ZHCSGC1F June 2017 – March 2021 OPA145 , OPA2145
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±18 V, VCM = VS / 2, RLOAD = 10 kΩ connected to VS / 2, and CL = 100 pF (unless otherwise noted)
Table 6-1 Table of Graphs
| DESCRIPTION | FIGURE |
|---|---|
| Offset Voltage Production Distribution | Figure 6-1 |
| Offset Voltage Drift Distribution From –40°C to +125°C | Figure 6-2 |
| Input Bias Current Production Distribution | Figure 6-3 |
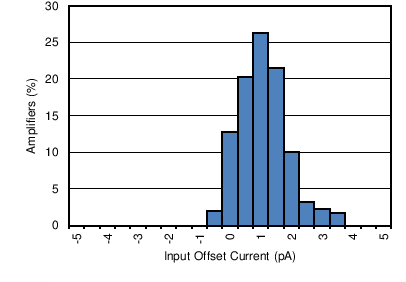
| Input Offset Current Production Distribution | Figure 6-4 |
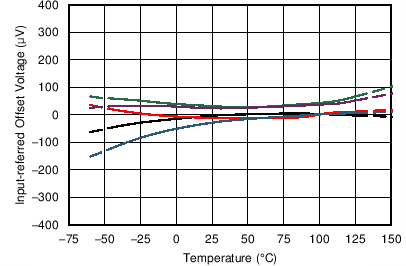
| Offset Voltage vs Temperature | Figure 6-5 |
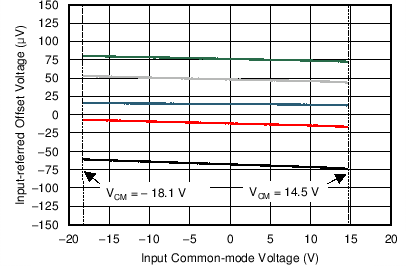
| Offset Voltage vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 6-6 |
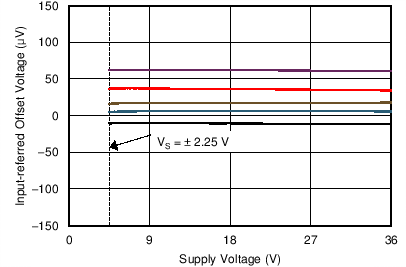
