ZHCS180L July 2011 – December 2017 MSP430FR5730 , MSP430FR5731 , MSP430FR5732 , MSP430FR5733 , MSP430FR5734 , MSP430FR5735 , MSP430FR5736 , MSP430FR5737 , MSP430FR5738 , MSP430FR5739
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagram – RHA Package – MSP430FR5731, MSP430FR5733, MSP430FR5735, MSP430FR5737, MSP430FR5739
- 4.2 Pin Diagram – DA Package – MSP430FR5731, MSP430FR5733, MSP430FR5735, MSP430FR5737, MSP430FR5739
- 4.3 Pin Diagram – RGE Package – MSP430FR5730, MSP430FR5732, MSP430FR5734, MSP430FR5736, MSP430FR5738
- 4.4 Pin Diagram – YQD Package – MSP430FR5738
- 4.5 Pin Diagram – PW Package – MSP430FR5730, MSP430FR5732, MSP430FR5734, MSP430FR5736, MSP430FR5738
- 4.6 Signal Descriptions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Low-Power Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.7 Schmitt-Trigger Inputs – General-Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5, RST/NMI)
- 5.8 Inputs – Ports P1 and P2 (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7)
- 5.9 Leakage Current – General-Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5, RST/NMI)
- 5.10 Outputs – General-Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5)
- 5.11 Output Frequency – General-Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5)
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics – Outputs
- 5.13 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, Low-Frequency (LF) Mode
- 5.14 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, High-Frequency (HF) Mode
- 5.15 Internal Very-Low-Power Low-Frequency Oscillator (VLO)
- 5.16 DCO Frequencies
- 5.17 MODOSC
- 5.18 PMM, Core Voltage
- 5.19 PMM, SVS, BOR
- 5.20 Wake-up Times From Low-Power Modes
- 5.21 Timer_A
- 5.22 Timer_B
- 5.23 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- 5.24 eUSCI (UART Mode)
- 5.25 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- 5.26 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode)
- 5.27 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode)
- 5.28 eUSCI (I2C Mode)
- 5.29 10-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 5.30 10-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 5.31 10-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- 5.32 REF, External Reference
- 5.33 REF, Built-In Reference
- 5.34 REF, Temperature Sensor and Built-In VMID
- 5.35 Comparator_D
- 5.36 FRAM
- 5.37 JTAG and Spy-Bi-Wire Interface
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Functional Block Diagrams
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Operating Modes
- 6.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 6.5 Memory Organization
- 6.6 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.7 JTAG Operation
- 6.8 FRAM
- 6.9 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 6.10
Peripherals
- 6.10.1 Digital I/O
- 6.10.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 6.10.3 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 6.10.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 6.10.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_B)
- 6.10.6 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 6.10.7 System Module (SYS)
- 6.10.8 DMA Controller
- 6.10.9 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 6.10.10 TA0, TA1
- 6.10.11 TB0, TB1, TB2
- 6.10.12 ADC10_B
- 6.10.13 Comparator_D
- 6.10.14 CRC16
- 6.10.15 Shared Reference (REF)
- 6.10.16 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM)
- 6.10.17 Peripheral File Map
- 6.11
Input/Output Diagrams
- 6.11.1 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.2 Port P1 (P1.3 to P1.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.3 Port P1 (P1.6 and P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.4 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.5 Port P2 (P2.3 and P2.4) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.6 Port P2 (P2.5 and P2.6) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.7 Port P2 (P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.8 Port P3 (P3.0 to P3.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.9 Port P3 (P3.4 to P3.6) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.10 Port Port P3 (P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.11 Port Port P4 (P4.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.12 Port Port P4 (P4.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11.13 Port Port PJ (PJ.0 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 6.11.14 Port Port PJ (PJ.4 and PJ.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.12 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 7器件和文档支持
- 8机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
订购信息
5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
over recommended operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)(3)| PARAMETER | EXECUTION MEMORY | VCC | Frequency (fMCLK = fSMCLK)(5) | UNIT | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 MHz | 4 MHz | 8 MHz | 16 MHz | 20 MHz | 24 MHz | ||||||||||
| TYP | MAX | TYP | MAX | TYP | MAX | TYP | MAX | TYP | MAX | TYP | MAX | ||||
| IAM, FRAM_UNI(6) | FRAM | 3 V | 0.27 | 0.58 | 1.0 | 1.53 | 1.9 | 2.2 | mA | ||||||
| IAM,0%(7) | FRAM 0% cache hit ratio |
3 V | 0.42 | 0.73 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 2.8 | 3.6 | 3.45 | 4.3 | mA |
| IAM,50%(7)(4) | FRAM 50% cache hit ratio |
3 V | 0.31 | 0.73 | 1.3 | 1.75 | 2.1 | 2.5 | mA | ||||||
| IAM,66%(7)(4) | FRAM 66% cache hit ratio |
3 V | 0.27 | 0.58 | 1.0 | 1.55 | 1.9 | 2.2 | mA | ||||||
| IAM,75%(7)(4) | FRAM 75% cache hit ratio |
3 V | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.82 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.8 | mA | ||||||
| IAM,100%(7)(4) | FRAM 100% cache hit ratio |
3 V | 0.2 | 0.43 | 0.3 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.8 | 0.73 | 1.15 | 0.88 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.5 | mA |
| IAM, RAM(4)(8) | RAM | 3 V | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 1.25 | 1.20 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 1.75 | mA |
(1) All inputs are tied to 0 V or to VCC. Outputs do not source or sink any current.
