ZHCSNP1A March 2021 – October 2021 MCT8316Z
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Stage
- 8.3.2 PWM Control Mode (1x PWM Mode)
- 8.3.3 Device Interface Modes
- 8.3.4 Step-Down Mixed-Mode Buck Regulator
- 8.3.5 AVDD Linear Voltage Regulator
- 8.3.6 Charge Pump
- 8.3.7 Slew Rate Control
- 8.3.8 Cross Conduction (Dead Time)
- 8.3.9 Propagation Delay
- 8.3.10 Pin Diagrams
- 8.3.11 Active Demagnetization
- 8.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Current Limit
- 8.3.13 Hall Comparators (Analog Hall Inputs)
- 8.3.14 Advance Angle
- 8.3.15 FGOUT Signal
- 8.3.16
Protections
- 8.3.16.1 VM Supply Undervoltage Lockout (NPOR)
- 8.3.16.2 AVDD Undervoltage Lockout (AVDD_UV)
- 8.3.16.3 BUCK Undervoltage Lockout (BUCK_UV)
- 8.3.16.4 VCP Charge Pump Undervoltage Lockout (CPUV)
- 8.3.16.5 Overvoltage Protections (OV)
- 8.3.16.6 Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
- 8.3.16.7 Buck Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.16.8 Motor Lock (MTR_LOCK)
- 8.3.16.9 Thermal Warning (OTW)
- 8.3.16.10 Thermal Shutdown (OTS)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 SPI Communication
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
8.3.13 Hall Comparators (Analog Hall Inputs)
Three comparators are provided to process the raw signals from the Hall-effect sensors to commutate the motor. The Hall comparators sense the zero crossings of the differential inputs and pass the information to digital logic. The Hall comparators have hysteresis, and their detect threshold is centered at 0. The hysteresis is defined as shown in Figure 8-39.
In addition to the hysteresis, the Hall inputs are deglitched with a circuit that ignores any extra Hall transitions for a period of tHDEG after sensing a valid transition. Ignoring these transitions for the tHDEG time prevents PWM noise from being coupled into the Hall inputs, which can result in erroneous commutation.
If excessive noise is still coupled into the Hall comparator inputs, adding capacitors between the positive and negative inputs of the Hall comparators may be required. The ESD protection circuitry on the Hall inputs implements a diode to the AVDD pin. Because of this diode, the voltage on the Hall inputs should not exceed the AVDD voltage.
Because the AVDD pin is disabled in sleep mode (nSLEEP inactive), the Hall inputs should not be driven by external voltages in sleep mode. If the Hall sensors are powered externally, the supply to the Hall sensors should be disabled if the MCT8316Z device is put into sleep mode. In addition, the Hall sensors' power supply should be powered up after enabling the motor otherwise an invalid Hall state may cause a delay in motor operation.
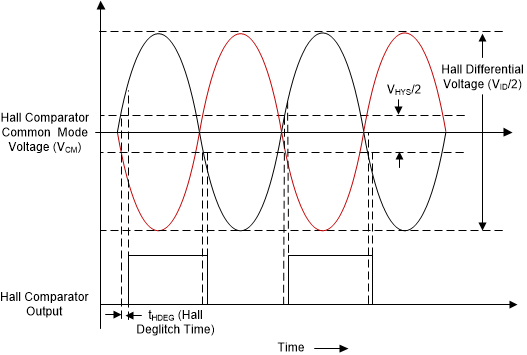 Figure 8-39 Hall Comparators Operation
Figure 8-39 Hall Comparators Operation