ZHCSR21I December 2003 – October 2024 OPA695
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics VS = ±5 V, OPA695ID, OPA695IDBV
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5 V, OPA695ID, OPA695IDBV
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics VS = ±5 V, OPA695IDGK
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics VS = 5 V, OPA695IDGK
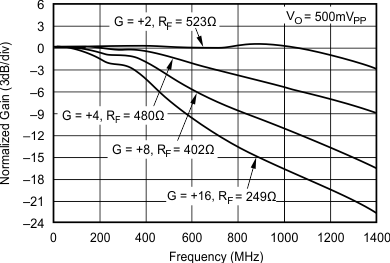
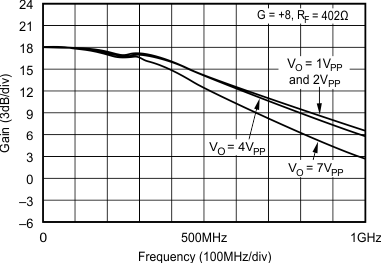
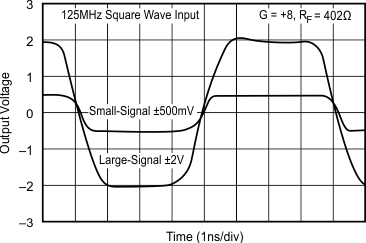
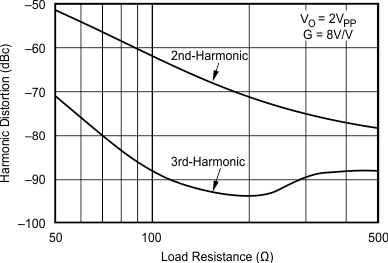
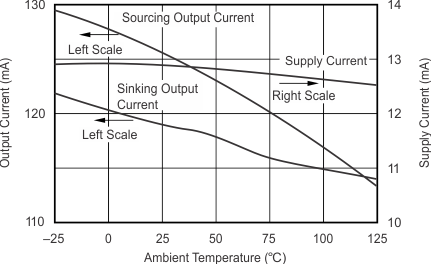
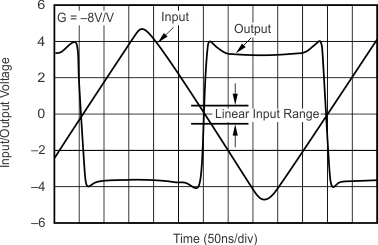
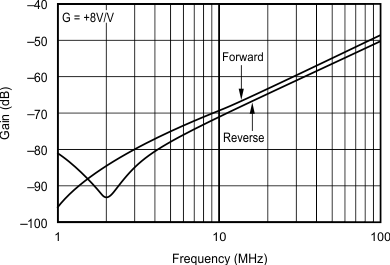
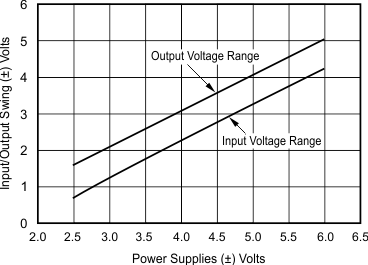
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, OPA695IDBV, OPA695ID
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5 V, OPA695IDBV, OPA695ID
- 5.11 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, OPA695IDGK
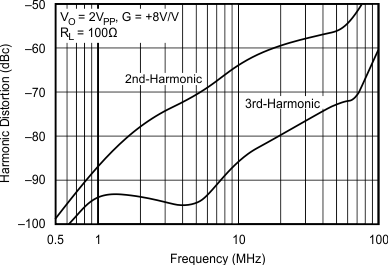
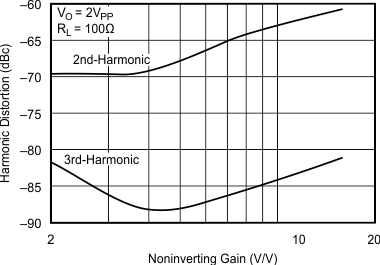