(2) The currents are characterized with a Micro Crystal CC4V-T1A SMD crystal with a load capacitance of 9 pF. The internal and external load capacitance are chosen to closely match the required 9 pF.
(3) Characterized with program executing typical data processing.
(4) See Figure 5-1 for typical curves. Each characteristic equation shown in the graph is computed using the least squares method for best linear fit using the typical data shown in Section 5.4.
fACLK = 32786 Hz, fMCLK = fSMCLK at specified frequency. No peripherals active.
XTS = CPUOFF = SCG0 = SCG1 = OSCOFF= SMCLKOFF = 0.
fACLK = 32786 Hz, fMCLK = fSMCLK at specified frequency. No peripherals active.
XTS = CPUOFF = SCG0 = SCG1 = OSCOFF= SMCLKOFF = 0.
(5) At MCLK frequencies above 8 MHz, the FRAM requires wait states. When wait states are required, the effective MCLK frequency, fMCLK,eff, decreases. The effective MCLK frequency is also dependent on the cache hit ratio. SMCLK is not affected by the number of wait states or the cache hit ratio. The following equation can be used to compute fMCLK,eff:
fMCLK,eff,MHZ = fMCLK,MHZ × 1 / [number of wait states × ((1 – cache hit ratio percent/100)) + 1]
fMCLK,eff,MHZ = fMCLK,MHZ × 1 / [number of wait states × ((1 – cache hit ratio percent/100)) + 1]
(6) Program and data reside entirely in FRAM. No wait states enabled. DCORSEL = 0, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 8 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
(7) Program resides in FRAM. Data resides in SRAM. Average current dissipation varies with cache hit-to-miss ratio as specified. Cache hit ratio represents number cache accesses divided by the total number of FRAM accesses. For example, a 25% ratio implies one of every four accesses is from cache, the remaining are FRAM accesses.
For 1, 4, and 8 MHz, DCORSEL = 0, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 8 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK. No wait states enabled.
For 16 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 0 (fDCO = 16 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. One wait state enabled.
For 20 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 2 (fDCO = 20 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. Three wait states enabled.
For 24 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 24 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. Three wait states enabled.
For 1, 4, and 8 MHz, DCORSEL = 0, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 8 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK. No wait states enabled.
For 16 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 0 (fDCO = 16 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. One wait state enabled.
For 20 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 2 (fDCO = 20 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. Three wait states enabled.
For 24 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 24 MHz).MCLK = SMCLK. Three wait states enabled.
(8) All execution is from RAM.
For 1, 4, and 8 MHz, DCORSEL = 0, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 8 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 16 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 0 (fDCO = 16 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 20 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 2 (fDCO = 20 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 24 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 24 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 1, 4, and 8 MHz, DCORSEL = 0, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 8 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 16 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 0 (fDCO = 16 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 20 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 2 (fDCO = 20 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
For 24 MHz, DCORSEL = 1, DCOFSELx = 3 (fDCO = 24 MHz). MCLK = SMCLK.
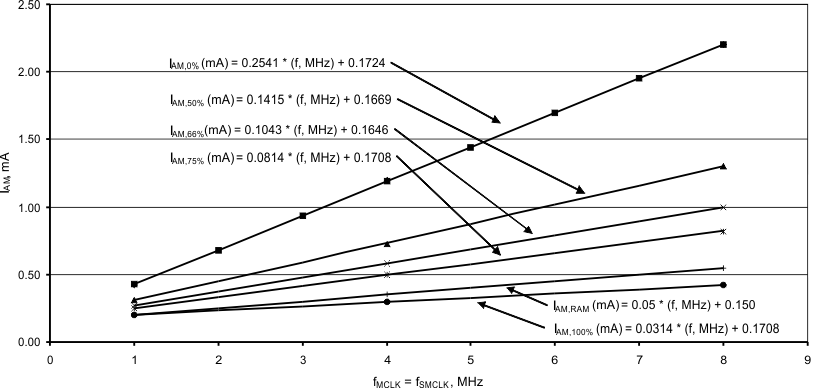 Figure 5-1 Typical Active Mode Supply Currents, No Wait States
Figure 5-1 Typical Active Mode Supply Currents, No Wait States