ZHCSCM7E July 2018 – February 2022 REF2025 , REF2030 , REF2033 , REF2041
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power-Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1 Solder Heat Shift
The materials used in the manufacture of the REF20xx have differing coefficients of thermal expansion, resulting in stress on the device die when the part is heated. Mechanical and thermal stress on the device die can cause the output voltages to shift, degrading the initial accuracy specifications of the product. Reflow soldering is a common cause of this error.
In order to illustrate this effect, a total of 92 devices were soldered on four printed circuit boards [23 devices on each printed circuit board (PCB)] using lead-free solder paste and the paste manufacturer suggested reflow profile. The reflow profile is as shown in Figure 8-1. The printed circuit board is comprised of FR4 material. The board thickness is 1.57 mm and the area is 171.54 mm × 165.1 mm.
The reference and bias output voltages are measured before and after the reflow process; the typical shift is displayed in Figure 8-2 and Figure 8-3. Although all tested units exhibit very low shifts (< 0.01%), higher shifts are also possible depending on the size, thickness, and material of the printed circuit board. An important note is that the histograms display the typical shift for exposure to a single reflow profile. Exposure to multiple reflows, as is common on PCBs with surface-mount components on both sides, causes additional shifts in the output bias voltage. If the PCB is exposed to multiple reflows, the device should be soldered in the second pass to minimize its exposure to thermal stress.
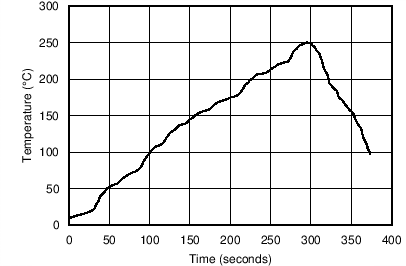 Figure 8-1 Reflow Profile
Figure 8-1 Reflow Profile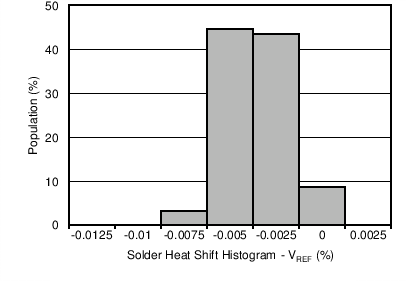 Figure 8-2 Solder Heat Shift Distribution, VREF (%)
Figure 8-2 Solder Heat Shift Distribution, VREF (%)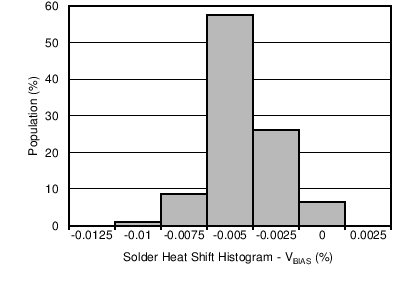 Figure 8-3 Solder Heat Shift Distribution, VBIAS (%)
Figure 8-3 Solder Heat Shift Distribution, VBIAS (%)