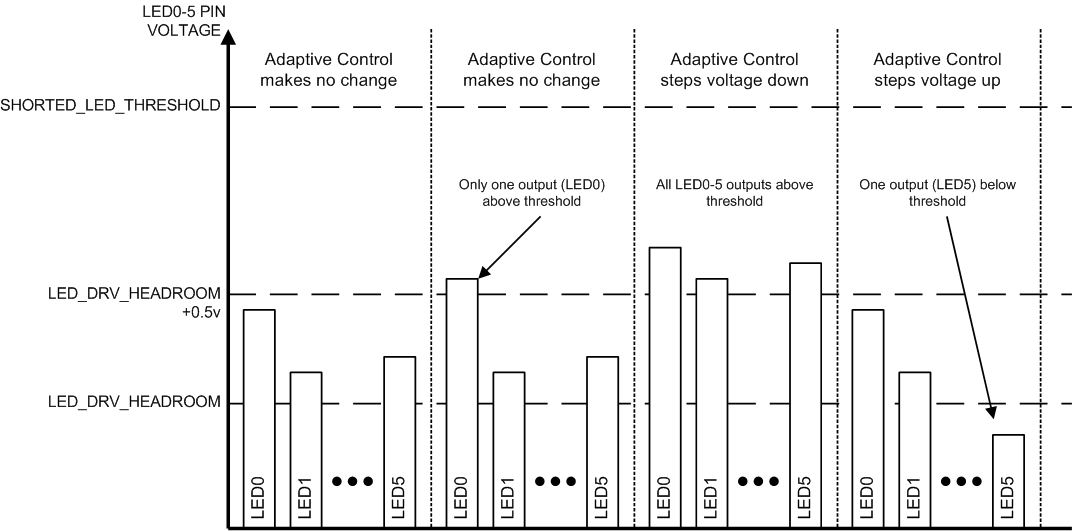 Figure 10. Adaptive Boost Voltage Control Loop Function
Figure 10. Adaptive Boost Voltage Control Loop Function The external resistive divider (RFB1, RFB2) defines both the minimum and maximum adaptive boost voltage levels. The FB circuit operates the same in boost and SEPIC topologies. Choose maximum boost voltage based on the maximum LED string voltage specification. Before the LED drivers are active the boost starts up to the initial boost level. The initial boost voltage is approximately 90% of maximum boost voltage. Once the LED driver channels are active, the boost output voltage is adjusted automatically based on LED current sink headroom voltage. The FB pin resistor divider also scales the boost OVP and undervoltage levels.