| Offset Voltage vs Power Supply | Figure 6-7 |
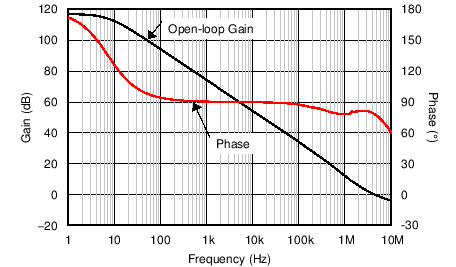
| Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs Frequency | Figure 6-8 |
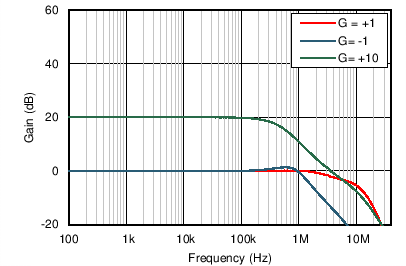
| Closed-Loop Gain vs Frequency | Figure 6-9 |
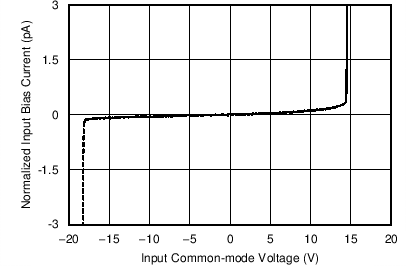
| Input Bias Current vs Common-Mode Voltage | Figure 6-10 |
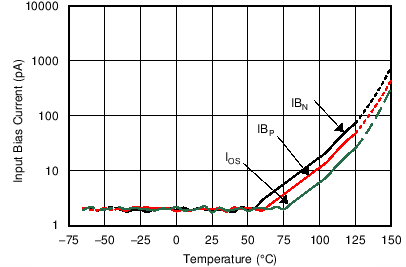
| Input Bias Current and Offset vs Temperature | Figure 6-11 |
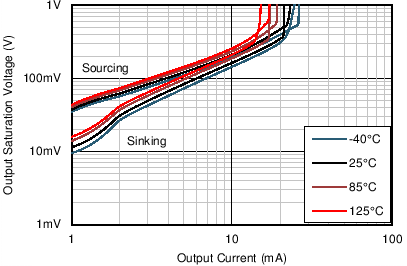
| Output Voltage Swing vs Output Current (Maximum Supply) | Figure 6-12 |
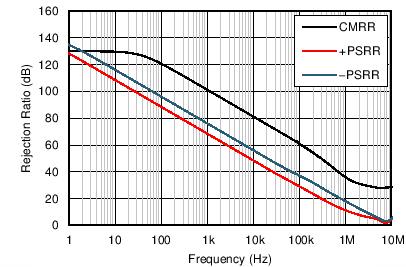
| CMRR and PSRR vs Frequency | Figure 6-13 |
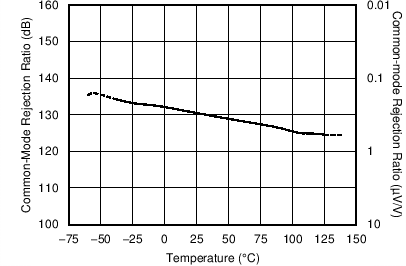
| CMRR vs Temperature | Figure 6-14 |
| PSRR vs Temperature | Figure 6-15 |
