ZHCSAC2C August 2012 – October 2018 PCM5121 , PCM5122
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Terminology
- 8.3.2 Audio Data Interface
- 8.3.3 XSMT Pin (Soft Mute / Soft Un-Mute)
- 8.3.4 Audio Processing
- 8.3.5 DAC Outputs
- 8.3.6
Reset and System Clock Functions
- 8.3.6.1 Clocking Overview
- 8.3.6.2 Clock Slave Mode With Master and System Clock (SCK) Input (4 Wire I2S)
- 8.3.6.3 Clock Slave Mode With BCK PLL to Generate Internal Clocks (3-Wire PCM)
- 8.3.6.4 Clock Generation Using the PLL
- 8.3.6.5 PLL Calculation
- 8.3.6.6 Clock Master Mode from Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.3.6.7 Clock Master from a Non-Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Register Maps
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
7.8 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DATA FORMAT (PCM MODE) | ||||||
| Audio data interface format | I2S, left-justified, right-justified, and TDM | |||||
| Audio data bit length | 16, 20, 24, 32-bit acceptable | |||||
| Audio data format | MSB first, twos-complement | |||||
| fS | Sampling frequency(1) | 8 | 384 | kHz | ||
| CLOCKS | ||||||
| System clock frequency | 64, 128, 192, 256, 384, 512, 768, 1024, 1152, 1536, 2048, or 3072
fSCK, up to 50 Mhz |
|||||
| PLL input frequency (2) | Clock divider uses fractional divide
D > 0, P=1 |
6.7 | 20 | MHz | ||
| Clock divider uses integer divide
D = 0, P=1 |
1 | 20 | MHz | |||
(1) One sample time is defined as the reciprocal of the sampling frequency. 1 × tS = 1 / fS
(2) With the appropriate P coefficient setting, the PLL accepts up to 50 MHz. This clock is then divided to meet the ≤ 20-MHz requirement. See PLL Calculation.
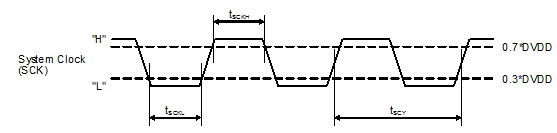 Figure 1. Timing Requirements for SCK Input
Figure 1. Timing Requirements for SCK Input 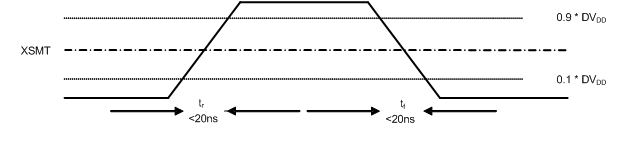 Figure 2. XSMT Timing for Soft Mute and Soft Un-Mute
Figure 2. XSMT Timing for Soft Mute and Soft Un-Mute