ZHCSGN5B March 2017 – July 2018 LP8863-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Protection Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 LED Current Sink and LED PWM Electrical Characteristics
- 7.8 Power-Line FET and RISENSE Electrical Characteristics
- 7.9 Input PWM Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Boost Converter Electrical Characteristics
- 7.11 Oscillator
- 7.12 Charge Pump
- 7.13 Logic Interface Characteristics
- 7.14 Timing Requirements for SPI Interface
- 7.15 Timing Requirements for I2C Interface
- 7.16 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
FullMap Registers
- 8.6.1.1 BL_MODE Register (Offset = 20h) [reset = 300h]
- 8.6.1.2 DISP_BRT Register (Offset = 28h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.3 GROUPING1 Register (Offset = 30h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.4 GROUPING2 Register (Offset = 32h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.5 USER_CONFIG1 Register (Offset = 40h) [reset = 8B0h]
- 8.6.1.6 USER_CONFIG2 Register (Offset = 42h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.7 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_3 Register (Offset = 4Eh) [reset = 200Ah]
- 8.6.1.8 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_1 Register (Offset = 50h) [reset = A02Ah]
- 8.6.1.9 INTERRUPT_ENABLE_2 Register (Offset = 52h) [reset = 80h]
- 8.6.1.10 INTERRUPT_STATUS_1 Register (Offset = 54h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.11 INTERRUPT_STATUS_2 Register (Offset = 56h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.12 INTERRUPT_STATUS_3 Register (Offset = 58h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.13 JUNCTION_TEMPERATURE Register (Offset = E8h) [reset = 100h]
- 8.6.1.14 TEMPERATURE_LIMIT_HIGH Register (Offset = ECh) [reset = 7Dh]
- 8.6.1.15 TEMPERATURE_LIMIT_LOW Register (Offset = EEh) [reset = 69h]
- 8.6.1.16 CLUSTER1_BRT Register (Offset = 13Ch) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.17 CLUSTER2_BRT Register (Offset = 148h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.18 CLUSTER3_BRT Register (Offset = 154h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.19 CLUSTER4_BRT Register (Offset = 160h) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.20 CLUSTER5_BRT Register (Offset = 16Ch) [reset = FFFFh]
- 8.6.1.21 BRT_DB_CONTROL Register (Offset = 178h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.22 LED0_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C2h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.23 LED1_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C4h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.24 LED2_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C6h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.25 LED3_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1C8h) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.26 LED4_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1CAh) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.27 LED5_CURRENT Register (Offset = 1CCh) [reset = FFFh]
- 8.6.1.28 BOOST_CONTROL Register (Offset = 288h) [reset = 1C0h]
- 8.6.1.29 SHORT_THRESH Register (Offset = 28Ah) [reset = 2882h]
- 8.6.1.30 FSM_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A4h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.31 PWM_INPUT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A6h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.32 PWM_OUTPUT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2A8h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.33 LED_CURR_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2AAh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.34 ADAPT_BOOST_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2ACh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1.35 AUTO_DETECT_DIAGNOSTICS Register (Offset = 2AEh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.1
FullMap Registers
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.6 Output Diode
- 9.2.1.2.7 Switching FET
- 9.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.9 Power-Line FET
- 9.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.11 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 9.2.1.2.12 Critical Components for Design
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Application With Basic/Minimal Operation
- 9.2.3
SEPIC Mode Application
- 9.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.2 Coupling Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.3.2.5 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 9.2.3.2.6 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 9.2.3.2.7 Switching FET
- 9.2.3.2.8 Output Diode
- 9.2.3.2.9 Switching Sense Resistor
- 9.2.3.2.10 Power-Line FET
- 9.2.3.2.11 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 9.2.3.2.12 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 9.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
- 9.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.6.4 Dither
The number of brightness steps when using LED output PWM dimming is equal to the 20-MHz oscillator frequency divided by the LED PWM frequency (set by PWM FSET resistor). The PWM duty cycle dither is a function the LP8863-Q1 uses to increase the number of brightness dimming steps beyond this oscillator clock limitation. The dither function modulates the LED driver output duty cycle over time to create more possible average brightness levels. The DITHER_SELECT[2:0] register bits control the level of dither, disabled, 1, 2, or up to 5 bits using the I2C or SPI interface. By default the dither has 3 bits enabled (default 011b).
When the 1-bit dither is selected, the width of every second PWM pulse is increased by one LSB (one 20-MHz clock period). When the 3-bit dither is selected, within a sequence of 8 PWM periods the number of pulses with increased length varies: dither value 000 - all 8 pulses at default length; 001 - one of the 8 pulses is longer; 010 - two of the 8 pulses are longer, etc., until at 111 seven of the 8 pulses have increased length. Figure 20 shows one example of PWM output dither.
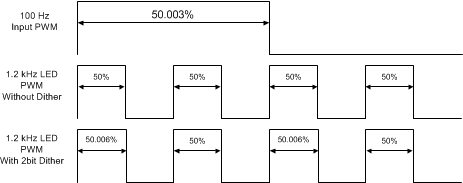 Figure 20. PWM Dither Example
Figure 20. PWM Dither Example The dither block also has an additional mode at low brightness levels when LED PWM duty cycle is less than the minimum pulse width (that is, less than the LED driver rise time). In this mode the dither block skips full PWM pulses to reduce the brightness further enabling very high dimming modes. The end result is the LED PWM frequency is reduced as more and more minimum pulses are skipped or dithered out. This function can be enabled using the I2C or SPI interface by programming the EN_MIN_PWM_LIMIT bit to 1. Figure 21 shows how the 2-bit minimum brightness dithering works.
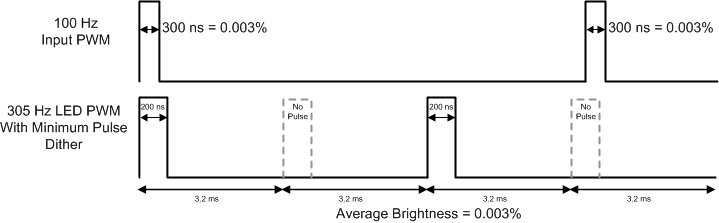 Figure 21. Minimum Brightness Dither Example
Figure 21. Minimum Brightness Dither Example