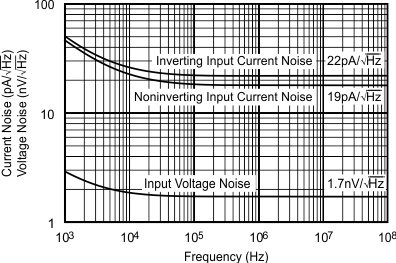
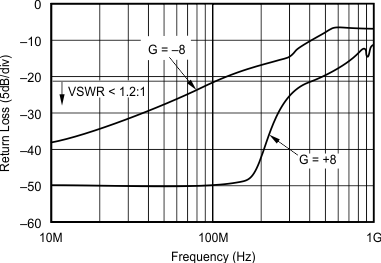
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics: VS = 5 V, OPA695IDGK
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
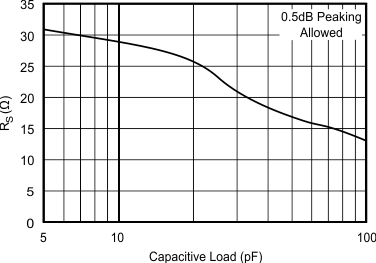
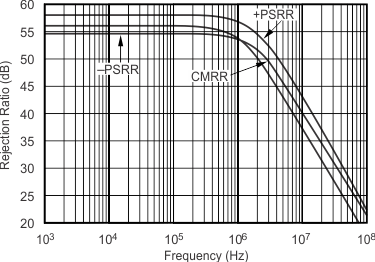
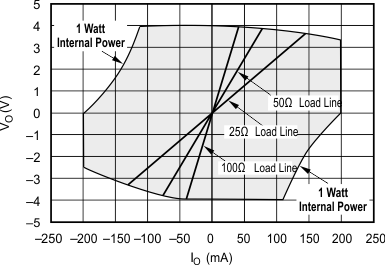
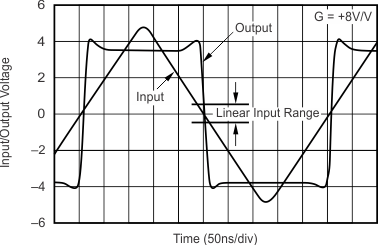
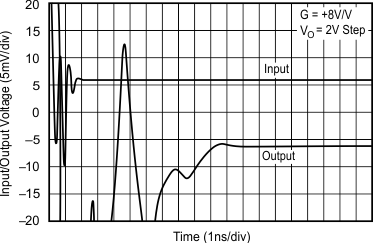
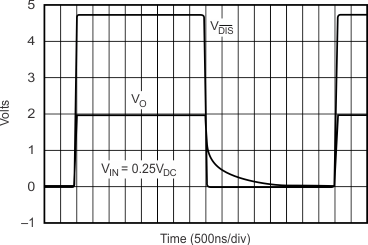
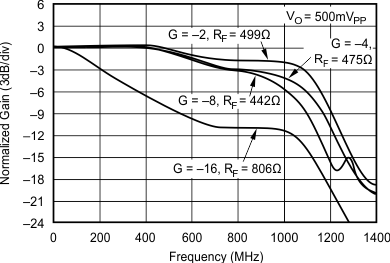
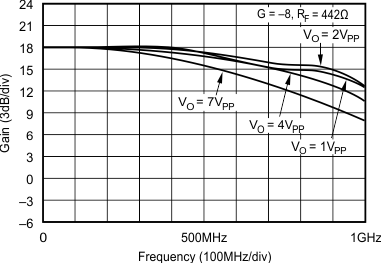
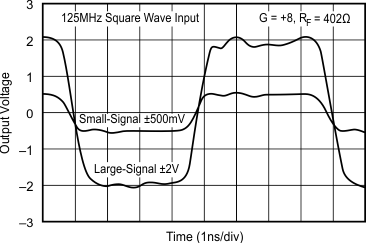
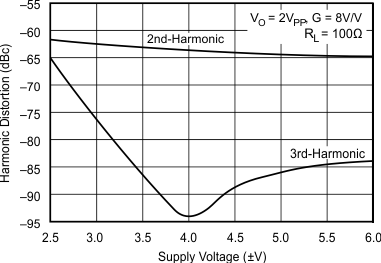
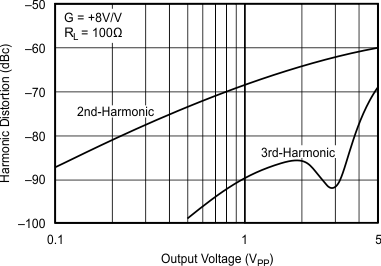
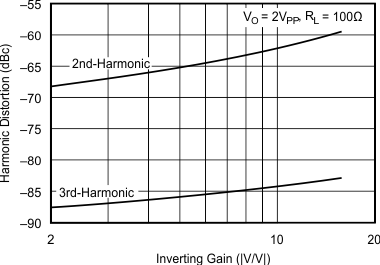
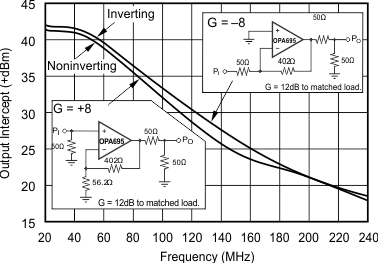
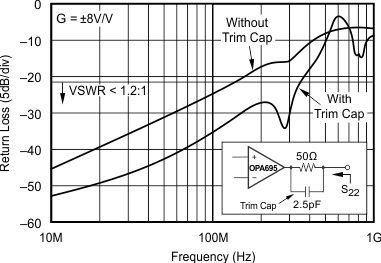
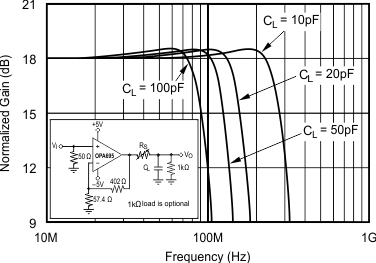
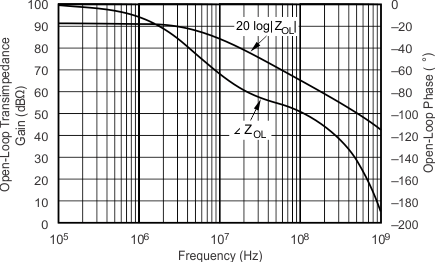
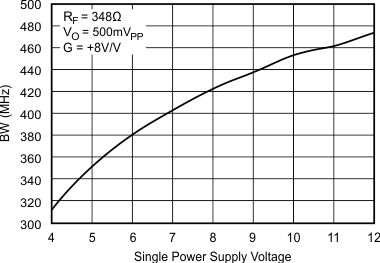
5.11 Typical Characteristics: VS = ±5 V, OPA695IDGK
at G = +8 V/V, RF = 402 Ω, and RL = 100 Ω (unless otherwise noted)