ZHCSGO9C June 2017 – September 2018 MSP430FR6035 , MSP430FR6037 , MSP430FR60371 , MSP430FR6045 , MSP430FR6047 , MSP430FR60471
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Typical Characteristics, Active Mode Supply Currents
- 5.6 Low-Power Mode (LPM0, LPM1) Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.7 Low-Power Mode (LPM2, LPM3, LPM4) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.8 Low-Power Mode With LCD Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.9 Low-Power Mode (LPMx.5) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics, Low-Power Mode Supply Currents
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics, Current Consumption per Module
- 5.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for 100-Pin LQFP (PZ) Package
- 5.13
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.13.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 5.13.2 Reset Timing
- 5.13.3 Clock Specifications
- 5.13.4 Wake-up Characteristics
- 5.13.5 Digital I/Os
- 5.13.6 LEA
- 5.13.7 Timer_A and Timer_B
- 5.13.8
eUSCI
- Table 5-16 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-17 eUSCI (UART Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-18 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- Table 5-19 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-20 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Switching Characteristics
- Table 5-21 eUSCI (I2C Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 5.13.9 Segment LCD Controller
- 5.13.10
ADC12_B
- Table 5-24 12-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- Table 5-25 12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- Table 5-26 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- Table 5-27 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With External Reference
- Table 5-28 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With Internal Reference
- Table 5-29 12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In V1/2
- Table 5-30 12-Bit ADC, External Reference
- 5.13.11 Reference
- 5.13.12 Comparator
- 5.13.13 FRAM
- 5.13.14 USS
- 5.13.15 Emulation and Debug
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Ultrasonic Sensing Solution (USS) Module
- 6.4 Low-Energy Accelerator (LEA) for Signal Processing
- 6.5 Operating Modes
- 6.6 Interrupt Vector Table and Signatures
- 6.7 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.8 JTAG Operation
- 6.9 FRAM Controller A (FRCTL_A)
- 6.10 RAM
- 6.11 Tiny RAM
- 6.12 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) Including IP Encapsulation
- 6.13
Peripherals
- 6.13.1 Digital I/O
- 6.13.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 6.13.3 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 6.13.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 6.13.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_C)
- 6.13.6 Measurement Test Interface (MTIF)
- 6.13.7 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 6.13.8 System Module (SYS)
- 6.13.9 DMA Controller
- 6.13.10 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 6.13.11 TA0, TA1, and TA4
- 6.13.12 TA2 and TA3
- 6.13.13 TB0
- 6.13.14 ADC12_B
- 6.13.15 USS
- 6.13.16 Comparator_E
- 6.13.17 CRC16
- 6.13.18 CRC32
- 6.13.19 AES256 Accelerator
- 6.13.20 True Random Seed
- 6.13.21 Shared Reference (REF)
- 6.13.22 LCD_C
- 6.13.23 Embedded Emulation
- 6.14
Input/Output Diagrams
- 6.14.1 Port Function Select Registers (PySEL1 , PySEL0)
- 6.14.2 Port P1 (P1.0 and P1.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.3 Port P1 (P1.2 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.4 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.5 Port P2 (P2.4 to P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.6 Port P3 (P3.0 to P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.7 Port P4 (P4.0 to P4.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.8 Port P5 (P5.0 to P5.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.9 Port P6 (P6.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.10 Port P6 (P6.1 to P6.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.11 Port P6 (P6.6 and P6.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.12 Port P7 (P7.0 to P7.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.13 Port P7 (P7.4) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.14 Port P7 (P7.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.15 Port P7 (P7.6 and P7.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.16 Port P8 (P8.0 to P8.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.17 Port P8 (P8.4 to P8.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.18 Port P9 (P9.0 to P9.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.19 Port PJ (PJ.0 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.20 Port PJ (PJ.4 and PJ.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.21 Port PJ (PJ.6 and PJ.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.15 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 6.16 Memory Map
- 6.17 Identification
-
7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 7.1.1 Power Supply Decoupling and Bulk Capacitors
- 7.1.2 External Oscillator (HFXT and LFXT)
- 7.1.3 USS Oscillator (USSXT)
- 7.1.4 Transducer Connection to the USS Module
- 7.1.5 Charge Pump Control of Input Multiplexer
- 7.1.6 JTAG
- 7.1.7 Reset
- 7.1.8 Unused Pins
- 7.1.9 General Layout Recommendations
- 7.1.10 Do's and Don'ts
- 7.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 7.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
6.6 Interrupt Vector Table and Signatures
The interrupt vectors, the power-up start address, and signatures are in the address range 0FFFFh to 0FF80h. Figure 6-2 summarizes the content of this address range.
