ZHCSFP9B December 2016 – November 2017 OPA170-Q1 , OPA2170-Q1 , OPA4170-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Figure 41 shows a unity-gain buffer driving a capacitive load. Equation 1 shows the transfer function for the circuit in Figure 41. Not shown in Figure 41 is the open-loop output resistance of the operational amplifier, RO.
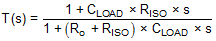
The transfer function in Equation 1 has a pole and a zero. The frequency of the pole (fp) is determined by (RO + RISO) and CLOAD. RISO and CLOAD determine the frequency of the zero (fz). A stable system is obtained by selecting RISO, so the rate of closure (ROC) between the open-loop gain (AOL) and 1/β is 20 dB / decade. Figure 42 depicts the concept. The 1/β curve for a unity-gain buffer is 0 dB.
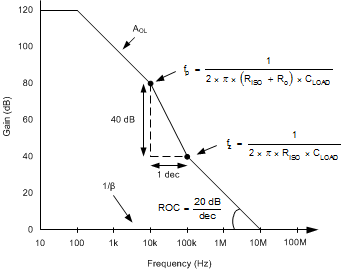 Figure 42. Unity-Gain Amplifier With RISO Compensation
Figure 42. Unity-Gain Amplifier With RISO CompensationROC stability analysis is typically simulated. The validity of the analysis depends on multiple factors, especially the accurate modeling of R O . In addition to simulating the ROC, a robust stability analysis includes a measurement of overshoot percentage and ac gain peaking of the circuit using a function generator, oscilloscope, and gain and phase analyzer. Phase margin is then calculated from these measurements. Table 6 shows the overshoot percentage and ac gain peaking that correspond to 45° and 60° phase margins. For more details on this design and other alternative devices that can be used in place of the OPAx170-Q1 family, see Capacitive Load Drive Solution Using an Isolation Resistor.
Table 6. Phase Margin versus Overshoot and AC Gain Peaking
| PHASE MARGIN | OVERSHOOT | AC GAIN PEAKING |
|---|---|---|
| 45° | 23.3% | 2.35 dB |
| 60° | 8.8% | 0.28 dB |