| 0.1-Hz to 10-Hz Voltage Noise | Figure 6-16 |
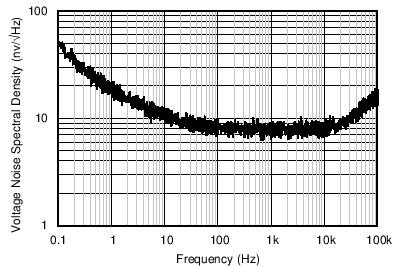
| Input Voltage Noise Spectral Density vs Frequency | Figure 6-17 |
| THD+N Ratio vs Frequency | Figure 6-18 |
| THD+N vs Output Amplitude | Figure 6-19 |
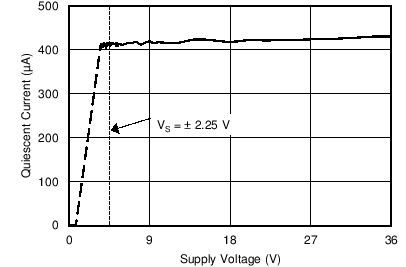
| Quiescent Current vs Supply Voltage | Figure 6-20 |
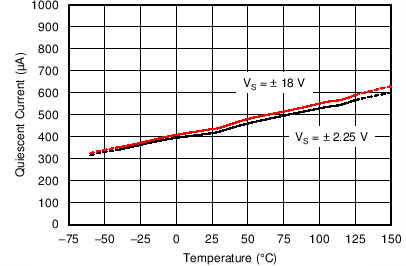
| Quiescent Current vs Temperature | Figure 6-21 |
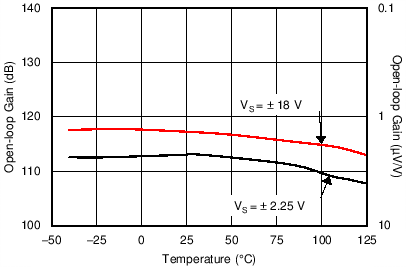
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature (10-kΩ) | Figure 6-22 |
| Open-Loop Gain vs Temperature (2-kΩ) | Figure 6-23 |
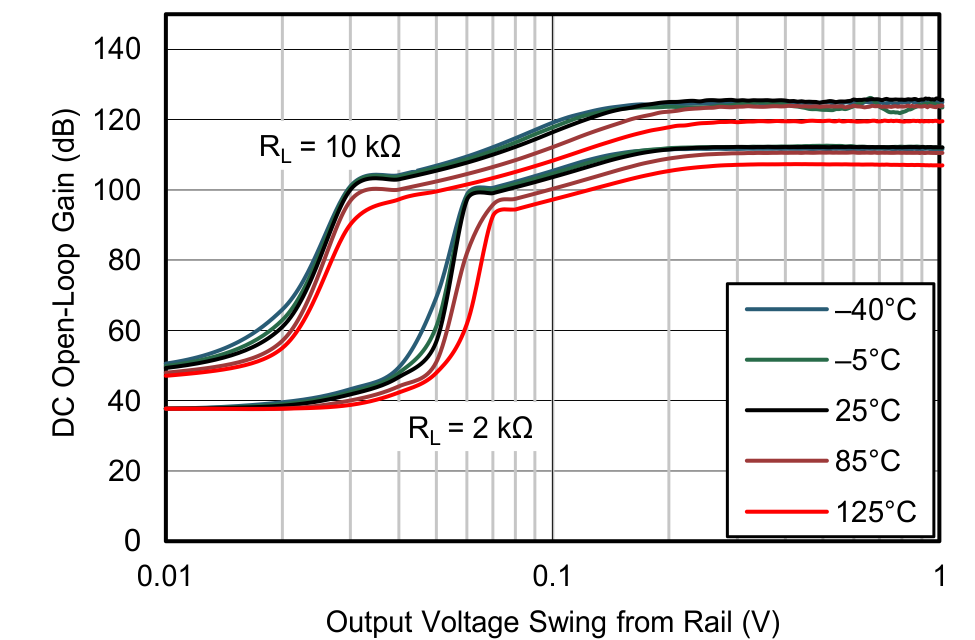
| DC Open-Loop Gain vs Output Voltage Swing Relative to Supply | Figure 6-24, Figure 6-25 |
