ZHCSBR3C December 2013 – May 2018 OPA355-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
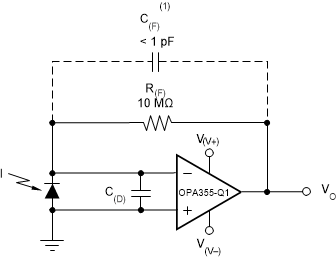
9.2.1 Transimpedance Amplifier
Wide gain bandwidth, low input bias current, low input voltage, and current noise make the OPA355-Q1 device a preferred wideband photodiode transimpedance amplifier. Low-voltage noise is important because photodiode capacitance causes the effective noise gain of the circuit to increase at high frequency.
The key elements to a transimpedance design, as shown in Figure 31, are the expected diode capacitance (C(D)), which must include the parasitic input common-mode and differential-mode input capacitance (4 pF + 5 pF), the desired transimpedance gain (R(FB)), and the gain-bandwidth (GBW) for the OPA355-Q1 device (20 MHz). With these three variables set, the feedback capacitor value (C(FB)) is set to control the frequency response. C(FB) includes the stray capacitance of R(FB), which is 0.2 pF for a typical surface-mount resistor.
NOINDENT:
C(FB) is optional to prevent gain peaking. C(FB) includes the stray capacitance of R(FB).