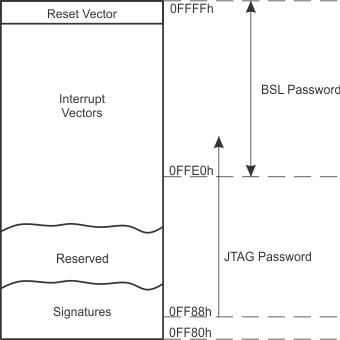 Figure 6-2 Interrupt Vectors, Signatures and Passwords
Figure 6-2 Interrupt Vectors, Signatures and Passwords The power-up start address or reset vector is at 0FFFFh to 0FFFEh. It contains the 16-bit address pointing to the start address of the application program.
The interrupt vectors start at 0FFFDh and extend to lower addresses. Each vector contains the 16-bit address of the appropriate interrupt-handler instruction sequence. Table 6-4 shows the device-specific interrupt vector locations.
The vectors programmed into the address range from 0FFFFh to 0FFE0h are used as BSL password (if enabled by the corresponding signature).
The signatures start at 0FF80h and extend to higher addresses. Signatures are evaluated during device start-up. Table 6-5 shows the device-specific signature locations.
A JTAG password can be programmed starting from address 0FF88h and extending to higher addresses. The password can extend into the interrupt vector locations using the interrupt vector addresses as additional bits for the password. The length of the JTAG password depends on the JTAG signature.
See the chapter System Resets, Interrupts, and Operating Modes, System Control Module (SYS) in the MSP430FR58xx, MSP430FR59xx, and MSP430FR6xx Family User's Guide for details.
Table 6-4 Interrupt Sources, Flags, and Vectors
| INTERRUPT SOURCE | INTERRUPT FLAG | SYSTEM INTERRUPT | WORD ADDRESS | PRIORITY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System Reset
Power up, brownout, supply supervisor External reset RST Watchdog time-out (watchdog mode) WDT, FRCTL MPU, CS, PMM password violation FRAM uncorrectable bit error detection MPU segment violation Software POR, BOR |
SVSHIFG PMMRSTIFG WDTIFG WDTPW, FRCTLPW, MPUPW, CSPW, PMMPW UBDIFG MPUSEG1IFG, MPUSEG2IFG, MPUSEG3IFG PMMPORIFG, PMMBORIFG (SYSRSTIV)(1)(2) |
Reset | 0FFFEh | Highest |
| System NMI
Vacant memory access JTAG mailbox FRAM access time error FRAM write protection error FRAM bit error detection MPU segment violation |
VMAIFG JMBINIFG, JMBOUTIFG ACCTEIFG, WPIFG CBDIFG, UBDIFG MPUSEG1IFG, MPUSEG2IFG, MPUSEG3IFG (SYSSNIV)(1)(3) |
(Non)maskable | 0FFFCh | |
| User NMI
External NMI Oscillator fault LEA RAM access conflict |
NMIIFG, OFIFG
DACCESSIFG (SYSUNIV)(1)(3) |
(Non)maskable | 0FFFAh | |
| Comparator_E | CEIFG, CEIIFG
(CEIV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFF8h | |
| TB0 | TB0CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFF6h | |
| TB0 | TB0CCR1.CCIFG to TB0CCR6.CCIFG,
TB0CTL.TBIFG (TB0IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFF4h | |
| Watchdog timer (interval timer mode) | WDTIFG | Maskable | 0FFF2h | |
| eUSCI_A0 receive or transmit | UCA0IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCA0IFG: UCSTTIFG, UCTXCPTIFG, UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (UART mode) (UCA0IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFF0h | |
| eUSCI_B0 receive or transmit | UCB0IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCB0IFG: UCALIFG, UCNACKIFG, UCSTTIFG, UCSTPIFG, UCRXIFG0, UCTXIFG0, UCRXIFG1, UCTXIFG1, UCRXIFG2, UCTXIFG2, UCRXIFG3, UCTXIFG3, UCCNTIFG, UCBIT9IFG (I2C mode) (UCB0IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFEEh | |
| ADC12_B | ADC12IFG0 to ADC12IFG31
ADC12LOIFG, ADC12INIFG, ADC12HIIFG, ADC12RDYIFG, ADC21OVIFG, ADC12TOVIFG (ADC12IV)(1)(4) |
Maskable | 0FFECh | |
| TA0 | TA0CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFEAh | |
| TA0 | TA0CCR1.CCIFG, TA0CCR2.CCIFG,
TA0CTL.TAIFG (TA0IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFE8h | |