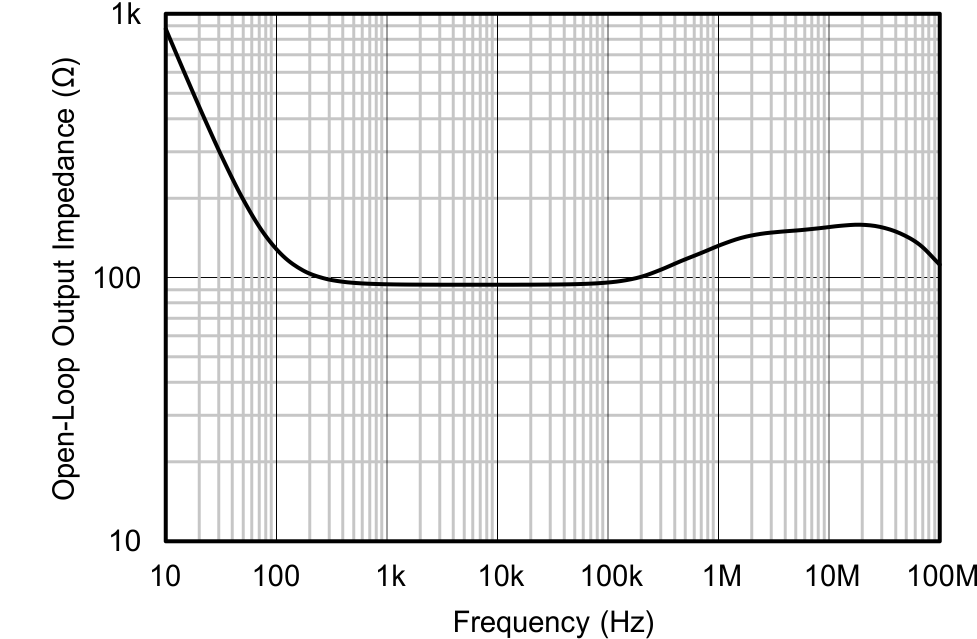
| Open-Loop Output Impedance vs Frequency | Figure 6-26 |
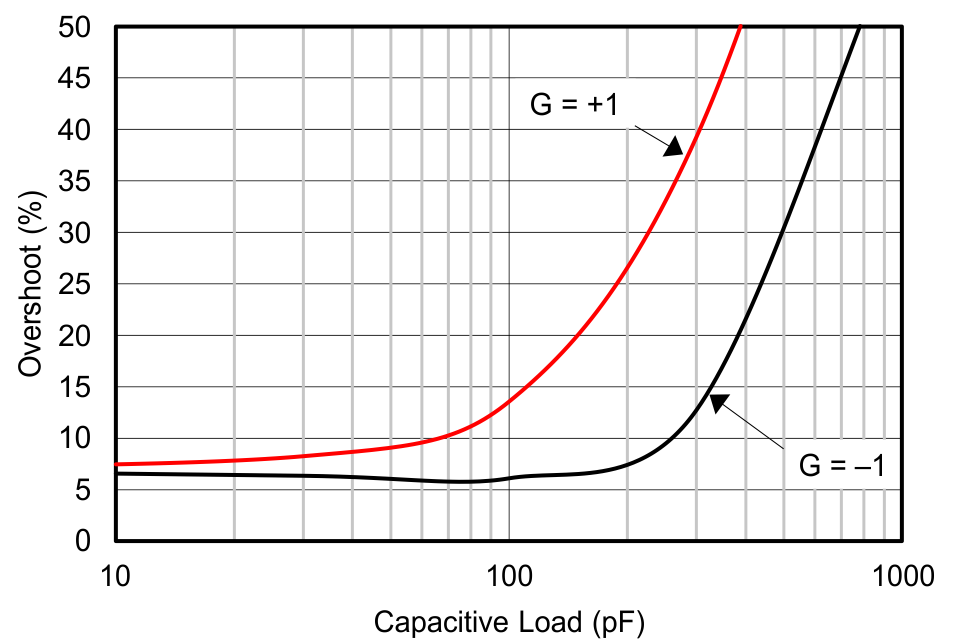
| Small-Signal Overshoot vs Capacitive Load (10-mV Step) | Figure 6-27 |
| No Phase Reversal | Figure 6-28 |
| Positive Overload Recovery | Figure 6-29 |
| Negative Overload Recovery | Figure 6-30 |
| Small-Signal Step Response (10-mV Step) | Figure 6-31, Figure 6-32 |
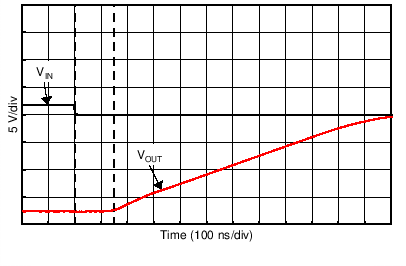
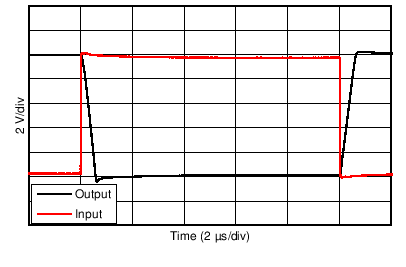
| Large-Signal Step Response (10-V Step) | Figure 6-33, Figure 6-34 |
| Settling Time | Figure 6-35 |
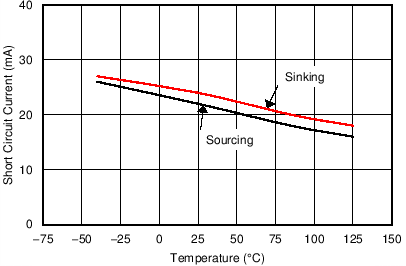
| Short-Circuit Current vs Temperature | Figure 6-36 |
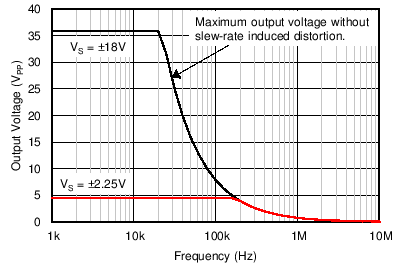
| Maximum Output Voltage vs Frequency | Figure 6-37 |
