ZHCSGB7A June 2017 – November 2017 OPA1641-Q1 , OPA1642-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
7.3.3 EMI Rejection Ratio (EMIRR)
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) rejection ratio, or EMIRR, describes the EMI immunity of operational amplifiers. An adverse effect that is common to many operational amplifiers is a change in the offset voltage as a result of RF signal rectification. An operational amplifier that is more efficient at rejecting this change in offset as a result of EMI has a higher EMIRR and is quantified by a decibel value. Measuring EMIRR can be performed in many ways, but this document provides the EMIRR IN+, which specifically describes the EMIRR performance when the RF signal is applied to the noninverting input pin of the operational amplifier. In general, only the noninverting input is tested for EMIRR for the following three reasons:
- Operational amplifier input pins are known to be the most sensitive to EMI, and typically rectify RF signals better than the supply or output pins.
- The noninverting and inverting operational amplifier inputs have symmetrical physical layouts and exhibit nearly matching EMIRR performance.
- EMIRR is easier to measure on noninverting pins than on other pins because the noninverting input pin can be isolated on a printed-circuit-board (PCB). This isolation allows the RF signal to be applied directly to the noninverting input pin with no complex interactions from other components or connecting PCB traces.
A more formal discussion of the EMIRR IN+ definition and test method is provided in application report EMI Rejection Ratio of Operational Amplifiers, available for download at www.ti.com.
The EMIRR IN+ of the OPA164x-Q1 is plotted versus frequency in Figure 30. If available, any dual and quad operational amplifier device versions have nearly identical EMIRR IN+ performance. The OPA164x-Q1 unity-gain bandwidth is 11 MHz. EMIRR performance below this frequency denotes interfering signals that fall within the operational amplifier bandwidth.
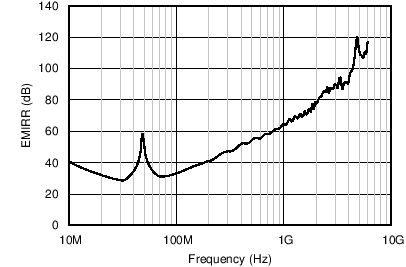 Figure 30. OPA164x-Q1 EMIRR vs Frequency
Figure 30. OPA164x-Q1 EMIRR vs FrequencyTable 1 lists the EMIRR IN+ values for the OPA164x-Q1 at particular frequencies commonly encountered in real-world applications. Applications listed in Table 1 can be centered on or operated near the particular frequency shown. This information can be of special interest to designers working with these types of applications, or working in other fields likely to encounter RF interference from broad sources, such as the industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) radio band.
Table 1. OPA164x-Q1 EMIRR IN+ for Frequencies of Interest
| FREQUENCY | APPLICATION AND ALLOCATION | EMIRR IN+ |
|---|---|---|
| 400 MHz | Mobile radio, mobile satellite, space operation, weather, radar, UHF | 53.1 dB |
| 900 MHz | GSM, radio communication and navigation, GPS (to 1.6 GHz), ISM, aeronautical mobile, UHF |
72.2 dB |
| 1.8 GHz | GSM, mobile personal comm. broadband, satellite, L-band | 80.7 dB |
| 2.4 GHz | 802.11b/g/n, Bluetooth™, mobile personal comm., ISM, amateur radio and satellite, S-band | 86.8 dB |
| 3.6 GHz | Radiolocation, aero comm./nav., satellite, mobile, S-band | 91.7 dB |
| 5 GHz | 802.11a/n, aero communication and navigation, mobile communication, space and satellite operation, C-band |
96.6 dB |