| eUSCI_A1 receive or transmit | UCA1IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCA1IFG: UCSTTIFG, UCTXCPTIFG, UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (UART mode) (UCA1IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFE6h | |
| DMA | DMA0CTL.DMAIFG, DMA1CTL.DMAIFG, DMA2CTL.DMAIFG
(DMAIV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFE4h | |
| TA1 | TA1CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFE2h | |
| TA1 | TA1CCR1.CCIFG, TA1CCR2.CCIFG,
TA1CTL.TAIFG (TA1IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFE0h | |
| I/O port P1 | P1IFG.0 to P1IFG.7
(P1IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFDEh | |
| TA2 | TA2CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFDCh | |
| TA2 | TA2CCR1.CCIFG
TA2CTL.TAIFG (TA2IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFDAh | |
| I/O port P2 | P2IFG.0 to P2IFG.7
(P2IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFD8h | |
| TA3 | TA3CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFD6h | |
| TA3 | TA3CCR1.CCIFG
TA3CTL.TAIFG (TA3IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFD4h | |
| I/O port P3 | P3IFG.0 to P3IFG.7
(P3IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFD2h | |
| I/O port P4 | P4IFG.0 to P4IFG.2
(P4IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFD0h | |
| LCD_C | LCD_C Interrupt Flags (LCDCIV)(1) | Maskable | 0FFCEh | |
| RTC_C | RTCRDYIFG, RTCTEVIFG, RTCAIFG, RT0PSIFG, RT1PSIFG, RTCOFIFG
(RTCIV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFCCh | |
| AES | AESRDYIFG | Maskable | 0FFCAh | |
| TA4 | TA4CCR0.CCIFG | Maskable | 0FFC8h | |
| TA4 | TA4CCR1.CCIFG
TA4CTL.TAIFG (TA4IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFC6h | |
| I/O port P5 | P5IFG.0 to P5IFG.2
(P5IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFC4h | |
| I/O port P6 | P6IFG.0 to P6IFG.2
(P6IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFC2h | |
| eUSCI_A2 receive or transmit | UCA2IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCA2IFG: UCSTTIFG, UCTXCPTIFG, UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (UART mode) (UCA2IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFC0h | |
| eUSCI_A3 receive or transmit | UCA3IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCA3IFG: UCSTTIFG, UCTXCPTIFG, UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (UART mode) (UCA3IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFBEh | |
| eUSCI_B1 receive or transmit | UCB1IFG: UCRXIFG, UCTXIFG (SPI mode)
UCB1IFG: UCALIFG, UCNACKIFG, UCSTTIFG, UCSTPIFG, UCRXIFG0, UCTXIFG0, UCRXIFG1, UCTXIFG1, UCRXIFG2, UCTXIFG2, UCRXIFG3, UCTXIFG3, UCCNTIFG, UCBIT9IFG (I2C mode) (UCB1IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFBCh | |
| I/O Port P7 | P7IFG.0 to P7IFG.2
(P7IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFBAh | |
| I/O Port P8 | P8IFG.0 to P8IFG.2
(P8IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFB8h | |
| I/O Port P9 | P9IFG.0 to P9IFG.2
(P9IV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFB6h | |
| LEA | CMDIFG, SDIIFG, OORIFG, TIFG, COVLIFG
(LEAIV)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFB4h | |
| UUPS | PTMOUT, PREQIG
(IIDX)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFB2h | |
| HSPLL | PLLUNLOCK
(IIDX)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFB0h | |
| SAPH | DATAERR, TAMTO, SEQDN, PNGDN
(IIDX)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFAEh | |
| SDHS | OVF, ACQDONE, SSTRG, DTRDY, WINHI, WINLO
(IIDX)(1) |
Maskable | 0FFACh | Lowest |
Table 6-5 Signatures
| SIGNATURE | WORD ADDRESS |
|---|---|
| IP Encapsulation Signature2 | 0FF8Ah |
| IP Encapsulation Signature1(1) | 0FF88h |
| BSL Signature2 | 0FF86h |
| BSL Signature1 | 0FF84h |
| JTAG Signature2 | 0FF82h |
| JTAG Signature1 | 0FF80h |