| EMIRR vs Frequency | Figure 6-38 |
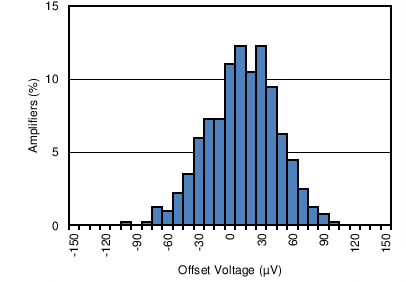
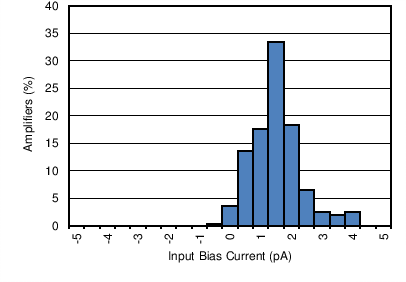
| 5 Typical Units |
| 5 Typical Units |

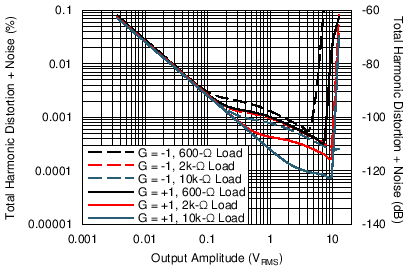
| f = 1 kHz | BW = 90 kHz |
| 2-kΩ Load |
| VS = ±2.25 V |
| 10-mV Step |
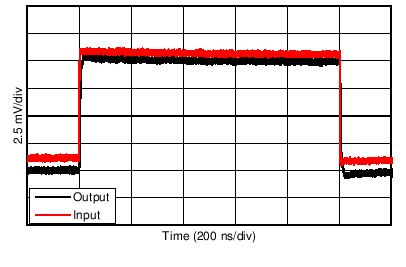
| G = +1 |
| 10-V Step | G = –1 |
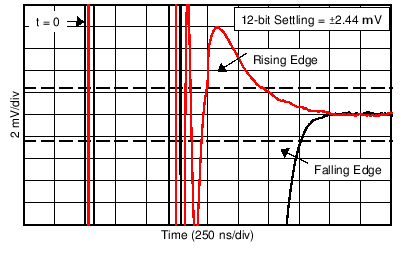
| 12-bit settling on 10-V step = ±2.44 mV | ||

| 5 Typical Units |

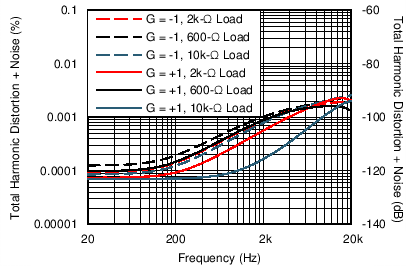
| VOUT = 3.5 | VRMS, BW = 90 kHz |

| 10-kΩ Load |
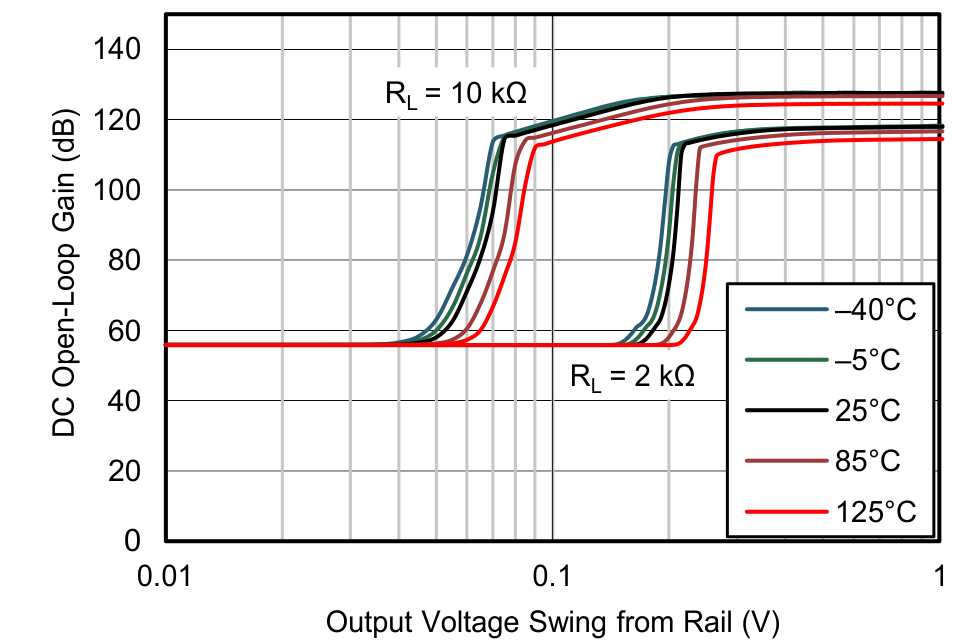
| VS = ±18 V |
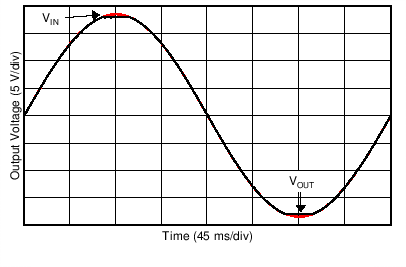
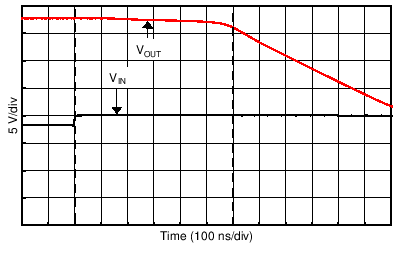

| 10-mV Step | G = –1 |
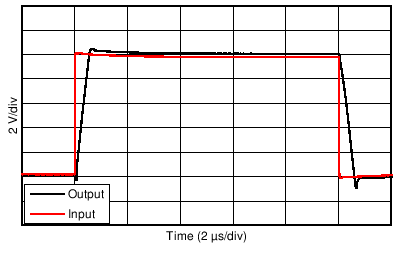
| 10-V Step | G = +1 |

| PRF = –10 dBm |